* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cerebrum
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
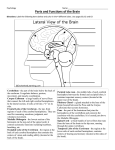
The Cerebrum • The Cerebrum • Is the largest part of the brain • Controls all conscious thoughts and intellectual functions • Processes somatic sensory and motor information » Voluntary and involuntary The Cerebrum • The Cerebrum • Gray matter found in… » Superficial layer of neural cortex » Deeper basal nuclei • White matter found in… » Deep to basal cortex » Around basal nuclei The Cerebrum • Structures of the Cerebral Hemispheres • Lateral and superior surfaces covered in neural cortex called cerebral cortex • Outer surface of cerebral cortex covered in a series of elevated ridges called gyri (JĪ-rī) » Increase surface area (number of cortical neurons) • Gryi are separated by shallow depressions called sulci (SUL-sī) The Cerebrum • Structures of the Cerebral Hemispheres • The cerebral hemipsheres are separated by a deep longitudinal fissure » From the fissure, each hemisphere can be divided into well-defined regions called lobes • Lobes are named after the overlying bones of the skull • QUESTION: » Can you remember the major bones of the cranium? The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Structures of the Cerebral Hemispheres • Extending laterally from the longitudinal fissure is a deep groove called the central sulcus » This a major dividing line to separate the different lobes • Major Lobes » Frontal lobe » Temporal lobe » Parietal lobe » Occipital lobe The Cerebrum • Review of key features: • Central sulcus divides: » Anterior frontal lobe from posterior parietal lobe • Lateral sulcus divides: » Frontal lobe from temporal lobe • Parieto-occipital sulcus divides: » Parietal lobe from occipital lobe Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. The Cerebrum • Review of key features: • In each lobe, some regions are concerned with sensory information and motor commands • Each hemisphere receives sensory information from, and sends motor commands to, the opposite side of the body » Left hemisphere controls right side of body » Right hemisphere controls left side of body The Cerebrum • Motor and Sensory Areas of the Cortex • Central sulcus separates motor and sensory areas • Primary Motor Cortex » Neurons control voluntary motor movements by controlling somatic motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord » Located on the frontal lobe (anterior to the central sulcus) The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Motor and Sensory Areas of the Cortex • Central sulcus separates motor and sensory areas • Primary Sensory Cortex » Neurons receive somatic sensory information from touch, pressure, pain, and temperature receptors » Located on the parietal lobe (posterior to the central sulcus) » Consciously aware due to information sent through brain stem The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Special Sensory Cortexes • Smaller regions (cortexes) of the brain process special sensory information • Visual Cortex: » Located on occipital lobe » Receives visual information The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Special Sensory Cortexes • Auditory Cortex: » Located on temporal lobe » Receives auditory information The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Special Sensory Cortexes • Olfactory Cortex: » Located on temporal lobe » Receives information from odor receptors The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Special Sensory Cortexes • Gustatory Cortex: » Located on frontal lobe » Receives information from taste receptors The Cerebrum The Cerebrum The Cerebrum • Association Areas • Regions that interpret incoming data or coordinate a motor response • Areas are located within the different “lobes” of the cerebrum » Each “lobe” has a different association area • Two Major Association Areas: » Sensory Association Area » Motor Association Area Sensory Association Areas • Frontal Lobe • Prefrontal Association Area » Reasoning skills » Coordinates information from other association areas » Controls some behaviors Sensory Association Areas Sensory Association Areas • Parietal Lobe • Somatic Sensory Association Area » Receives and interprets information from skin, musculoskeletal system, vicera (organs), and taste buds » Works with primary sensory cortex Sensory Association Areas Sensory Association Areas • Temporal Lobe • Auditory Association Area » Receives and interprets information for sound and hearing from the auditory cortex Sensory Association Areas Sensory Association Areas • Occipital Lobe • Visual Association Area » Receives and interprets information for sight from the visual cortex Sensory Association Areas Motor Association Area • Somatic Motor Association Area • Responsible for coordinating learned movements • Usually associated with a voluntary movements • Also called the premotor cortex • Located on the frontal lobe The Cerebrum • General Interpretive Area • Also called Wernicke area • Present in only one hemisphere » Usually the left hemisphere • Receives information from all sensory association areas • Coordinates access to complex visual and auditory memories • Damage Report: » Can affect the ability to interpret what is read or heard The Cerebrum • Other Integrative Areas • Speech center (Brocha Area): » Is associated with general interpretive area » Coordinates all vocalization functions, including breathing and vocalization » Motor commands from this area are adjusted by auditory association area • Damage Report: » Difficulty speaking (mixing words or continuous speaking) The Cerebrum • Other Integrative Areas • Prefrontal cortex of frontal lobe: » Integrates information from sensory association areas » Performs abstract intellectual activities » Feelings of frustration, tension and anxiety are generated here • Damage Report: » Difficulty estimating time relationships between events Hemispheric Lateralization • Hemispheric Lateralization • Functional differences between left and right hemispheres • Each cerebral hemisphere performs certain functions that are not ordinarily performed by the opposite hemisphere • Hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum Hemispheric Lateralization • Corpus Callosum • Region of white matter that lies beneath the cerebral cortex • Axons of different lengths interconnect within a single hemisphere Hemispheric Lateralization • The Left Hemisphere • In most people, the left brain (dominant hemisphere) controls: » Reading, writing, and math » Decision making » Speech and language » Analytical tasks and logical reasoning • Location of premotor cortex involved with hand movements » Control of right-handedness or left-handedness Hemispheric Lateralization Hemispheric Lateralization • The Right Hemisphere • Right cerebral hemisphere relates to: » Analyzes sensory information » Interpretative ability based on senses (touch, smell, sight, taste, hearing) » Recognition (faces, voice inflections) Hemispheric Lateralization The Cerebrum • The Basal Nuclei • Also called cerebral nuclei • Are masses of gray matter • Are embedded in white matter of cerebrum • Direct subconscious activities The Cerebrum • Functions of Basal Nuclei • Involved with: » The subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone » The coordination of learned movement patterns (walking, lifting) • Example walking » Basal nuclei controls cycles of arm and thigh movements that occur while walking The Basal Nuclei The Basal Nuclei The Limbic System • The Limbic System • Is a functional grouping that: » Establishes emotional states » Links conscious functions of cerebral cortex with autonomic functions of brain stem » Facilitates memory storage and retrieval The Limbic System • Functions of the Limbic System • Regulation of heart rate during “fight or flight” response • Linking of memories to emotions • Storage of long-term memories • Control of emotional states • Reflex movements that can be consciously activated The Limbic System The Diencephalon • Functions of the Diencephalon • Made up of the thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus • Integrates conscious and unconscious sensory information and motor commands The Diencephalon • Functions of the Epithalamus • Contains the pineal gland » Secretes hormone melatonin » Helps to regulate day-night cycles • Functions of the Thalamus • Final relay point for all ascending sensory information • Acts as a filter to pass on ONLY the most important sensory information • Coordinates voluntary and involuntary motor commands The Diencephalon • Functions of the Hypothalamus • Subconscious control of skeletal muscle contractions • Coordinates activities between nervous and endocrine systems • Produces feelings of “hunger” and “thirst” • Regulates normal body temperature • Coordinates cycles of activity The Diencephalon and Brain Stem The Midbrain • Functions of the Midbrain • Helps to process visual and auditory sensations » Causes you to flinch when you hear a loud noise • Maintenance of muscle tone and body posture • Integrates information from cerebrum and cerebellum The Diencephalon and Brain Stem The Pons • Functions of the Pons • Links cerebellum with midbrain, dienchephalon, cerebrum and spinal cord • Involuntary control of respiration pace and depth The Diencephalon and Brain Stem The Medulla Oblongata • Function of the Medulla Oblongata • Allows brain and spinal cord to communicate • Coordinates complex autonomic reflexes • Controls visceral functions • Nuclei in the medulla: » Autonomic nuclei: control visceral activities » Sensory and motor nuclei: of cranial nerves » Relay stations: along sensory and motor pathways The Diencephalon and Brain Stem