* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hippocampus - Solon City Schools
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
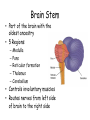
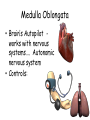
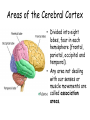
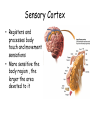
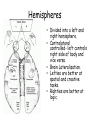
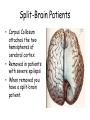
The Brain The Brain • Made up of neurons • 23 billion nerve cells and 300 trillion synapses • Glial cells – support, nourish (soma) and protect interneurons (provide insulating myelin) My husband is my glial cell. He takes care of me!!! Whose yours? Ways we Study the Brain • • • • • • Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story • Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? • That different part of the brain control different aspects of who we are. Lesions • Removal or destruction of some part of the brain. • Frontal Lobotomy Electroencephalogram • EEG • Detects brain waves through their electrical output. • Used mainly in sleep research. Computerized Axial Tomography • CAT Scan • 3D X-Ray of the brain. • Quick views of brain injury, tissue damage due to trauma • Shows tumors Magnetic Resonance Imaging • MRI • Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce images of brain structures • Does not provide info about how actively the brain in functioning Positron Emission Tomography • PET Scan • Measures the concentration of glucose in active areas of the brain • Limited to monitoring short tasks • Still pictures Functional MRI • Identifies most active areas of the brain during a specific mental task • Measures oxygen levels and blood flow to the brain • Structures and functions of the brain Brain Structures • Scientists divide the brain up into three parts. • Brain Stem • Limbic System • Cerebral Cortex Brain Regions • Brainstem – medulla, pons, reticular formation, thalamus, cerebellum • Limbic System – Hippocampus, Amygdala, Hypothalamus • Cerebral Cortex – frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, Brain Stem • Part of the brain with the oldest ancestry • 5 Regions: – – – – – Medulla Pons Reticular formation Thalamus Cerebellum • Controls involuntary muscles • Routes nerves from left side of brain to the right side Medulla Oblongata • Brain’s Autopilot works with nervous systems…. Autonomic nervous system • Controls: Pons • Acts as a bridge between the brain stem and cerebellum • Involved in forming facial expressions. • Coordinates functions between left and right side of brain Cerebellum • “little brain” attached near brain stem • Coordinates muscle movements - Like tracking a target. • Controls balance • Relies on visual information to coordinate voluntary movement Reticular Formation • Responsible for arousal and ability to focus attention. If stimulated If destroyed Thalamus • Receives sensory information and routes it to appropriate areas of the brain. - all sensory information accept smell. • Like a switchboard. Limbic System • EMOTIONAL CONTROL CENTER of the brain. • Located between the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres • Made up of Hypothalamus, Amygdala and Hippocampus. Hypothalamus • • • • • • Controls the 4 F’s. Fight (endocrine system) Flight Food (hunger & thirst) Fornication (sex drive) Endocrine System – Pituitary Gland • Maintains homeostasis • Brain’s Reward system – what neurotransmitter? Hippocampus • Hippocampus is involved in memory formation, processing, and storage. Amygdala • Amygdala is vital for our basic emotions. • Fear and Aggression Cerebral Cortex • Cerebral cortex - thin layer of interconnected neural cells • Glial cells • Fissures – folds that increase the surface area of the brain. – Laid out it would be about the size of a large pizza. Areas of the Cerebral Cortex • Divided into eight lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). • Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. Parietal Lobes • Located at the top of our head. • Receives sensory input for touch Sensory Cortex • Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations • More sensitive the body region , the larger the area devoted to it Frontal Lobe • Planning, • emotional control • abstract thought, logic, • Moral Reasoning • personality development. Motor Cortex • Controls Muscle Movement • Body areas requiring precise control occupy the greatest space Temporal Lobes • Process sound sensed by ears. • Receive info from the opposite ear. Occipital Lobes • In the back of our head. • Handles visual input from eyes. • Right half of each retina goes to left occipital lobe and vice versa. Language Development • Aphasia – impairment of language • Frontal Lobe – Broca’s Area – directs muscle movements involved in speech • Temporal Lobe – Wernicke’s Area – language comprehension and express Hemispheres • Divided into a left and right hemisphere. • Contralateral controlled- left controls right side of body and vice versa. • Brain Lateralization. • Lefties are better at spatial and creative tasks. • Righties are better at logic. Split-Brain Patients • Corpus Collosum attaches the two hemispheres of cerebral cortex. • Removed in patients with severe epilepsi • When removed you have a split-brain patient. Brain Plasticity • The ability for our brains to form new connections after the neurons are damaged. • The younger you are, the more plastic your brain is.