* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 and 16
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
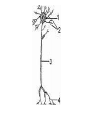
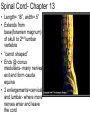
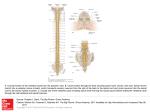
Chapter 12, 13 Nervous Tissue, Spinal Cord Divisions of NS 1. CNS-central nervous system A. Brain B. Spinal Cord 2. PNS-peripheral nervous systemprimarily nerves of body A. Spinal nerves- 31 pairs B. Cranial nerves- 12 pairs Divisions of PNS a. Somatic- controls skeletal muscle, skin b. Autonomic-controls smooth, cardiac muscle 1. Sympathetic- fight/flight, emergencies 2. Parasympathetic-relaxation, “vegetative” reflexes 3 Basic Functions 1. Sensory (afferent) Receptors send impulses to CNS 2. Motor (efferent) CNS sends impulses to effectors (muscles or glands) 3. Integrated Functions- intelligence, creativity, personality, etc. Organelles in a neuron 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nucleus Granular ER(Nissl bodies) Mitochondria Neurofibrils(microtubules) No centrioles - Classification of Neurons • P365 1. Anaxonic- located in brain, special sense organs 2. Bipolar-special sense organs 3. Unipolar-sensory neurons of PNS 4. Multipolar- most common Neuroglia 2. Neuroglia in PNS A. Satellite Cells- similar to astrocytes B. Schwann Cells- similar to oligodenedrocytes, produce myelin sheath in PNS Neuroglia 1.Neuroglia in CNS A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid Synapse • A specialized site where neurons communicate with one another • http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/syna pse.html Myelin • Acts like electrical insulation • Nodes of ranvier-gaps between schwann cells on axon; allows nerve impulse to jump between nodes; leads to high conduction speeds= 100m/s • LocationsA. All motor neurons B. All spinal nerves C. 99% of brain Unmyelinated • Slow conductions speed, .5 m/s • Located A. In autonomic nervous system Spinal Cord- Chapter 13 • Length= 18”, width=.5” • Extends from base(foramen magnum) of skull to 2nd lumbar vertebra • “carrot shaped” • Ends @ conus medullaris- many nerves exit and form cauda equina • 2 enlargements=cervical and lumbar- where more nerves enter and leave the cord # of spinal nerves-31 • • • • Cervical- 8 Thoracic-12 Lumbar-6 Sacral-5 Organization 1. White matter- myelinated sections on outermost parts • can be ascending- going to brain -carry sensory info -called afferent • Can be descending- coming from brain - carry motor info - called efferent • Root- where nerve enters or exits cord dorsal root=sensory/afferent ventral root= motor/efferent ** In back door out front door** Organization 1. Gray matter- unmyelinated sections forming H pattern in the interior • posterior horns- contain afferent neurons • anterior horns- contain efferent neurons • “cross bar”=commissure Plexuses • 1. 2. 3. 4. Plexus- interwoven network of nerves Cervical plexus Brachial plexus Lumbar plexus Sacral plexus Reflexes • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rapid automatic response to a specific stimuli Work through a reflex arc- a simple neural pathway reception transmission via sensory neuron integration transmission via motor neuron response Classifying Reflexes p 424 1. By response A. Somatic reflex- involves skin, skeletal muscle, function in protection B. Visceral reflex- involves cardiac, smooth muscle, glands, bl.v, function in homeostasis 2. By development A. Innate- w/drwal fr. pain, suckling, tracking objects w/ eye B. Acquired- driving, sports 3. By processing site A. Spinal- patellar reflex B. Cranial- sudden noise, bright light, respiration 4.Complexity of circuit A. MonosynapticB. Polysynaptic