* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous system
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
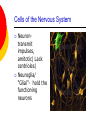
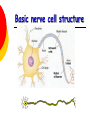
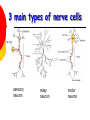
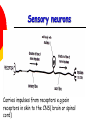
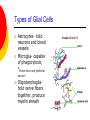
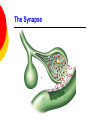
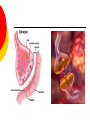
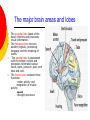
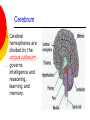
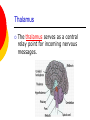
Nervous System By the end of the lesson you should be able to Describe the transmission of impulses from senses to central nervous system and back to muscles. Describe the reflex action and the pathway of the reflex arc. Describe the function of reflex response. Describe the role of the central nervous system. nervous system Cells of the Nervous System Neurontransmit impulses, amitotic( Lack centrioles) Neuroglia/ “Glial”- hold the functioning neurons Basic nerve cell structure Cross section of myelin sheaths that surround axons 3 main types of nerve cells sensory neuron relay neuron motor neuron Sensory neurons Carries impulses from receptors e.g pain receptors in skin to the CNS( brain or spinal cord) Relay neuron Carries impulses from sensory nerves to motor nerves. Motor neuron Carries impulses from CNS to effector e.g. muscle to bring about movement or gland to bring about secretion of hormone e.g ADH Types of Glial Cells Astrocytes- hold neurons and blood vessels Microglia- capable of phagocytosis, “Police force and janitorial service” Oligodendrogliahold nerve fibers together, produce myelin sheath Transmission of signals The Synapse Neurotransmitters small molecules, some are even hormones. The time for neurotransmitter action is between 0,5 and 1 millisecond. Neurotransmitters are either destroyed by specific enzymes in the synaptic cleft, diffuse out of the cleft, or are reabsorbed by the cell. More than 30 organic molecules are thought to act as neurotransmitters. The neurotransmitters cross the cleft, binding to receptor molecules on the next cell, prompting transmission of the message along that cell's membrane. neurotransmitters are active for only a short time. Enzymes in the cleft inactivate the neurotransmitters. Inactivated neurotransmitters are taken back into the axon and recycled. This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. Main parts of the Brain cerebrum (seat of consciousness), cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata (these latter two are "part of the unconscious brain"). The major brain areas and lobes The occipital lobe (back of the head) receives and processes visual information. The temporal lobe receives auditory signals, processing language and the meaning of words. The parietal lobe is associated with the sensory cortex and processes information about touch, taste, pressure, pain, and heat and cold. The frontal lobe conducts three functions: -motor activity and integration of muscle activity -speech -thought processes Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres are divided by the corpus callosum . . governs intelligence and reasoning, learning and memory. Cerebellum The cerebellum is the third part of the hindbrain, but it is not considered part of the brain stem. Functions of the cerebellum include fine motor coordination and body movement, posture, and balance. Midbrain and pons The midbrain and pons are also part of the unconscious brain. Thalamus The thalamus serves as a central relay point for incoming nervous messages. Hypothalamus regulates homeostasis It has regulatory areas for thirst, hunger, body temperature, water balance, and blood pressure, and links the Nervous System to the Endocrine System. The Spinal Cord The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendrites. The surrounding white matter is made up of bundles of interneuronal axons (tracts). Some tracts are ascending (carrying messages to the brain), others are descending (carrying messages from the brain). The spinal cord is also involved in reflexes that do not immediately involve the brain. 1Spinal Nerve 5Central Canal 2Dorsal Root Ganglion 6Grey Matter3Dorsal Root (Sensory) 7White Matter 4Ventral Root (Motor) Protective membranes of the Spinal Cord Dura Mater- tough tube that encases the two inner membranes (arachnoid and pia mater) •spinal fluid, commonly called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). •cushions, protects and nourishes the spinal cord and nerve roots.