* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of CNS
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Olfactory bulb wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural binding wikipedia , lookup
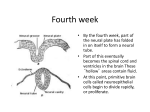
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey’s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto’s Dev Neuroscience lecture from 2003) Central Nervous System Lateral view of the ventricles of the brain Dorsal view of the spinal cord • The brain is an astonishingly complex structure. • However not only is it an amazing structure it is also, to a large degree, self assembling. • When development goes wrong it causes great problems as, unlike for example cardiac problems, it does not always lead to death • About 1.3% of total births have some neural abnormality Comparative neurology optic lobe olfactory bulb cerebral cortex cerebellum forebrain CODFISH pituitary olfactory bulb cerebellum HORSE optic lobe forebrain cerebellum olfactory bulb cerebral hemisphere FROG optic lobe forebrain superior and inferior colliculi olfactory bulb cerebellum HUMAN cerebellum ALLIGATOR olfactory bulb The degree of complexity of the brain in the different vertebrate species reflects its evolution. forebrain cerebellum olfactory bulb GOOSE optic lobe The basic subdivisions of the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain are seen in all vertebrates and during evolution the most striking changes have taken place in the rostral part of the forebrain, which gives rise to the olfactory bulb and the telencephalon. Development of the CNS Formation of major brain divisions via Flexures and swellings of neural tube • • Prosencephalon Forebrain – cerebral hemispheres (cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, lateral ventricles etc) - Telencephalon • • Diencephalon Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus • • Mesencephalon - (cephalic flexure) Midbrain • • • Rhombencephalon – (pontine and cervical flexures) Metencephalon – pons, cerebellum Myelencephalon - medulla • Spinal cord More specifically: 1- Specification of neural tissue 2- Origin, birth and migration of cells 3- Acquisition of cell phenotype 4- Formation of correct connections 1- Specification of neural tissue & neural tube formation Gastrulation stage Neural default model of induction Frog blastula Ectoderm (animal cap) Ventral Meso Meso Endoderm (vegetal region) Mesoderm (marginal zone) Dorsal Marginal zone Endoderm Organizer (Nieuwkoop centre) BMPs (↑ectod diff/↓neuroectod diff) BMP antagonists (chordin, follistatin, noggin) Weinstein and Hemmati-Brivanlou Curr. Opin. Neurobiol (1997) 7:7-12 Formation of neural plate, neural groove and neural tube 22-23 days Human neural tube closure Anterior neuropore 22 days 23 days Normal Anencephaly Spina bifida Dorsal and transverse sections Anterior and Posterior neuropores are open to amniotic fluid. Neural tube closure in mammals us initiated at several places along the anterior-posterior axis. Different neural tube defects are caused when various parts of the neural tube fail to close. Failure to close the human posterior neural tube at day 27 results in spina bifida. Failure to close the anterior neural tube results in a lethal condition, anencephaly. In this condition, the forebrain remains in contact with the amniotic fluid and subsequently degenerates. Anterior neuropore 23 days ns pores Normal Anencephaly Spina bifida Neural crest cells and peripheral NS 2- Origin, birth and migration of CNS-cells Neuroepithelial cells “bounce” up and down Cell migration and radial glia 3- Acquisition of cell phenotype in CNS Signalling centres Isthmus - midbrain/hindbrain boundary mouse Shh Wnt1 Fgf8 Dopaminergic neurons Serotonergic neurons Wurst and Bally-Cuif Nature Rev Neurosci 2001 2:99-108 chick What is a morphogen? Diffusible factor that carries information relating to the position in the embryo, and thus determines the fate of cells perceiving this information Secreted factors Shh - Sonic hedgehog, Fgf8 - Fibroblast growth factor 8 vs Transcription factors Wnt1, En - Engrailed, Pax 2/5/8 Neuronal differentiation Specification of neuronal identity by SHH Neuronal induction SHH expression V1, V2, V3 interneruons; MN motor neurons; FP floor plate; N notochord • SHH is a morphogen • SHH can induce naive neuroepithelial cells to differentiate • SHH is secreted from the notochord and decreases in concentration towards the dorsal neural tube • Concentration specific induction of floor plate, motorneurons and interneurons Briscoe and Ericson Sem Cell Dev Biol (1999) 10:353 Patterning Hindbrain segmentation (AP Axis) Identity is conferred onto each rhombomere by the expression of different transcription factors Hox gene family of proteins Sek gene family of proteins Rhombomere 1 (metencephalon) is not specified by these transcription factors... Lateral view of a 48 h chick embryo Lumsden and Krumlauf Science 1996:1109-1115 Patterning Hindbrain segmentation (AP Axis) Why form segments? Hox genes encode positional value along the AP axis This forms developmental compartments that provide a way of allocating blocks of cells with distinct properties Restriction of neuron axonal projectories (cranial nerves V, VII, VIII, IX) Confer rhombomere-specific identities to motor neurons Flatmount of neural tube Lumsden and Krumlauf Science 1996:1109-1115 4- Formation of correct connections Rodent brain Human CNS Synaptogenesis and Synaptic Pruning Adolescent brain maturation Human Brain Development; Thompson & Nelson 2001