* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Reflex Arc
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
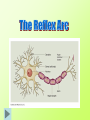
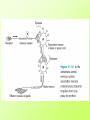
Aim: What are the parts of a reflex arc? I. Reflex – involuntary response to a stimulus. A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, skin, and nose) D. Effector – part of the body that respond to a stimulus (muscles or glands). E. Parts of neuron 1. Cyton (cell body) – contains the nucleus and decides what the impulse will do (stop or continue. 2. Dendrites – branches off the cyton that receive impulses from other neurons. 3. Axon – part of neuron that takes the impulse from the cyton towards the terminal branch. 4. Terminal branch – end of the neuron which takes impulse to next neuron. II. Parts of a reflex arc A. Stimulus B. Receptor C. Sensory Neuron - carries impulses towards the spinal cord. D. Synapse – microscopic gap between the terminal branch and the dendrite. E. Interneuron – small neuron that lies between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. Found in spinal cord. F. Motor neuron – carries impulses away from the spinal cord toward the effector. G. Effector