* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
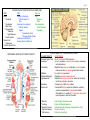
Download CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Reconstructive memory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
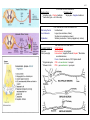
J.C.C. THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE SIMPLIFIED CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon * Thalamus * Hypothalamus * Limbic System Spinal Cord * Interneuron Cerebral Spinal Fluid PNS Nervous Somatic (Voluntary) Cell * CNS to Muscle & * Neurons Skin * Glial Autonomic (Involuntary) Communication * CNS to Visceral * Acton Potential Organs * Synapses * Sympathetic (Fast) * Parasympathetic (Slow) Motor Neuron (Efferent) Sensory Neuron (Afferent) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM PATHWAYS FUNCTIONALITY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTION(S) Cerebral Spinal Fluid Shock absorber for CNS protection Cerebrum Speech, sensation, communication, memory, reasoning, will and emotions Cerebellum Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Contains major ANS reflex centers Spinal cord Contains ANS reflex centers for defecation, urination, erection and ejaculation; extends from medulla Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory Hold thought; recall past events Retain & utilize past memory Numbers & words (language is dependent on this) Persons & events Perform motor activity J.C.C. VOLTAGE GATED CHANNELS Sodium (Na+) Potassium (K+) * Activation gate – Positive feedback * Single gate – Negative feedback * Inactivation gate – volt & time dep. Refractory Period Axon Diameter Myelination CHARACTERISTIC Neurons Glial (neuroglia) * Oligodendrocytes * Schwann Cells FACTORS AFFECTING PROPAGATION Unidirectional Larger (less resistance, faster); Smaller (more resistance, slower) Saltatory conduction = Faster propagation (in nodes) THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS FUNCTION(S) Electrochemical via synapses Homeostasis, Supports, Protects, Repairs*, Modulates neurotransmission, Forms - blood brain barrier, CSF, Myelin sheath CNS – no neurilemma = no repair PNS – yes neurilemma = yes repair