* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
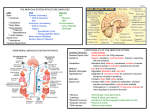
Our Very Own Human Computer CHAPTER 9 – THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OUR STANDARD THAT WE WILL COVER… Standard 4.1 – Investigate the anatomy and physiology of the central and peripheral nervous systems from the microscopic to the systemic levels OUR OBJECTIVE FOR TODAY By the end of this class, you will be able to describe the neural tissue, the meninges, and the cerebrum NEURAL TISSUE Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia cells (glial cells): that support and protect neurons https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vyNkAuX29OU ORGANS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain and spinal cord Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) Nerves connect nervous system with other systems ANATOMICAL DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. 2. Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) Consists of the spinal cord and brain Contain neural tissue, connective tissues, and blood vessels FUNCTIONS OF THE CNS Are to process and coordinate: sensory data: motor commands: higher functions of brain: intelligence, memory, learning, emotion THE BRAIN THE HUMAN BRAIN Ranges from 750 cc (cubic cm) to 2100 cc Contains almost 98% of the body’s neural tissue Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb) Some other interesting facts… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Jd0ahtfd74 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D33Aj5w061g MENINGES There are 3 layers (meninges) that surround the brain and spinal cord Pia mater – covers the brain Arachnoid – middle layer Dura mater – outermost layer that is attached to the interior of the skull MENINGES 6 REGIONS OF THE BRAIN Cerebrum Cerebellum Diencephalon Mesencephalon Pons Medulla oblongata REGIONS OF BRAIN Cerebrum Largest part of brain Controls higher mental functions Memory storage Skeletal Muscle Control Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres Surface layer of gray matter (neural cortex) REGIONS OF BRAIN Cerebrum Neural Cortex Also called cerebral cortex Folded surface increases surface area Elevated ridges (gyri) Shallow depressions (sulci) Deep grooves (fissures) “Squiggly Lines” REGIONS OF BRAIN TODAY’S OBJECTIVE By the end of today’s class, you will be able to describe and label all portions of the human brain by labeling a diagram and filling in the “Structure and Functions” worksheets REGIONS OF BRAIN Cerebellum Second largest part of brain Coordinates repetitive body movements 2 hemispheres Covered with cerebellar cortex REGIONS OF BRAIN Diencephalon Located under cerebrum and cerebellum Links cerebrum with brain stem Contains thalamus and hypothalamus REGIONS OF BRAIN Diencephalon (Con’t) Thalamus: relays and processes sensory information Hypothalamus: hormone production emotion thirst/hunger body temp. controls circadian rhythms (day–night cycles) REGIONS OF BRAIN The Brain Stem Processes spinal infomation between: cord and cerebrum or cerebellum Includes: mesencephalon pons medulla oblongata REGIONS OF BRAIN The Brain Stem (Con’t) Mesencephalon Also called midbrain Processes sight, sound, and associated reflexes Maintains consciousness Pons Connects cerebellum to brain stem Is involved in somatic and visceral motor control REGIONS OF BRAIN The Brain Stem (Con’t) Medulla Oblongata Connects brain to spinal cord Relays information Regulates autonomic functions: Cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems LIMBIC SYSTEM Includes tracts between the cerebrum and diencephalon. Functions are: Establishing emotional states Linking the conscious, intellectual functions of the cerebral cortex with the unconscious functions of the brain stem. Facilitating memory storage and retrieval. The cortices of the brain enable you to do tasks, the limbic system makes you want to do them. WRAPPING IT ALL UP Can you live without part of your brain? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uWkJnS8RHyE BELL WORK Pull out your fully-labeled diagram of the brain Just like previous chapters – color code each part of the brain that we labeled Use this time to review as you color coordinate You have 12 minutes for this activity TODAY’S OBJECTIVE By the end of the day, students will be proficient in “special areas” of the brains and their functions by group discussion. SENSORY AND MOTOR AREAS OF THE CEREBRUM THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Figure 14–12b OTHER INTEGRATIVE AREAS Speech center (Broca’s Area): Prefrontal cortex of frontal lobe: is associated with general interpretive area coordinates all vocalization functions integrates info from sensory association areas performs abstract intellectual activities (e.g., predicting consequences of actions) Hippocampus sorts and integrates emotions and memories deep portion on the temporal lobe THE LEFT HEMISPHERE In most people, left brain (dominant hemisphere) controls: reading, writing, and math decision-making speech and language THE RIGHT HEMISPHERE Right cerebral hemisphere relates to: senses (touch, smell, sight, taste, feel) recognition (faces, voice inflections) MEN’S VS. WOMEN’S BRAIN – THE GREAT MIND GAME For all your hard work so far, enjoy your treat… https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xDf0WJPqLE4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BxckAMaTDc THE SPINAL CORD SPINAL CORD Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long 1/2 inch (14 mm) wide Ends between vertebrae L1 and L2 Carries signals between brain and PNS Responsible for reflexes WRAPPING IT ALL UP Spinal Cord Dissection https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLMoP5bTvI8 BELL WORK Take a few of minutes to jot down a couple of examples of people that you have known in your life that have experienced or struggled with a nervous system disorder. What were the symptoms and struggles? After you finish, get out your notes. TODAY’S OBJECTIVE By the conclusion of class, you will be able to differentiate between common diseases and disorders of the CNS, along with introductory material of the PNS. COMMON DISORDERS AND DISEASES OF THE CNS MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS (MS) 200,000-400,000 people in the US affected The body ceases to function in certain areas due to demyleniation No known cure Some are chronic Some are flare-ups Vision, speech, and balance can be severely affected https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M7O78LvrNSQ TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY (TBI) Can range from mild concussions to severe brain damage Can cause a hematoma Symptoms can include dizziness, vomiting, blurred vision, head-ache, etc. Severe cases can lead to a vegetative state https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=eXqkBmjPeBs CEREBRAL PALSY (CB) Child is usually born with this Can affect gross motor skills and speech Most live normally with some assistance Some severe cases lead to paralysis or severe mental deficiencies Even in pop culture: https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=g9gBVn_KzBA Everything Not in the Brain or Spinal Cord THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (PNS) Includes all neural tissue outside the CNS PRIMARY FUNCTIONS OF THE PNS 1. 2. Deliver sensory information to the CNS Carry motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems WRAPPING IT ALL UP Group discussion about someone that you know that has been affected by one of the brain conditions that you wrote down today, or one that we just discussed - only share if you feel comfortable doing so. I will go first to get everyone started. TODAY’S OBJECTIVE By the end of class today you will be able to differentiate between the portions of the PNS and perform a cranial nerve test. NERVES Also called peripheral nerves: bundles of axons with connective tissues and blood vessels carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS: cranial nerves—connect to brain 12 pair spinal nerves—attach to spinal cord RECEPTORS AND EFFECTORS Receptors: detect changes or respond to stimuli neurons and specialized cells complex sensory organs (e.g., eyes, ears) Effectors: respond to efferent signals cells and organs FUNCTIONAL DIVISIONS OF THE PNS Afferent division: carries sensory information from PNS sensory receptors to CNS Efferent division: carries motor commands from CNS to PNS muscles and glands THE EFFERENT DIVISIONS OF THE PNS Somatic nervous system (SNS) Autonomic nervous system (ANS) THE SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (SNS) Includes all somatic motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles Controls skeletal muscle contractions: voluntary muscle contractions involuntary muscle contractions (reflexes) THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) Controls subconscious actions: contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle glandular secretions DIVISIONS OF THE ANS Sympathetic division: has a stimulating effect Fight or flight https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FBnBTkcr6No Parasympathetic division: has a relaxing effect STANDARD Standard 4.1 – Investigate the anatomy and physiology of the central and peripheral nervous systems from the microscopic to the systemic levels TODAY’S OBJECTIVE By the end of class today, you will be able to describe the neuron and its components. NEURONS The basic functional units of the nervous system More than 100 BILLION! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vyNkAuX29OU FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATIONS OF NEURONS Sensory neurons: afferent neurons of PNS Motor neurons: efferent neurons of PNS FUNCTIONS OF SENSORY NEURONS Monitor internal environment Monitor effects of external environment MOTOR NEURONS Carry instructions from CNS to peripheral effectors Via efferent fibers (axons) THE STRUCTURE OF NEURONS Figure 12–1 DENDRITES Highly branched many fine processes receive information from other neurons 80–90% of neuron surface area THE AXON Long shaped Carries electrical signal to target Axon structure is critical to function THE SYNAPSE Area where a neuron communicates with another cell Synaptic Cleft The small gap Synaptic Knob Is expanded area of axon THE SYNAPSE Figure 12–2 MYELINATION Increases speed of action potentials Insulation Makes nerves appear white NEURON SCHWANN CELLS Form myelin sheath around peripheral axons 1 Schwann cell sheaths 1 segment of axon: many Schwann cells sheath entire axon SCHWANN CELLS Figure 12–5a ELECTRICAL IMPULSES IN NERVES ION MOVEMENTS AND ELECTRICAL SIGNALS All cell membranes produce electrical signals by ion movements Transmembrane potential is particularly important to neurons MEMBRANE PROCESSES IN NEURAL ACTIVITIES Figure 12–7 (Navigator) ACTION POTENTIALS ALL-OR-NONE PRINCIPLE If a stimulus exceeds threshold amount: the action potential is the same no matter how large the stimulus Action potential is either triggered, or not