* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
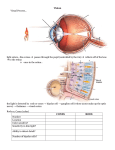
The process by which our sensory systems receive stimuli from our environment . Bottom-up processing – information that enters our senses (eyes, ears, nose) vs Top-down processing – information processing which draws on our experiences & expectations to interpret incoming sensations. (Perception) Is the study of how the physical properties of stimuli relate to people’s experience of stimuli MEASURING THE SENSES 1. The absolute threshold – is the minimum amount of stimulation needed to detect a stimulus 50% of the time. 2. The difference threshold is the smallest difference in stimulation that can be detected 50% of the time (also called jnd-just noticeable difference) The size of the just noticeable difference is proportional to the strength of the original stimulus. Signal detection Theory is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. 3. Diminished sensitivity as a result of constant stimulation. You just get used to the stimulus and don’t notice it anymore. SELECTIVE ATTENTION Focusing our conscious awareness on a particular stimulus (one stimulus at a time) to the exclusion of others. “the cocktail party effect” The visual system transduces light waves into neural impulses that the brain processes into what we consciously see. 1. Cornea-transparent, protective outer membrane of the eye. 2. Pupil-The small opening in the middle of the iris, which changes size to let in different amounts of light. 3. Iris-the colored part of the eye is a ring of muscle. 4. Lens-is located behind the pupil & iris and adjusts its shape to focus light from objects near or far away. Retina is the light sensitive membrane at the back of the eye. The retina contains receptor cells called rods: allow you to see black & white Cones: allow you to see color Bi-polar cells – neurons that connect the rods & cones to the ganglion cells Ganglion cells – connect to the bipolar cells. The bundled axons form the optic nerve. Blind spot – the point where the optic nerve leaves the eye & there are no rods or cones. 5. The optic nerve carries visual information to the brain’s visual cortex, which lies in the occipital lobe in the back of the brain. 1. Tri-chromatic or Three color theory There are 3 primary colors: red, green & blue. Any color we see is a combination of the waves of these 3 colors. 2. The opponent process theory Color processing works in the cones. There are opposing pairs of red-green, blackwhite, blue-green Used to explain afterimages Depends on the presence of sound waveswhich are changes in pressure generated by vibrating molecules. Loudness depends on amplitude or height of the sound wave. Pitch depends on frequency of sound wavewhich is the number of times per second a sound wave cycles from the highest to the lowest point. The higher the frequency the higher the pitch. Place TheoryStates that sound waves of different frequencies trigger receptors at different places on the basilar membrane. The brain figures out the pitch of sound by detecting the position of hair cells that send the neural signal. FREQUENCY THEORY Sound waves of different frequencies make the basilar membrane vibrate at different rates & causes neural impulses to be sent at different rates. Pitch is determined by how fast the neural signals move along to the brain. CONDUCTION DEAFNESS - loss of hearing as a result of structural damage. NERVE DEAFNESS – damage to the cochlea, hair cells,. This damage may result from disease or prolonged exposure to loud noise. The 5 tastes are: salty, sweet, sour, bitter. & umami. Gustation refers to taste Smell occurs when chemicals are inhaled into the nose. Smell receptors send impulses along the olfactory nerve to the brain. Kinesthesis is the sense & movement of body parts. The vestibular sense is your sense of equilibrium or body orientation. Touch-the sense of touch is a collection of several senses Cold Pressure Warmth Pain Warmth + Cold = Hot The theory that the spinal cord contains a “gate” that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass onto the brain. The “gate” is opened by the activity of pain signals traveling up small nerve fibers and is closed by activity in larger fibers or by information coming from the brain.