* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuroscience01_Introduction
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
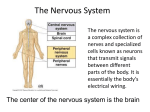
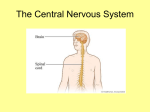
Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Neuroscience Introduction / Terminology Neuroscience Neuroscience is the study of the nervous system. It is a composite of several disciplines of study: Neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, neurology, neuropathology, neuropharmacology, behavioral sciences, and cell biology. 2 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Neuroanatomical Directional Terms (5 paired terms) Medial-lateral Medial means towards the median plane. Lateral means away from the median plane. Anterior-posterior Above the midbrain, anterior means towards the front of the brain and posterior means towards the back of the brain. At and below the midbrain, anterior means toward the ventral surface of the body and posterior means toward the dorsal surface of the body. Rostral-caudal Above the midbrain, rostral means toward the front of the brain and caudal means towards the back of the brain. At and below the midbrain, rostral means towards the cerebral cortex and caudal means towards the sacral end (or bottom) of the spinal cord. 3 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Neuroanatomical Directional Terms (5 paired terms) Dorsal-ventral Rostral to the midbrain, dorsal refers to the top of the brain and ventral refers to the bottom of the brain. At the level of the midbrain and caudal to it, dorsal means towards the posterior surface of the body and ventral refers to the anterior surface of the body. Superior-inferior Superior means towards the top of the cerebral cortex and inferior means toward the bottom of the spinal cord. 4 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Neuroanatomical Directional Terms 5 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Neuroanatomical Terms Ipsilateral-contralateral Ipsilateral means on the same side with reference to a speciifc point. Contralateral means on the opposite side. Commissure and decussation Commissure is a group of nerve fibers connecting one side of the brain with the other. Decussation is the crossing over of these nerve fibers. Neuron A neuron is the anatomical and functional unit of the nervous system, which consists of a nerve cell body, dendrites, and an axon. 6 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Clusters of Neuronal Cell Bodies Nucleus A nucleus is a cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the central nervous system. These neurons typically have a similar appearance, receive information from similar sources, project their axons to similar targets, and share similar functions. Ganglia A ganglion is a cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. 7 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Bundles of Axons Tract A tract is a bundle of axons in the central nervous system. These typically pass from a given nucleus to a common target. Tracts interconnect neurons in the spinal cord and brain. Nerve A nerve is a bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system. Cranial nerves connect the brain to the periphery. Spinal nerves connect the spinal cord to the periphery. 8 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie White and Gray Matter White matter The white matter consists of aggregations of primarily myelinated and some unmyelinated axons. (Myelin is whitish in color) Gray matter The gray matter consists of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and neuroglia. (Nissl bodies impart a gray color) 9 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Glial Cells Glial cells are non-neural cells that form the interstitial tissue of the nervous system. The comprise half the volume of the CNS. They are typically smaller than neurons, but 5 to 50 times more numerous. They can multiply and divide. Gliomas are brain tumors derived from glia. 10 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Anatomic subdivisions of the nervous system. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord. It is protected by 3 protective layers called the meninges. It has fluid filled chambers called ventricles. The bone of the skull and vertebral column surround and protect the brain and spinal cord respectively. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of the spinal nerves, cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, enteric nervous system, nerve receptors. It is comprised of all neuronal tissue that is outside of the CNS. 11 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie Autonomic and Somatic Nervous Systems Functional subdivisions of the nervous system. The autonomic nervous system innervates smooth muscle and glands. The somatic nervous system innervates musculoskeletal structures and the sense organs of the skin. 12 Dr. Michael P. Gillespie