* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fahime_sheikhzadeh
Animal consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
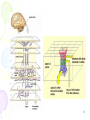
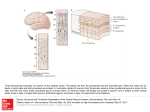
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Visual search wikipedia , lookup
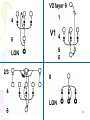
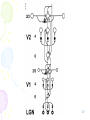
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
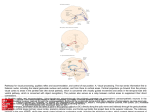
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Visual extinction wikipedia , lookup
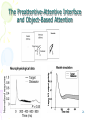
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
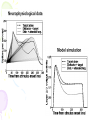
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
C1 and P1 (neuroscience) wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
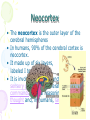
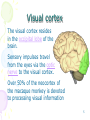
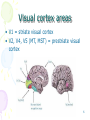
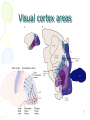
Towards a unified model of neocortex laminar cortical circuits for vision and cognition By: Fahime Sheikhzadeh 1 Outlines • Why computational models • A brief description about neocortex • Towards a unified theory of neocortex: laminar cortical circuits for vision and cogniton • Conclusion 2 Computational models Why should one use computational models to address questions in neuroscience? • Dealing with complexity • Checking conceptual models and revealing assumptions • Comparing and discovering hypotheses • Suggesting fruitful areas for new experiments 3 Neocortex • The neocortex is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres • In humans, 90% of the cerebral cortex is neocortex. • It made up of six layers, labeled I to VI • It is involved in higher functions such as sensory perception, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, conscious thought and, in humans, language. 4 Visual cortex The visual cortex resides in the occipital lobe of the brain. Sensory impulses travel from the eyes via the optic nerve to the visual cortex. Over 50% of the neocortex of the macaque monkey is devoted to processing visual information 5 Visual cortex areas • V1 = striate visual cortex • V2, V4, V5 (MT, MST) = prestriate visual cortex 6 Visual cortex areas 7 8 Towards a unified theory of neocortex: laminar cortical circuits for vision and cognition Stephen Grossberg Technical Report CAS/CNS TR-2006-2008 Invited article to appear in: Book Title: “Computational Neuroscience: From Neurons to Theory and Back Again” Publisher: Elsevier, Amsterdam 9 Abstract LAMINART architecture unifies properties of • visual development • Learning • perceptual grouping • Attention • 3D vision. A key modeling theme: mechanisms which enable development and learning to occur in a stable way imply properties of adult behavior 10 Introduction Researchers have tried to establish link between brain and mind by the use of application of classical concepts to the brain, like: • hydraulic systems • digital Computers • Holograms • control theory circuits • Bayesian networks None of these approaches has managed to explicate the unique design principles and mechanisms that characterize biological intelligence. 11 Computational paradigms of modeling of brain and behavior • Complementary Computing : matching and learning processes within the What and Where cortical streams • Laminar Computing: cerebral cortex is organized into layered circuits which undergo characteristic bottom-up, top-down, and horizontal interactions 12 Model • Some visual processes and their anatomical substrates that are being modeled as part of a unified vision system • • • • • • LGN = Lateral Geniculate Nucleus V1 = striate visual cortex V2, V4, MT, MST = prestriate visual cortex IT = inferotemporal cortex PPC = posterior parietal cortex PFC = prefrontal cortex. 13 14 Laminar Computing by Visual Cortex Unifying; (1) Adaptive Filtering: the developmental and learning processes (2) Grouping: the binding process (3) Attention 15 16 17 A New Way to Compute Properties: • A new type of hybrid between feedforward and feedback computing • A hybrid computing that simultaneously realizes the stability of digital computing and the sensitivity of analog computing • The ability to self-stabilize development and learning using the intracortical feedback loop 18 Attention Arises from Top-Down Cooperative-Competitive Matching • Provide only excitatory modulation to cells in the on-center, • Strongly inhibit cells in the off-surround. 19 20 The Preattentive-Attentive Interface and Object-Based Attention 21 Stable Development and Learning through Adaptive Resonance • attentionally relevant stimuli are learned • irrelevant stimuli are suppressed and prevented from destabilizing existing representations There is a link between attention and learning 22 3D LAMINART model • LAMINART model • Non-laminar FACADE model 3D LAMINART 3D LAMINART model has clarified how the laminar circuits of cortical areas V1, V2, and V4 are organized for purposes of stereopsis, 3D surface perception, and 3D figure-ground perception 23 24 Conclusion The family of LAMINART models now allows us to understand as variations of a shared cortical design brain processes that seem to be totally unrelated on the level of behavioral function. 25 References • “TOWARDS A UNIFIED THEORY OF NEOCORTEX: Laminar Cortical Circuits for Vision and Cognition”, Stephen Grossberg, Boston University. Invited article to appear in: Book Title: “Computational Neuroscience: From Neurons to Theory and Back Again”, Editors: Paul Cisek, Trevor Drew, and John Kalaska, Publisher: Elsevier, Amsterdam Supported • “Principles of Neural Science”, 4th_Edition, Eric R. Kandel, James H. Schwartz, Thomas M. Jessell 26 Thank u 27