* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Biology - St Mary's College, Wallasey
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
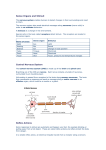
24/05/2017 OCR Additional Science Brain and Mind A slideshow that covers the entire OCR 21st Century 2006 Syllabus “Brain and Mind” Module W Richards The Weald School The Nervous System 24/05/2017 The CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) enables us to react to our surroundings. It consists mainly of the brain, the spinal chord, nerve cells (“neurones”) and receptors. Types of receptor: 1) Light receptors in the eyes 2) Sound receptors in the ears 3) Taste receptors on the tongue 4) Smell receptors in the nose 5) Touch, pressure and temperature receptors in the skin 6) Changes of position receptors in the ears (balance) Nervous Reactions 24/05/2017 When we react to a stimulus our bodies use the following pattern: Stimulus Receptor For example, consider a man and a camel: Coordinator Effector Response Oh No! What are the stimulus, receptor, coordinator, effector and response in this situation? Examples of reactions Stimulus Bright light Sour taste Losing balance Sit on a drawing pin Receptor (i.e. the thing that detects the stimulus) Effector (i.e. the thing that will do the reaction) 24/05/2017 Response (i.e. action taken) Types of nerve cell (“neuron”) 24/05/2017 Nucleus Axon Fatty sheath Muscle strands (effector) Nerve cells (neurons) are elongated with branched endings to connect to many muscles fibres. 1) Motor neurone 2) Sensory neurone Impulse Impulse 3) Relay neurone Synapses 24/05/2017 Neurones never ____ each other – there is a small gap between them called a _____. A signal is sent from one _______ to the next by a _______ transmitter across the synapse (called a “neurotransmitter”). These transmitters are then ________ back into the sensory neurone to be used again. Children have around 1000 trillion synapses whereas adults only have between 100 and 500 trillion. Words – chemical, synapse, neurone, touch, reabsorbed Conscious actions 24/05/2017 A conscious action is one where the brain makes a considered response. Here’s what happens: 4) The brain 3) Here another sensory neurone decides to move carries the signal to the brain away the hand 5) This impulse is sent by MOTOR NEURONES to the hand muscles (the effectors) via the spinal chord… 2) The impulse is carried by SENSORY NEURONES to the spinal chord 1) Receptors in your skin detect a stimulus Stimulus 6) Which then moves the hand away Receptor Motor Neurone Sensory Neurone Effector Coordinator Response Reflex actions 24/05/2017 Sometimes conscious action is too slow to prevent harm, e.g… In situations like this the body bypasses the brain to produce a quicker response. Here’s how it works… Reflex actions 2. Sensory neurone 1. Receptor 24/05/2017 3. Relay neurone in the spinal chord 4. Motor neurone 5. Effector Simple reflexes in humans 24/05/2017 Babies can demonstrate simple reflexes: 1) Stepping reflex 2) Startle (or moro) reflex 3) Grasping reflex 4) Rooting reflex 5) Sucking reflex The Iris Reflex When the light is bright the radial muscles relax, the circular muscles contract and the pupil increases in size. 24/05/2017 When the light is bright the radial muscles _____, the circular muscles _______ and the pupil ________ in size. Conditioned reflexes - Pavlov’s Dog 24/05/2017 I won the Nobel Prize in 1904 and am most famous for investigating “conditioned responses”: Ivan Pavlov, 1849-1936 1) Steak + dog = saliva 2) Steak + bell + dog = saliva 3) Bell + dog = saliva Complex Behaviour 24/05/2017 PET scan showing areas “activated” by doing algebra. When the brain is asked to do certain tasks different areas are “activated”. New experiences cause new neuron pathways to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. Feral children 24/05/2017 Task: to find out what “feral children” are, what has caused their condition and what the consequences are. The Cerebral Cortex 24/05/2017 By studying the effects (e.g. memory/sight loss) when different parts of the brain are damaged scientists have been able to identify which parts of the brain control which functions. 24/05/2017 Other techniques of studying the brain 1) An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a visual record of the electrical activity generated by neurons in the brain. It works by amplifying and detecting the electrical signals from the brain. 2) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning is a new technique that produces images of different cross sections of the brain and uses colours to represent activity. Memory 24/05/2017 Our memory is divided into two types: short term and long term. Short term memory is capable of storing a limited amount of information for a limited amount of time. Long term memory is when more information is stored over a much longer time. Ways of improving short term memory, e.g. a phone number Ways of improving long term memory e.g. exam revision The Effect of Drugs 24/05/2017 Drugs can have different effects on the nervous system. For example, alcohol _____ reactions down by affecting chemical transmitters in the brain whereas caffeine causes nerve impulses to be sent ______, thereby _______ reaction time. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system that is associated with feeling ____. The drug ecstasy blocks the synapses where the serotonin is removed, making the feeling last longer. However, the neurons are harmed in this process and taking ecstasy can lead to long term _____ loss. Words – memory, slows, increasing, faster, happy 24/05/2017 This slideshow has been made freely available on the TES Resources website. More Science PowerPoints like this can be found at the website www.educationusingpowerpoint.com. This site contains slideshows that cover the AQA, EdExcel, OCR Gateway and OCR 21st Century courses, including the 2011 units, and A Level Physics and KS3 material. Some slideshows are free, others require a small subscription fee to be taken out (currently only £50 for a year). Further details can be found at Education Using PowerPoint.