* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sensory neurone
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
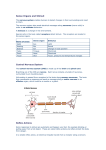
The Nervous System and Reflex Arc Name:__________ Parts of the Nervous System The NERVOUS SYSTEM is made up of three main parts; THE BRAIN THE SPINAL CORD NERVE FIBRES It detects STIMULI such as light, sounds, temperature, pressure, pain and co-ordinates the bodies response. What are the 5 sense organs and what do they sense? Organs Stimulus it detects… SKIN (the largest in the body) Touch Nose Smell (Chemicals) Eyes Light/Colour Tongue Taste (Chemicals) Sound (Vibrations) Ears You put your hand near a flame. What is happening? STIMULUS RECEPTOR SENSORY NEURONE COORDINATOR (CNS) RELAY NEURONE MOTOR NEURONE EFFECTOR (MUSCLE) RESPONSE Your body’s SENSE organs contain NERVE cells. SENSORY neurons detect CHANGES/STIMULI in the environment and send messages called NERVE IMPULSES along nerves to the BRAIN and SPINAL CORD. An EFFECTOR is any part of the body that produces the RESPONSE Effectors: Here are some examples of effectors: • a muscle contracting to move the arm • a muscle squeezing saliva from the salivary gland • a GLAND releasing a HORMONE. into the blood Nerve Fibres • Nerve fibres are bundles of nerve cells (NEURONES) that pass on electrical signals (IMPULSES) to the brain. • From the brain, nerve fibres send impulses to EFFECTORS (muscles/glands). There are three types of neruones 1. Sensory neurons 2. Relay neurons 3. Motor neurones SENSE ORGAN/ RECEPTOR Senses stimuli from our surroundings. VOLUNTARY SENSORY NEURONE Takes impulses from the sense organ to the relay neurone. SPINAL CORD Where the relay neurones are found. BRAIN Receives impulses from the spinal cord and sends out new impulses. RELAY NEURONE Takes impulses to the brain and from the brain. INVOLUNTARY MOTOR NEURONE Takes impulses from the relay neurone to the effector. EFFECTOR The muscle that receives the impulse from motor neurone. Reflex arcs Automatic responses to stimuli are called REFLEX ACTIONS. A reflex response is RAPID and its function is PROTECTION The spinal cord mediates REFLEX RESPONSES to some sensory impulses DIRECTLY ie. without going to the brain. This makes it much FASTER The messages pass through a REFLEX ARC 1. We need reflex actions because: a) They conserve energy for your body b) They are required for survival c) They ensure all nerves in the body are used equally 2. You step on a plug- which of the sentences below is accurate? a) light receptors in the eyes are allowing you to feel the plug. b) temperature receptors in the skin allow you to feel the plug. 4. You burn your hand on a hot plate- which of the following order of events is correct? a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector c) receptor-->sensory neurone-->CNS->motor neurone-->effector d) receptor-->sensory neurone-->CNS-->relay neurone->effector c) pressure receptors in the skin allow you to feel the plug. d) pressure receptors in the mouth allow you to feel the plug. 3. You see a football and kick it- which of the following order of events is correct: a) receptor--> motor neurone--> brain--> sensory neurone--> effector b) receptor--> sensory neurone--> relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector c) receptor-->sensory neurone-->brain-->motor neurone--> effector d) receptor-->sensory neurone-->motor neurone--> effector