* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
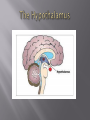
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
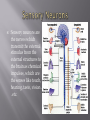
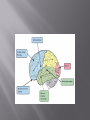
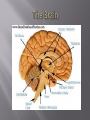
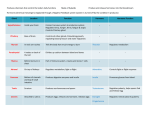
Mrs Morgan Biology The brain communicates with the different parts of the body to make it move. The body communicates with the brain to keep the body in homeostasis. The bodies interactions with the environment are communicated to the brain. The hypothalamus is located in the brain. The hypothalamus gland does most of the work to keep the body in homeostasis. The hypothalamus controls the endocrine system which regulates hormones These hormones regulate: Hunger Thirst Emotions Body Temperature Fatigue And many more Positive feedback loops A hormone is released to speed up a process. Example: a mother producing breast milk. As a mother begins to breast feed, she produces a hormone that makes the milk come out faster. Negative feedback loops A hormone is released that will slow down a process Hormones can regulate enzyme production meaning it changes how fast processes are happening in your body. Examples: Blood glucose regulation The main function of the nervous system is to send signals to other parts of the body How do we send these signals to make the body do what we want? Hormones Neural signaling (The neurons send signals to the body part it wants to change) The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of chemical changes across the membrane of the Neuron. . Sensory neurons are the nerves which transmit the external stimulus from the external structures to the brain as chemical impulses, which are the senses like touch, hearing, taste, vision . . etc. Motor neurons pass their impulses to muscle cells. The location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell is a called a synapse. Neurotransmitters are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse • • • • • • The brain relays messages to the entire body. It processes information and helps you analyze what you see feel and think. The brain has four major lobes. Each lobe provides a different function. Frontal LobeParietal lobeOccipital lobeTemporal lobe- Somatic Nervous system Regulates activities that are under conscious control If you can think about it and do it then it is somatic Examples include: running, jumping, tapping your fingers Autonomic Nervous system Regulates activities that are automatic or involuntary. These are activities that you can not control. Examples include: heart rate, secretion of enzymes, digestions of food, bladder control The five main sections of the brain are: Cerebrum-largest part/conscious activity in the body/intelligence, learning, judgment Cerebellum- located at back of the skull/ coordinates muscles so body can move gracefully Brain Stem-connects brain and spinal cord/regulates flow of information between brain and body Thalamus-receives messages from all of the sensory receptors in the and relays the messages to the proper places in the brain Hypothalamus- control center for recognition of hunger, thirst body temp etc.