* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain-Class Notes
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
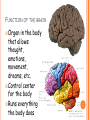
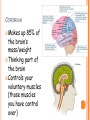
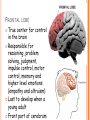
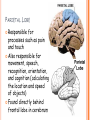
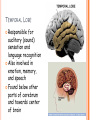
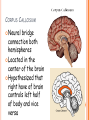
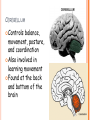
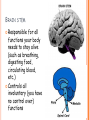
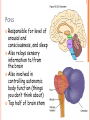
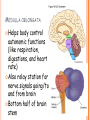
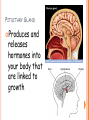
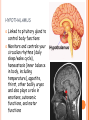
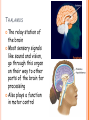
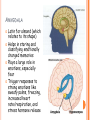
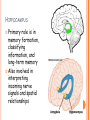
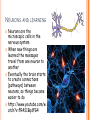
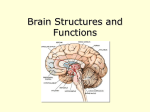
PARTS OF THE BRAIN FUNCTION Organ OF THE BRAIN in the body that allows: thought, emotions, movement, dreams, etc. Control center for the body Runs everything the body does CEREBRUM Makes up 85% of the brain’s mass/weight Thinking part of the brain Controls your voluntary muscles (those muscles you have control over) FRONTAL True LOBE center for control in the brain Responsible for reasoning, problem solving, judgment, impulse control, motor control, memory and higher level emotions (empathy and altruism) Last to develop when a young adult Front part of cerebrum PARIETAL LOBE Responsible for processes such as pain and touch Also responsible for movement, speech, recognition, orientation, and cognition (calculating the location and speed of objects) Found directly behind frontal lobe in cerebrum OCCIPITAL LOBE Responsible for visual sense and processing Found at back of cerebrum TEMPORAL LOBE Responsible for auditory (sound) sensation and language recognition Also involved in emotion, memory, and speech Found below other parts of cerebrum and towards center of brain CORPUS CALLOSUM Neural bridge connection both hemispheres Located in the center of the brain Hypothesized that right have of brain controls left half of body and vice versa CEREBELLUM Controls balance, movement, posture, and coordination Also involved in learning movement Found at the back and bottom of the brain BRAIN STEM Responsible for all functions your body needs to stay alive (such as breathing, digesting food, circulating blood, etc.) Controls all involuntary (you have no control over) functions PONS Responsible for level of arousal and consciousness, and sleep Also relays sensory information to/from the brain Also involved in controlling autonomic body function (things you don’t think about) Top half of brain stem MEDULLA OBLONGATA Helps body control autonomic functions (like respiration, digestions, and heart rate) Also relay station for nerve signals going/to and from brain Bottom half of brain stem PITUITARY GLAND Produces and releases hormones into your body that are linked to growth HYPOTHALAMUS Linked to pituitary gland to control body functions Monitors and controls your circadian rhythms (daily sleep/wake cycle), homeostasis (inner balance in body, including temperature), appetite, thirst, other bodily urges and also plays a role in emotions, autonomic functions, and motor functions THALAMUS The relay station of the brain Most sensory signals like sound and vision, go through this organ on their way to other parts of the brain for processing Also plays a function in motor control AMYGDALA Latin for almond (which relates to its shape) Helps in storing and classifying emotionally charged memories Plays a large role in emotions, especially fear Trigger responses to strong emotions like sweaty palms, freezing, increased heart rate/respiration, and stress hormone release HIPPOCAMPUS Primary role is in memory formation, classifying information, and long-term memory Also involved in interpreting incoming nerve signals and spatial relationships NEURONS AND LEARNING Neurons are the microscopic cells in the nervous system When new things are learned the messages travel from one neuron to another Eventually the brain starts to create connections (pathways) between neurons, so things become easier to do http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=FR4S1BqdFG4