* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Truth about Weed - Copley
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
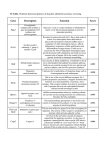
The Truth about Weed Nia Forbes Samuel Joseph Outline Normal Brain Function Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Body Overall Brain Function, under THC Influence Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Body Overall Disclaimer As scientists, our job is present facts. These facts are non-biased, genuine truths about the effects of the neurochemicals in marijuana. We do not represent CopleyFairlawn City Schools, nor do we condone the illegal recreational use of marijuana. The Human Brain Need-to-Know Vocabulary Axon – a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body Pons – a structure located on the brain stem that conduct signals from the cerebrum down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus Synapse - a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell Neuron – an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals receptor antagonist - a type of receptor ligand that does not provoke a biological response upon binding to a receptor, but blocks or dampens agonist-mediated responses Agonist - a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell Two Neurons to Rub Together The Central Nervous System As the communication and decision center, your brain’s maintained health is essential to your daily survival. Three parts make up the brain: 1. Forebrain 2. Midbrain 3. Hindbrain Forebrain Cerebrum Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebrum Cerebrum, in detail Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech The bulk of the cerebrum is made of the neocortex, a six-layered structure associated with higher mammals. Cerebellum (little brain) associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance Limbic System (emotional brain) emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction (sense of smell) a large mass of gray matter deeply situated in the forebrain at the topmost portion of the diencephalon sensory and motor functions Limbic System: Thalamus Limbic System: Hypothalamus involved including homeostasis, emotion, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythms, and control of the autonomic nervous system. In addition, it controls the pituitary. Limbic System: Amygdala almond-shaped groups of nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain primary role in the processing of memory and emotional reactions Limbic System: Hippocampus important in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation In Alzheimer's disease, the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage Midbrain a region of the brain, specifically the dorsal part Tectum of the mesencephalon a multi-synaptic network of neurons that is involved in many Tegmentum unconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways Hindbrain, or Brain Stem a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation The Effects of Marijuana Cannabinoid Receptors Cannabinoid receptor type 1 Can be found everywhere in the brain except the brain stem Will not effect breathing or heartbeat Responsible for the euphoria Cannabinoid receptor type 2 Found mainly in the immune system (spleen) Responsible for anti-inflammatory and therapeutic actions 5-HT1A receptor a G-coupled protein receptor that binds to serotonin Activation of this receptor has been shown to have the following effects: Decreases blood pressure Decreased aggression Increased sociability Decreased impulsivity Inhibition of drug-seeking behavior Facilitation of sex drive and arousal Inhibition of penile erection Diminished food intake Prolongation of REM sleep latency Reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor A G-coupled protein receptor that binds to norepinephrine and epinephrine Activation of this receptor may result in: Vasoconstriction of arteries Vasoconstriction of coronary artery Constriction of some vascular smooth muscle Venoconstriction of veins Decreased motility of smooth muscle in gastrointestinal tract Inhibition of lipolysis What is Marijuana? a dry, shredded mix of flowers, stems, seeds and leaves of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa Cannabis-derived cannabinoids Tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabidiol (THC) (CBD) Cannabinol (CBN) Cannabichromene (CBC) Cannabigerol (CBG) Cannabidivarin (CBDV) Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) the primary psychoactive component of the Cannabis plant How THC Works By mimicking anandamide, a pleasure-inducer in the CNS, THC activates the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain. Cannabidiol (CBD) Cannabidiol (CBD) Not psychoactive Higher concentrations in cannabis consumption is proven to prevent schizophrenia Anti-depressant, anxiolytic, neuroprotective relieve convulsion, inflammation, anxiety, and nausea Higher affinity for CB2 Cannabinol (CBN) By-product of THC decomposition Higher affinity for CB2 References http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/bb/kinser/Stru cture1.html http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/161990 61 http://leg.mt.gov/content/Committees/Interi m/2009_2010/Children_Family/EmergingIssue/mmga-presentation-plant-chemistry.pdf montanabiotech.com/cannabinoid-factsthc-cbd-cbn-cbc-thcv-cbg/