* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rexed`s Lamina
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
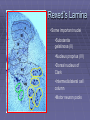
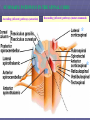
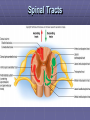
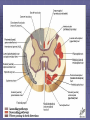
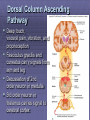
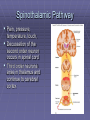
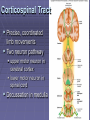
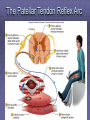
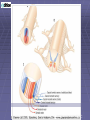
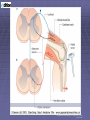
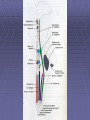
Rexed’s Lamina •Some important nuclei •Substantia gelatinosa (II) •Nucleus proprius (IV) •Dorsal nucleus of Clark •Intermediolateral cell column •Motor neuron pools SUMMARY: PATHWAYS IN THE SPINAL CORD Ascending (afferent) pathways (sensation) Descending (efferent) pathways (motor commands) * * Spinal Tracts Dorsal Column Ascending Pathway Deep touch, visceral pain, vibration, and proprioception Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus carry signals from arm and leg Decussation of 2nd order neuron in medulla 3rd order neuron in thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex Spinothalamic Pathway Pain, pressure, temperature, touch, Decussation of the second order neuron occurs in spinal cord Third order neurons arise in thalamus and continue to cerebral cortex Spinoreticular Tract Pain signals from tissue injury Decussate in spinal cord and ascend with spinothalamic fibers End in reticular formation (medulla and pons) 3rd and 4th order neurons continue to thalamus and cerebral cortex Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column Corticospinal Tract Precise, coordinated limb movements Two neuron pathway upper motor neuron in cerebral cortex lower motor neuron in spinal cord Decussation in medulla Descending Motor Tracts Tectospinal tract (tectum of midbrain) reflex turning of head in response to sights and sounds Reticulospinal tract (reticular formation) controls limb movements important to maintain posture and balance Vestibulospinal tract (brainstem nuclei) postural muscle activity in response to inner ear signals The Patellar Tendon Reflex Arc Downloaded from: Gray's Anatomy (on 1 October 2007 07:22 PM) © 2007 Elsevier Downloaded from: Gray's Anatomy (on 1 October 2007 07:22 PM) © 2007 Elsevier Downloaded from: Gray's Anatomy (on 1 October 2007 07:22 PM) © 2007 Elsevier