* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Central Nervous System
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
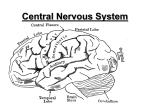
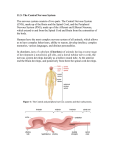
Central Nervous System Neuron Review Video You Need: Blue, Yellow, Green and Pink Pencils CNS=Central Nervous System Main parts of the CNS: 1. BRAIN (cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem) A large mass of nerve cells located in the cranium 2. SPINAL CORD Carries information (nerve impulses) between the body and brain Is the reflex center 1. The Brain Cerebrum Cerebellum Brain Stem Protection for the Brain What happened to Phineas Gage? Intro Video Questions 1) How did Phineas Gage change after the accident? 2) How did Phineas Gage’s accident change scientists’ understanding of the brain? A. Cerebrum Made up of 2 hemispheres, each controlling one half of the body • The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body, logical thinking, mathematical thinking, language, problem-solving and comparing information • The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, artistic expression, creativity and spatial understanding (ex. reading a map) White Matter and Gray Matter • The cerebrum is composed of: – gray matter (cell bodies which process information) – white matter (axons of neurons which convey messages). A. The Cerebrum • Also known as the cerebral cortex, is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal – Each lobe has its own particular responsibilities: • Frontal: movement, thinking, problemsolving • Parietal: touch, pain and pressure information • Occipital: visual information • Temporal: auditory information The Cerebrum Basics of the Brain: to 3:45 Probe the Brain • Beginning in the 1940s, Canadian brain surgeon Wilder Penfield mapped the brain's motor cortex -- the area that controls the movement of your body's muscles. He found the secrets to epileptic seizures… • He did this by applying mild electric currents to the exposed brains of patients while they were in surgery. •Canadian Heritage Moment: Burnt Toast B. Cerebellum (“small brain”) • Coordinates – movement – Balance – learned skills B. Cerebellum • Receives messages from most of the muscles in your body, from the eyes, inner ear. • Communicates with the other parts of the brain • Sends messages about movement and balance back to your body. C. Brain Stem • Transmits information from the brain to spinal cord and vice versa. • Coordinates – Heartbeat – Breathing – Digestion – Swallowing, Blinking, – coughing, sneezing – Sleep, waking & dreaming 2.The Spinal Cord 2. Spinal Cord • Long tube of nerve tissue running from the brain down the length of the back inside of the spine • Protected by the vertebrae • Function: 1) carries nerve impulses between the brain and the rest of the body. 2) Is responsible for reflexes Damage to the C.N.S. Concussion: temporary, hit to the head, may produce unconsciousness or bleeding in or around the brain. Paralysis: injury to the spinal cord Cerebral palsy: lack of muscle control due to brain damage before or soon after birth Epilepsy: muscular seizures and body convulsions caused by abnormal action potentials Multiple sclerosis: hardening of the nerve tissue in the brain or spinal cord Ways to improve the power of your brain… (or, how to become more intelligent) Interesting Video: Power of Thoughts Lead a balanced lifestyle by: A. Eating a Proper diet: The nervous system needs a regular supply of B vitamins because these vitamins: - strengthen the neurons - facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses Foods that are rich in B vitamins are: - egg yolks, milk, whole grain cereals, fresh meat B. Exercise regularly The brain needs 20% of the body’s oxygen to function properly, so it’s important for your circulatory system be in tip-top shape. You can achieve this by exercising on a regular basis. C. Get enough sleep While you sleep your neurons reset themselves and prepare for a new day of activity. If the body does not get enough sleep: – Intellectual performance will be impaired – Reflexes slow down – It becomes difficult to concentrate PBS clip: From Zzzz’s to A’s. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/sho ws/teenbrain/view/ ← Click here 1. How many hours of sleep to you need to get in order to be fully alert? 2. What is the name of your Biological Timing System and how does it change during the teenage years? 3. What analogy does the announcer use for a teen that is trying to function with not enough sleep? 4. What are three daily life functions that sleep affects your ability to do? 5. What is REM sleep and what happens during this time? 6. What is the best predictor of whether or not you will succeed at school? 7. What were the results of the study of the relationship between learning and sleep in teens Charlie and Nicole? From Zzzz’s to A’s ANSWERS 1. 9 ¼ hours. 2. The circadian clock: it shifts forwards (in the day) during the teenage years. 3. It’s like a car trying to run on an empty tank. 4. Your mood, your ability to think and your ability to perform and react appropriately. 5. Rapid Eye Movement. Dreaming and learning happens during this time. 6. Whether or not you get a good night’s sleep. 7. Nicole got more REM sleep than Charlie did. She also improved more on the learning tasks than Charlie; thus, the more REM sleep you get the better you learn. Review Questions - CNS 1) What are the main parts of the central nervous system? 2) What is the brain? 3) What are the 3 major structures of the brain? 4) What are the 4 different layers of protection of the brain? 5) What functions are controlled by the left cerebral hemisphere? Review Questions - CNS 6) What functions are controlled by the right cerebral hemisphere? 7) What did the study of Phineas Gage teach us about the brain? 8) What are the different lobes of the cerebral cortex and what are their functions? 9) What is the difference between white matter and grey matter? 10) Who is Wilder Penfield and how did he contribute to our understanding of the brain? Review Questions - CNS 11) What is the function of the cerebellum? 12) What parts of your body does the cerebellum communicate with? 13) What is the function of the brainstem? 14) What is the function of the spinal cord? 15) What protects the spinal cord? 16) What is a consequence of damage to the spinal cord? 17) What 3 things can you do to improve the power of you brain? Review Questions – CNS 1) What are the main parts of the central nervous system? Brain, spinal cord 2) What is the brain? The brain is the main organ of the CNS. It is composed of nearly 100 billion nerve cells which are folded together in order to fit inside the cranium. 3) What are the 3 major structures of the brain? cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem 4) What are the 4 different layers of protection of the brain? 1- Cerebrospinal fluid 2 – Meninges 3 – the skull 4 – skin of the scalp 5) What functions are controlled by the left cerebral hemisphere? The left hemisphere controls logical thinking, mathematical thinking, language, 6) What functions are controlled by the right cerebral hemisphere? The right hemisphere controls artistic expression, creativity and spatial understanding. 7) What did the study of Phineas Gage teach us about the brain? The brain is not only responsible for language and movement but it is also responsible for determining one’s emotions and personality. The Cerebrum 8) What are the different lobes of the cerebral cortex and what are their functions? – Frontal: movement, thinking, problem-solving – Parietal: touch, pain and pressure info. – Occipital: visual information – Temporal: auditory information 9) What is the difference between white matter and grey matter? Grey matter is a collection of neuronal cell bodies, including dendrites. It is the region of the cerebrum where synapses are made. White matter refers to the collection of axons of those neurons. It is where nerve fibers are located. 10) Who is Wilder Penfield and how did he contribute to our understanding of the brain? Wilder Penfield was a Canadian brain surgeon whocreated of map of the motor cortex (which regions of the brain control which body parts). 11) What is the function of the cerebellum? The cerebellum coordinates movement and learned skills. It is also responsible for your sense of balance. 12) What parts of your body does the cerebellum communicate with? Your cerebellum receives messages from most of the muscles in the body, the eyes, and the inner ear. It passes on this information to other parts of the brain. 13) What is the function of the brainstem? The brainstem transmits information from the brain to spinal cord and vice versa. It coordinates a wide range of vital functions including: heartbeat, breathing, digestion, swallowing, blinking, coughing, sneezing, sleep, waking & dreaming. 14) What is the function of the spinal cord? The spinal cord carries nerve impulses between the brain and the rest of the body. It is also responsible for reflexes. 15) What protects the spinal cord? The vertebrae protect the spinal cord. 16) What is a consequence of damage to the spinal cord? Damage to the spinal cord can result in paraplegia (the loss of movement and sensation in all 4 limbs) or quadriplegia (the loss of movement and sensation in the legs). 17) What 3 things can you do to improve the power of you brain? Maintain a healthy diet rich in B vitamins, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep (9 ¼ hours/ night)