* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerves, structures, and organs of the head 1. Left cerebral
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
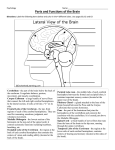
Nerves, structures, and organs of the head
1. Left cerebral hemisphere (cut away)
2. Right cerebral hemisphere
3. Cerebral cortex ("gray matter")
4. Cerebrum ("white matter")
5. Corpus callosum
6. Fornix
7. Third ventricle
8. Thalamus
9. Massa intermedia
10. Pineal body
11. Sinus rectus
12. Pituitary gland
13. Midbrain
14. Pons (part cut away)
15. Medulla oblongata (part cut away)
16. Fourth ventricle
17. Cerebellum
18. Olive
19. Spinal cord (part cut away)
20. Arachnoid sheath
21. Dura mater (sheath of spinal cord)
22. Eyeball
23. Tongue
24. Lingual nerve
25. First cervical nerve
26. Second cervical nerve
Sensory and motor areas of the cortex and cerebral lobes
27. Frontal lobe
28. Parietal lobe
29. Temporal lobe
30. Occipital lobe
31. Sensory cortex
32. Motor cortex
33. Auditory cortex
34. Broca's area (speech)
Central and peripheral nervous systems (silhouette)
35. Brain (cerebrum)
36. Brachial plexus
37. Peripheral nerves to arm
38. Nerves to thorax
39. Sacral plexus
40. Peripheral nerves to leg
Demonstration of simple spinal reflex
41. Needle-point stimulus
42. Skin section
43. Sensory nerve endings (axon terminal)
44. Axon of sensory nerve
45. Sensory nerve cell
46. Synapse
47. Dendritic nerve endings (dendrite)
48. Intermediate nerve cell (in spinal cord)
49. Motor nerve cell
50. Axon of motor nerve
51. Bouton nerve endings of motor cell
52. Muscle cell
The twelve cranial nerves
A. Olfactory nerve
B. Optic nerve
C. Oculomotor nerve
D. Trochlear nerve
E. Trigeminal nerve
E1 Opthalmic branch
E2 Maxillary branch
E3 Mandibular branch
F. Abducens nerve
G. Facial nerve
H. Acoustic nerve (Vestibulocochlear nerve)
I. Glossopharyngeal nerve
J. Vagus nerve
K. Accessory nerve
L. Hypoglossal nerve
GLOSSARY
Arachnoid sheath (20) A delicate weblike membrane between the dura rnater and the meninges.
Cerebellum (17) The second largest part of the brain. It has three functions, the unconscious
maintenance of muscle coordination, equilibrium, and posture.
Cerebral cortex (3) The outer layer, or "gray matter/' of the cerebrum that is composed mainly
of nerve cell bodies which gives it the gray appearance.
Cerebral hemisphere (1,2,4) The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and controls voluntary
and higher mental functions. It is divided into the right and left hemisphere.
Corpus callosum (5) A broad band of nerve fibers through which the two cerebral hemispheres
communicate.
Dura mater (21) A sheath of dense fibrous elastic tissue which lines the inner surfaces of the
cranium and the vertebrae,
Fornix (6) An arch of fold found in the cerebral hemispheres of man,
Medulla oblongata (15) Composed primarily of white matter, the medulla communicates
between the higher brain centers and the spinal cord.
Midbrain (13) Also called the mesencephalon, it is located between the diencephalon and the
pons,
Olive (18) Two structures on the surface of the medulla which relay impulses from the
cerebellum down the spinal cord, then to skeletal muscles.
Pineal body (10) An endocrine gland found in the brain that serves as an important intermediary
between photoperiodic output and endocrine function, especially the regulation of reproductive
activity,
Pituitary gland (12) An endocrine gland that secretes growth hormone which controls general
metabolism, and adrenocorticotropic hormone which controls the adrenal glands.
Pons (14) A short section of the hindbrain which serves as a communication bridge between the
two halves of the cerebellum and between the midbrain and the medulla.
Spinal cord (19) A soft oval-shaped cylinder about 45 cm long, and about as big around as the
little finger. This structure is protected by the spinal column and is composed of afferent and
efferent neurons and internucial neurons.
Thalamus (8) Two rounded lobes of gray matter that serves as a major sensory integration
center.
Ventricle (7) One of four cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which lies
below the longitudinal fissure of the brain.
Sensory and motor areas of the cortex and cerebral lobes
Auditory cortex (33) That portion of the brain that receives sensory information from the ears.
Broca's area (34) That portion of the brain responsible for speech.
Frontal lobe (27) The area of the cerebrum behind the bones that make up the forehead.
Motor cortex (32) The outer layer of the brain that sends instructions for contraction to the
skeletal muscles of the body.
Occipital lobe (30) The area of the cerebrum at the back of the brain. Parietal lobe (28) That
portion of the cerebrum behind the frontal lobes; the top back portion of the
cerebrum.
Sensory cortex (31) The outer layer of the brain that receives sensory (input) impulses from the
environment.
Temporal lobe (29) The area of the cerebrum behind the ears and the temple.