* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biopsychology - WordPress.com
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
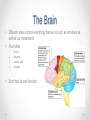
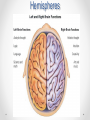
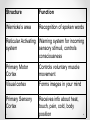
Biopsychology An introduction What is Biological Psychology? • This approach tries to explain human behaviour in terms of our biology. • What behaviour do you think can be determined by our biology? Assumptions • All behaviour has a biological basis (a physical cause) • Our biology is a result of the interaction between the genes we inherited and the environment we grew up in • Our genes have evolved over thousands of years to make us adaptive to our changing environment • We are biological machines made up of chemicals and cells Central Nervous System • • • • • Our Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain and spinal cord Our Peripheral Nervous System Our Genes Our hormones Disease, injury, substance abuse Topics of interest • • • • • • • • • • Sensation and perception Hormones and sex Drug addiction Consciousness and attention Sleep, dreaming and circadian rhythms Memory and amnesia Neuroplasticity and learning Emotions, stress, illness (schizophrenia, anxiety, etc) Language and cognition Lateralization of function Divisions... • Physiological psychology ~ Studies neural mechanisms of behaviour through direct manipulation of the brain • Psychopharmacology ~ Studies the manipulation of neural activity and behaviour with drugs • Neuropsychology ~ Studies the psychological effects of brain damage • Cognitive neuroscience ~ Studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception The Brain can affect Behaviour • Researchers looked at individuals who have suffered a brain injury and observing a change in their behaviour • Without researching brain injury it would have been hard to show any evidence that the brain was playing a part in behaviour. Research Methods • Visualize the brain o CAT, MRI, PET, fMRI • Record activity o EEG, muscle tension, eye movement, skin conductance, cardiovascular activity • Invasive surgery o E-stim, lesions • Brain damage patients Phineas Gage • Phineas Gage suffered an accident where a large rod was blasted through his skull and brain. • He survived this ordeal but it was reported that his behaviour changed after the event. He became anti-social and ill-mannered. • His friends said “Gage was no longer Gage.” The Brain • Different areas control everything that we do such as emotions as well as our movements • Four lobes : 1. 2. 3. 4. frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital. • Each has its own function. Hemispheres Cortex • Frontal lobe o personality o social-emotional o plans • Parietal lobe o joints and skin • Temporal lobe o hearing and speech • Occipital lobe o vision Inside the Brain - Neurons • The brain is full of neurons – more than 100 billion! Neurons • Neurons carry signals electrically along their axon and chemically across a synapse • Synapse is a gap between two neurons • Neurons never touch ~ to communicate they send chemicals across the synapse and these are picked up by the other neuron Neuron sending the chemical signal Chemicals being released into the synapse Neuron picking up the chemical signal Structure Function Angular Gyrus Internal monologue, written language processing, visual and auditory input processing Hippocampus Short term memory formation, sequential actions Thalamus Controls flow of info to cortex, relay station Amygdala Emotional behaviour, motivation Corpus Callosum Connects left and right hemispheres Medulla Controls respiration, heart rate, blood pressure, etc. (autonomic functions) Broca’s area Comprehension of language Hypothalamus Maintains homeostasis (eating, sleeping, temp, etc.) Cerebellum Controls involuntary movement (balance, coordination) Structure Function Wernicke’s area Recognition of spoken words Reticular Activating Warning system for incoming system sensory stimuli, controls consciousness Primary Motor Cortex Controls voluntary muscle movement Visual cortex Forms images in your mind Primary Sensory Cortex Receives info about heat, touch, pain, cold, body position The Core Studies • Maguire et al. – brain scans on taxi drivers • Sperry – split brain patients • Dement and Kleitman – sleep and dreaming