* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEARING
Survey
Document related concepts
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory brainstem response wikipedia , lookup
Otitis media wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
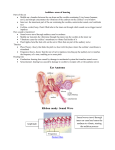
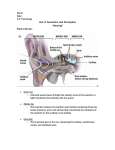
HEARING Pitch: how high or low a sound is (frequency of waves) Decibel: measures how loud a sound is 0-20: Absolute threshold (whispering) 30-60: Moderate (leaves rustling) 70-90: Loud (subway train) 100-120: Pain threshold (rock concert) 130-150: severe pain (jet engine) HEARING Eardrum: gateway from the outer ear to the middle ear; thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves strike it Middle ear: amplifies sound Cochlea: bony tube that contains fluid as well as neurons that move in response to the vibrations of the fluids HEARING Auditory Nerve: nerve that carries sound from the cochlea to the brain for interpretation Conductive Deafness: occurs because of damage to the middle ear; can be helped with hearing aids Sensorineural Deafness: caused by damage to the inner ear; neurons in the cochlea are destroyed