* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download einsteins-brain
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
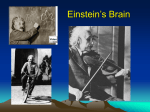
Einstein’s Brain • 1879-1955 Einstein’s Brain • Einstein died in 1955 at age 76. His brain was stored by Dr Thomas Harvey, pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sent parts out to be studied to various researchers in the 1980s and 1990s. (Reference: Abraham, C., Possessing Genius: The Bizarre Odyssey of Einstein's Brain, New York: St. Martin's Press, 2002) Einstein’s Brain: Smaller Size • 1879-1955 Einstein’s Brain: Parietal lobe • Parietal lobes are responsible for visual and 3D representation and mathematical reasoning. • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance and his ability to put spatial representations into mathematical concepts” Einstein’s Brain: Hippocampus • E’s left hippocampal neurons were larger in 4 of 5 five regions compared to right. – Controls showed minimal and inconsistent asymmetry. – Larger neurons in left hippocampus, DW Zaidel noted, imply that Einstein's left brain may have had stronger nerve cell connections between the hippocampus and neocortex than his right. Einstein’s Brain: Other Differences • Total brain weight of only 1,230 grams (average same-aged male = 1,350 grams). • Thickness of area 9 (prefrontal cortex) was thinner than that of 5 controls, but same number of neurons. – Thus density of neurons in AE’s brain greater. "On the Brain of a Scientist: Albert Einstein” Diamond, Scheibel, & Murphy (1985) • Surveyed neurons and glia in left and right area 9 (important in planning) and area 39 (language and integration) – More glial cells per neuron in AE compared to 11 age-matched male controls. – Left area 39 most significant difference • Conclusion: AE’s neurons may have had an increased "metabolic need"