* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Inferior temporal gyrus wikipedia , lookup
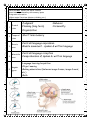
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain (or cerebrum) Which is made up of: Diencephalon Telencephalon Hindbrain The Hindbrain consists of three major parts: •Lower part of hindbrain 1. Myelencephalon The Mylencephalon has one primary part: Medulla A. oblongata •Controls autonomic functions •Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. •Upper part of hindbrain 2. Metencephalon The Metencephalon has two primary parts: A. Pons B. Cerebellum •Regulates brain activity during sleep •Connects cerebrum & cerebellum •Respiration •Coordinating muscle action (balance & coordination) •Implicit learning/memory C. Reticular formation What it is: •Network of nerves that passes through hindbrain •Extends from spinal cord to thalamus What it does: a. Alerts cortex to new stimuli b. Helps sift incoming stimulus so only important stuff sent to conscious mind c. Plays role in arousal (ability to receive stimuli) Midbrain The Midbrain is also known as the Mesencephalon. The Midbrain consists of two main parts: •Processes auditory information 1. Inferior colliculi Superior 2. colliculi •Processes spatial information •Directs eye/head coordination The Forebrain It is divided into a right and a left hemisphere The forebrain consists of two parts; an inner and an outer region: •Inner part of the forebrain 1. Diencephalon The Diencephalon consists of five major parts: •Master gland for endocrine system A. Pituitary gland B. Thalamus C. Hypothalamus •Brain’s sensory switchboard •Receives information from all senses (except smell) •Relay & distribution of many sensory & motor signals to specific parts of cerebral cortex •Regulation of sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous systems •Controls pituitary gland •Releases dopamine Both work closely with limbic system Sometimes considered part of limbic system D. Limbic system •Emotional center of the brain •Instinctual motivations (food, drink, sex, etc.) •Basic emotions (anger, fear, pleasure, etc.) •Link between hind & forebrain The Limbic System consists of three major parts: 1. Amygdala •Influences aggression & fear •Formation of long term memories associated with emotional events •Emotional responses •Formation of explicit memory •Consolidates information into long-term memory •Decides what information goes into long-term memory •Spatial memory & navigation 2. Hippocampus 3. Cingulate gyrus •Coordinates sensory input with emotions •Emotional responses to pain •Regulates aggressive behavior •Motivation & voluntary movements •Cognitive & emotional functions E. Basal ganglia The Basal Ganglia consists of two major parts: •Part of both the limbic system & basal ganglia 1. Amygdala 2. Caudate nucleus •Learning & memory •Comprehension of language •Response to visual beauty? 2. Telencephalon The outer region of the forebrain The Telecephalon consists of one major part: A. Cerebral Cortex •Wrinkled outer layer of the brain •Controls mostly sense & motor functions •Wrinkled - increase surface of the brain (15 square feet) •Gyri: ridges •Sulci: valleys •2mm to 4mm thick •20-23 billion neurons •2/3 of body’s neurons in cerebral cortex Cerebral Cortex, continued •Divided into two hemispheres •Each hemisphere divided into four lobes Interior: •Mostly axon connections, glial cells •Links cerebral cortex with rest of brain Glial cells (‘nanny cells’) •Non-neuron support cells in CNS •Provides nutrients Cerebrum: usually categorized as the lobes, and the interior parts of the forebrain The four lobes and each one’s function are: 1. 2. 3. 4. Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Occipital Lobe Temporal Lobe •Primary motor cortex (voluntary motion) •Efferent neurons •Sensory functions (Touch & Taste) •Primary sensory cortex •Afferent neurons •Sensory functions (visual) •Primary visual cortex •Afferent neurons •Sensory functions (auditory) •Primary auditory cortex •Afferent neurons The Sensory & the Motor Cortexes Sensory Cortex More sensitive the body region, the more space it takes up in sensory cortex (Tongue, lips, genitals, etc.) Motor Cortex Areas of the body that require precise control (fingers, mouth) take up more space in the motor cortex There are two other important parts that are associated with the cerebrum: B. C. Olfactory bulb Corpus callosum •Receives nerve impulses from olfactory receptors •Goes directly to cerebral cortex •Bypasses thalamus •Band of neural fibers •Connects left hemisphere with right hemisphere Association Areas •Functions NOT sensory nor motor related •Associates stored memory with sensory inputs •Integrates information •Higher mental functions (abstract thinking, etc.) There are five major Association Areas: 1. Frontal Lobe 2. Temporal Lobe •Judgment •Planning (long term) •Organization •Short •Behavior •Personality term memory Broca’s 3. area •Controls language expression •Muscle movement - spoken & written language Wernick’s 4. area •Controls language reception •Comprehension of spoken & written language 5. Angular gyrus •Language learning/acquisition •Object naming •Making associations (between image & name, image & word, etc.) •Math