* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Process tracing wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
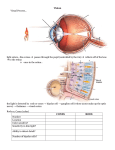
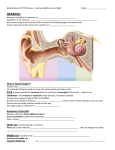
Unit 8 Review Sheet – Sensation and Perception General Terms Sensation: the process by which you detect physical energy from your environment and encode it as neural signals. Perception: the process that organizes sensory input and makes it meaningful. Psychophysics: the study of the relationship between physical energy and psychological experiences. Transduction: the transformation of stimulus energy (physical energy) to electrochemical energy (neural impulses.) Thresholds Absolute Threshold: the weakest level of stimulus that can be detected at least half of the time. Signal Detection Theory: holds that there is no actual absolute threshold because the threshold changes with a variety of factors, including fatigue, attentions, expectations, motivation, and emotional distress. Subliminal stimulation: the receipt of messages that are below ones absolute threshold. Difference threshold: the minimum difference between two stimuli that a person can detect 50% of the time. You experience the difference threshold as the Just Noticeable Difference (JND). Weber’s law: states that difference thresholds increase in proportion to the size of the stimulus. Sensory adaptation: When a stimulus is unchanging and you become less sensitive to the stimulus. Vision Visual Pathway Cornea: the translucent outer coating on the eye. Pupil: the hole in your eye that light passes through. Iris: the colored muscle in your eye that controls the size of the pupil. Lens: focuses light rays onto the retina Accommodation: the bending of the retina to focus an image on the retina Far sighted: the lens focuses the image behind the retina Near sighed: the lens focuses the image in front of the retina Retina: the photo-sensitive tissue in the back of your eye. Cones: photoreceptors that process detail, color, and day time vision Rods: photoreceptors that process night vision, and black and white Blindspot: where the optic nerve leaves the retina Order of information processing in the eye 1. Reaches rods and cones where transduction occurs 2. Neural impulse is sent to the bipolar cells 3. Neural impulse is sent to the ganglion cells. 4. The axons of the ganglion cells merge to form the optic nerve 5. The optic nerve sends information to the thalamus 6. The thalamus routes the information to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe Feature detectors: specific neurons that respond only to specific features of visual stimuli. Parallel processing: simultaneous processing of stimulus elements (combining the information from each of the feature detector cells: Color Vision Wavelength: the distance from the top of one wave to another; determines hue. If an object absorbs all light waves, the color appears to be black. If it reflects all light waves, then the color is white. Amplitude: the height of a light wave; determines brightness or intensity of color. Two Theories of Color Vision: (we now believe that they both are true and that they are just steps in seeing color) 1. Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory: There are three different photoreceptors or cones in the eye that detect red, blue, and green. Color blindness is caused by a lack of one or more of these. Red/Green color blindness is the most common form of color blindness. 2. Opponent Process Theory: Certain neurons in the brain can only detect couplings of colors: red/green; blue/yellow; black/white. The phenomenon of afterimages supports this theory. Audition Frequency: number of complete sound waves that pass a point in a second; determines pitch. Amplitude: height of the sound wave; determines volume. Pathway of a Sound: 1. Funneled into the ear by the ear flap (pinna) 2. Into auditory canal 3. Vibrates the ear drum 4. The ear drum vibrates the three small bones in the middle ear called the ossicles (hammer, anvil, stirrup) 5. The stirrup vibrates the oval window on the cochlea 6. Inside the cochlea is the basilar membrane with tiny hair cells that transduce this physical energy into neural impulses 7. Hair cells send this information to auditory neurons that form the auditory nerve. 8. Information sent to the thalamus and then to the auditory cortex in the temporal lobes. Determining Pitch – two theories: 1. Place Theory – we can determine pitch by detecting how far up the basilar membrane the vibration travels. Higher pitched sounds travel lower down the basilar membrane, while low pitched sounds travel further up the basilar membrane. Accounts well for high pitched sounds. 2. Frequency Theory – the rate of neural impulse traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the sound. Our brains can determine the frequency by calculating how fast the impulse is traveling. Accounts well for low pitched sounds. *A combination of these two theories seems to account for intermediate pitched sounds. Two kinds of deafness: 1. Conduction deafness: damage to the eardrum or the three small bones of the middle ear. Regular hearing aids may help to correct this kind of deafness b/c they can still detect vibrations in their inner ear. 2. Sensorineural deafness: damage to the inner ear, including the hair cells. Cochlear implants can help people with this kind of damage. Perception Gate Control Theory of Pain: Pain can only get to our brains if the “gate” in our spine is open. Small nerve fibers open these gates. Things like anxiety, depression, and focusing on the pain keep these small nerve gates open. Large nerve fibers close the gate. Massage, electrical stimulation, acupuncture, ice, and the natural release of endorphins can activate these large nerve fibers to close the gate. Body Senses: Kinesthesis (Kinesthetic Sense): senses the position of different parts of the body. Receptors located in the muscles and joints. Vestibular Sense: senses the position of the body. Receptors in the inner ear. Gestalt Principle: Your mind fills in the blanks due to our prior knowledge. Depth Perception: Our ability to see the world in 3D. Review Gibson’s and Walk’s visual cliff. Binocular Cue: Depth cues that depend on two eyes. - Retinal Disparity: Your brain receives two images of the world that are different your brain makes them one image. Monocular Cues: Depth cues that are available to either eye alone. Allows you to judge distance between objects. Optical Illusions: Why do they happen? (Physiological and cognitive) - 4 types of illusions o Ambiguous o Distorting o Paradox o Motion Phi Phenomenon: An illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off. Perceptual, light and color constancy: Perceiving objects, light or color as unchanged even as retinal image changes. ESP: The controversial claim that perception can occur apart from sensory input. Parapsychology: The study or paranormal phenomena. - Telepathy - Clairvoyance - Precognition - Psychokinesis