* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch03.pps
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
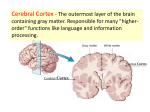
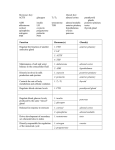
CHAPTER The brain is remarkable in what it can do. This lecture will show that the brain plays an important part in everything we think and do. © West Educational Publishing 3 Brain, Body and Behavior EXIT Cerebral Cortex The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the brain and controls very high level thought processes. © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Corpus Callosum is a thin band of tissues inside the fissure. Front Left Right Rear © West Educational Publishing EXIT Tasks of the Cerebral Hemispheres The brain is divided into halves. Each half, or hemisphere, controls the opposite side of the body. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Click on the arrows for more information. Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Hippocampus Pituitary Cerebellum Amygdala © West Educational Publishing Reticular activating system EXIT The Lower Brain The cerebral cortex covers, protects, and influences the lower brain structures. Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Hippocampus Pituitary Click for more information. Cerebellum Amygdala Reticular activating system Cerebral cortex Hypothalamus Thalamus Cerebellum © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Lower Brain The thalamus acts as a relay station to send incoming and outgoing messages to appropriate areas in the brain. Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Hippocampus Pituitary Click for more information. Cerebellum Amygdala Reticular activating system Cerebral cortex Hypothalamus Thalamus Cerebellum © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Lower Brain The hypothalamus controls hunger, pleasure, thirst, rage, and sexual desire. Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Thalamus Hypothalamus Hippocampus Pituitary Click for more information. Cerebellum Amygdala Reticular activating system Cerebral cortex Hypothalamus Thalamus Cerebellum © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Lower Brain The cerebellum helps you to stand upright and keeps your movements coordinated. Cerebral cortex Corpus callosum Thalamus Hippocampus Hypothalamus Pituitary Click for more information. Cerebellum Amygdala Reticular activating system Cerebral cortex Hypothalamus Thalamus Cerebellum © West Educational Publishing EXIT Other Lower Brain Structures The Limbic System is involved with basic emotions and memory. Two important structures include the amygdala (emotional responses and aggression) the hippocampus (the formation of new memories) The Reticular Activating System keeps track of nerve impulse activity and helps regulate how alert or sleepy we feel. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Brain Communication A NEURON is a nerve cell. It is the smallest part of the nervous system. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Brain Communication Dendrites branch off the body of the neuron and receive impulses from other neurons. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Brain Communication Axons gather impulses from dendrites and carry them to other neurons. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Brain Communication The synapse is the space between the axon of the sending neuron and the dendrites of the receiving neuron. © West Educational Publishing EXIT Neurotransmitters are messenger molecules (pain, pleasure, movement) © West Educational Publishing EXIT Acetylcholine • sends information to other nerve cells when some part of the body moves • can affect memory • production of this neurotransmitter can be shut down by food poisoning Dopamine • involved in movement • a shortage can cause Parkinson’s disease Endorphins • relieve pain and • increase the sense of well-being (“natural morphine”) © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Nervous System Central Nervous System The Brain and the Spinal Cord Peripheral System Somatic Voluntary Muscles and Sense Organs © West Educational Publishing Autonomic Involuntary Muscles and Internal Organs Parasympathetic calms body after action Sympathetic prepares body for action slows heartbeat contracts pupils stimulates digestion etc. dilates eyes accelerates heartbeat inhibits digestion etc. EXIT The Endocrine System Pituitary gland Click on the arrows for more information. Thyroid Adrenal gland Female gonads (ovaries) © West Educational Publishing Male gonads (testes) EXIT The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland Pituitary gland • the master gland • controlled by the hypothalamus • sends a message to other glands to begin working • determines how tall or short a person will be Click for more information. Pituitary gland Thyroid Gonads Adrenal gland © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Endocrine System The Gonads • sex glands that produce either sperm or eggs used in reproduction Click for more information. Pituitary gland Thyroid Gonads Adrenal gland © West Educational Publishing Female gonads (ovaries) Male gonads (testes) EXIT The Endocrine System The Thyroid Gland • controls metabolism • overactive thyroid may Thyroid cause restlessness and anxiety • underactive thyroid may result in sadness and even depression Click for more information. Pituitary gland Thyroid Gonads Adrenal gland © West Educational Publishing EXIT The Endocrine System The Adrenal Gland • secretes adrenaline into the bloodstream • blood pressure goes up, muscles tense, and hands tremble Adrenal gland Click for more information. Pituitary gland Thyroid Gonads Adrenal gland © West Educational Publishing EXIT Summary of Main Topics Covered Parts of the Brain The Lower Brain Brain Communication Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The Endocrine System © West Educational Publishing EXIT