* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
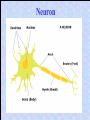
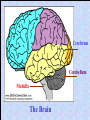
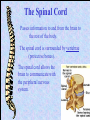
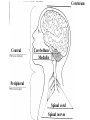
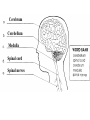
The Nervous System Controls activities using electrical signals. Made up of: • Brain • Spinal Cord • Nerves There are two parts to the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain & Spinal Cord – process incoming & outgoing messages 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves – connects all neurons to the central nervous system The Peripheral Nervous System Neurons are specialized cells that carry electrical messages through the body very quickly. Electrical messages (impulses) sent to and from the brain travel through neurons inside nerves. There are two types of neurons: Sensory: Gather information from around the body and send it to the brain. Receptors detect change inside and outside the body.(Ex. Eyes) Motor: Send messages from the brain to the rest of the body. They cause a reaction to occur. (Ex. Muscles to contract) Neuron How do sensory and motor neurons work together? Sensory neurons are your receptors, like skin on your fingers. They sense changes (heat, pain) and send a message to the brain. The brain interprets the messages and sends a response to do something in the motor neurons (move your hand off of the stove). Nerves are groups of neurons that work together to send messages. The Central Nervous System Sends and receives electrical messages to and from the body. Made up of: • Brain • Spinal Cord The brain is the control center of the brain. It controls voluntary and involuntary movements in the body. Voluntary movements are actions under your control. Involuntary movements are actions you do without thinking. Brain Made up of three connected parts: 1. Cerebrum: Controls voluntary movement and detects light, touch, odors, sound, taste, pain, hot and cold. Right hemisphere: controls imagination, creativity Left hemisphere: controls speaking, reading, writing 2. Cerebellum: Controls your balance (keeps you upright). 3. Medulla: Controls involuntary movement: breathing, blood pressure, heart rate. Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla The Brain The Spinal Cord Passes information to and from the brain to the rest of the body. The spinal cord is surrounded by vertebrae (protective bones). The spinal cord allows the brain to communicate with the peripheral nervous system. A reflex is a reaction to a stimulus. Something you do without really thinking about it. It is an automatic response. Ex. Blinking when someone gets near your face. Touching a hot stove and screaming! Cerebrum Central Cerebellum Medulla Peripheral Spinal cord Spinal nerves Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla Spinal cord Spinal nerves