* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
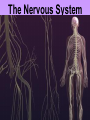
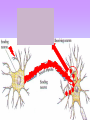
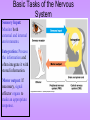
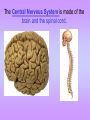
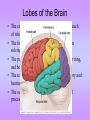
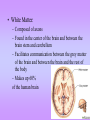
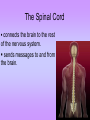
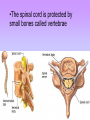
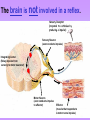
The Nervous System • The nervous system has a coordinating role where it receives, processes, stores, and transmits information that comes from the body and the outside world Structure of a Neuron •The neuron is the basic unit (cell) of nervous system •Impulses are carried throughout the body by nerves. dendrites are small extensions surrounding the cell body which receive impulses (0.005 - 0.5mm long) Axon Is the longest part of the neuron which propagates the impulse Away from the cell body (0.5mm to 1m long) The neurons are the only cells that react to a A stimulus is a change in the environment that results in nerve excitation. Example: sun shining in your eyes or hearing a sound • Nerves are structures that help transmit information between the central nervous system and the various regions of the body • * Neurotransmitter released in synapse Impulse transmitted to next neuron • Neurons must pick up stimuli, transform them into nerve impulses and then transmit these impulses on to the next neuron • A nerve impulse is therefore any electric signal transmitted by a neuron • As signals move from one neuron to another, they must cross the synapse. This is the transition zone between two neurons (a very small gap) Basic Tasks of the Nervous System Sensory Input: Monitor both external and internal environments. Integration: Process the information and often integrate it with stored information. Motor output: If necessary, signal effector organs to make an appropriate response. The Central Nervous System The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Brain •The brain controls everything in the body. •The brain contains more than 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) and is the biggest part of the central nervous system! Parts of the Brain The Brain has three main parts… 1. The Cerebrum 2. The Cerebellum 3. Medulla oblongata (The Brain Stem) The Cerebrum •the largest part of the brain. •It controls your: 1. thinking. 2. memory. 3. speaking. 4. Movement 5. Identifies information gathered by your sense organs. Lobes of the Brain • The cerebrum is divided into several lobes, each of which is responsible for different tasks • The frontal lobes are responsible for problem solving and judgment and motor function. • The parietal lobes manage sensation, handwriting, and body position. • The temporal lobes are involved with memory and hearing. • The occipital lobes contain the brain's visual processing system. The Cerebellum • below and to the back of the cerebrum. •controls your balance and posture. The Medulla Oblongata (Brain Stem) • connects the brain to the spinal cord. • controls your heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure. •Responsible for certain reflexes : coughing, swallowing, hiccups, vomiting and sneezing Brain Stem Grey Matter vs White Matter • The brain can be divided into two types of tissue: grey and white matter • Grey matter: – The part of the brain controlled by nerve cell bodies and dendrites. – It is grey in appearance and is where the true processing occurs – Makes up 40% of the human brain and requires 94% of available oxygen • White Matter: – Composed of axons – Found in the center of the brain and between the brain stem and cerebellum – Facilitates communication between the grey matter of the brain and between the brain and the rest of the body – Makes up 60% of the human brain The Spinal Cord connects the brain to the rest of the nervous system. sends messages to and from the brain. •The spinal cord is protected by small bones called vertebrae Peripheral Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System Consists of all the nerves that leave the spinal cord or brain reaching all parts of the body. It has 2 types of nerves Sensory nerves – sending info to CNS Motor nerves – sending info to muscles Voluntary Acts This system contains the skeletal muscles Responsible for the conscious control of our movement Signals from the brain effectuate contractions of the muscles Reflex • is an involuntary automatic reaction that happens without thinking about it. • A reflex happens quickly in less than a second. The brain is not involved in a reflex. Sensory Receptor (responds to a stimulus by producing a impulse) Sensory Neuron (axon conducts impulse) Integrating Center (Relay impulse from sensory to motor neurons) Motor Neuron (axon conducts impulse to effector) Effector (muscle that responds to A motor nerve impulse)