* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous and Endocrine System
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Response priming wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
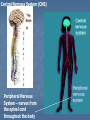
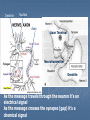
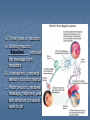
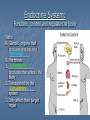
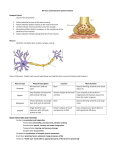
Nervous and Endocrine System Vocabulary Gland – an organ that produces and secretes (releases) hormones Hormone – a chemical created by the body that regulates (control) specific body functions Response – a reaction to a stimulus Stimulus – a change in the environment that causes you to react Nervous System: Function: control and regulate all Body __________ activities Respond (response) to a Allows you to __________ __________(change in the environment) Stimulus Stimulus: Smell of Food Response: Cat jump on the stove Stimulus: Hot stove Response: Cat screams and jumps off the stove Organs: A. Brain 1. receives and ______________ messages Interprets 2. Sends out ____________ messages Response 3. Three areas a) Cerebrum Hemispheres i. Divided into two halves (______________) ii. Largest part of the brain iii. Controls ______________ muscles Voluntary iv. Allows you to think, remember and speak b) Cerebellum Movements i. Allows for smooth body _______________ ii. Controls ____________ and posture Balance c) Brain Stem i. Medulla Oblongata Automatic ii. Controls _______________ processes ex. Breathing and heart rate Organs: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System – nerves from the spinal cord throughout the body Organs: B. Spinal Cord: sends messages between the Brain __________ and the body C. Nerves Carries 1. ____________ messages (nerve impulse) Dendrite 2. Messages always travel from ___________ to Axon Terminal ________________ 3. Messages travel in the form of chemical and Electrical ______________ signals Synapse 4. _____________ is the space between two neurons 5. Messages travel across the synapse by Neurotransmitter _____________(chemicals released from the axon terminal to trigger the nerve impulse on the next neuron) Dendrite Nucleus Axon Axon Terminal Neurotransmitter Dendrite As the message travels through the neuron it’s an electrical signal As the message crosses the synapse (gap) it’s a chemical signal 6. Three types of neurons: A. Sensory neuron: Receives ____________ (stimulus) the message from receptors B. Interneuron: connects sensory to motor neuron C. Motor neuron: receives message (response) and tells effectors (muscles) what to do Neurons Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrical signals Endocrine System: Function: control and regulate the body Parts: A. Glands: organs that produces and secrete Hormones _____________ B. Hormones Substances 1. _______________ produced that affects the body 2. Transported by the Circulatory ________________ system 3. Only affect their target organ Negative Feedback Mechanism 1. Controls the levels of hormones in your blood 2. Production of one hormone is controlled by the amount of another hormone in the blood 3. Maintains homoeostasis Review – Simple Machines Simple Machines make work easier by reducing the amount force needed or the distance that the work is done for Six Types: Incline Plane ex. Ramp Screw ex. Screw or jar lid Wedge ex. Ax or knife Pulley ex. Flagpole or clothesline the more pulleys the less force you need Wheel and Axle ex. Bicycle wheel Lever ex. See saw or bat or wheel barrow Review – Simple Machines Levers – three classes FRE…123 F- Fulcrum (pivot point) R- Resistance (object you want to move) E- Effort (force you apply) 1st Class the fulcrum in the center ex. See saw or crowbar 2nd class the resistance in the center ex. Wheel barrow 3rd class the effort in the center ex. Shovel or bat Complex Machine is two or more simple machines used together