* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 슬라이드 1
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
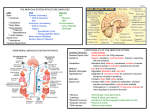
Chapter 7 THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Nervous System The structure of the nervous system will tell us about brain function Brain organization General organization and terms used to describe it Examine how the 3D structure of the brain arises through development Cerebral neocortex GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM Nervous System of all mammals has two divisions CNS (central nervous system) PNS (peripheral nervous system) Anatomical References GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central Nervous System The parts of the nervous system that are encased in bone Brain : Cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem Spinal cord Relayas information among Cerebral hemispheres, Contains many neurons cerebrum, spinal cord bycerebellum, the deep sagittal fissure asseparated both cerebral hemispheres combined The sitewith where vital functions are regulated Sensations andmovements movements Concerned Breathing, consciousness, temperature the contralateral of the body of on ipsilateral side of theside body GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central Nervous System Spinal cord Surrounded by bony vertebral column, attached to the brain stem Conduit of information (brain body) Skin, joints, muscles Communication with body via the spinal nerves Dorsal root : into the spinal cord Ventral root : away from the spinal cord GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The Peripheral Nervous System Nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord Somatic PNS Innervates skin, joints, muscles that are under voluntary control Visceral PNS = autonomic nervous system (ANS) Innervates internal organs, blood vessels, glands Afferent and Efferent Axons afferent : sensory axons bringing information into the CNS efferent : axons that emerge from the CNS GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The Cranial Nerves 12 nerves from brain stem Mostly innervate the head Axons from CNS, somatic PNS, visceral PNS The Meninges Three membranes that surround the brain Dura mater Arachnoid membrane Pia mater Brain floats in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) GROSS ORGANIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The Ventricular System CSF-filled caverns and canals inside brain Choroid plexus : specialized tissue in ventricles that secretes CSF Path : Cerebrum brain stem core subarachnoid space special structures called arachnoid villi absorb CSF Imaging the Living Brain Computed Tomography (CT) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Functional Brain Imaging Positron emission tomography (PET) Functional MRI (fMRI) UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Ventricular System and the CNS The entire CNS forms from the walls of a fluid-filled tube The tube ultimately becomes ventricular system Formation of the Neural Tube The embryo begins as a flat disk with 3 distinct layers Endoderm : the lining of many of the internal organs Mesoderm : the bones of the skeleton and the muscles Ectoderm : the nervous system – the neural plate UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Formation of the Neural Tube Neural plate neural groove Fusion of neural folds Neural tube (forms CNS neurons) Neural crest (forms PNS neurons) Somites : vertebrae : skeletal muscle Somatic motor nerves Neurulation : the process which the neural plate becomes the neural tube UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Three Primary Brain Vesicles Differentiation : the process by which structures become more complex and functionally specialized during development Primary vesicles : the entire brain derives from the three primary vesicles UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Forebrain The secondary brain vesicles of the forebrain UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Forebrain Differential of the Telencephalon and Diencephalon Telencephalon : cerebral hemispheres, olfactory bulbs, basal telencephalon Diencephalon : thalamus, hypothalamus Ventricles : lateral ventricles, third ventricle Major white matter systems : Axons extend from developing forebrain to other parts of the NS Cortical white matter : cerebral cortex Corpus callosum : two cerebral hemispheres Internal capsule : brain stem, particularly the thalamus UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Forebrain Forebrain Structure-Function Relationships Cerebral cortex : Analyze sensory input and command motor output Thalamus : Gateway of the cortex : Carry information from contralateral side of the body Hypothalamus : Control of visceral (autonomic) nervous system UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Midbrain UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Midbrain Midbrain Structure-Function Relationships Information conduit from spinal cord to forebrain and vice versa : Sensory systems, the control of movements… contralateral side Tectum Superior colliculus (216p) : receives direct input from the eye, controls eye movements Inferior colliculus : the ear instead of the eye Tegmentum : Substantia nigra (black substance), red nucleus : Control of voluntary movement UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Hindbrain Three structures Cerebellum : Movement control : Sensory systems, the control of movements Pons : Switchboard connecting cerebral cortex to cerebellum Medulla Decussation : Crossing of axons from one side to the other Neurons that perform many different sensory and motor function UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Differentiation of the Spinal Cord UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Putting the Pieces Together UNDERSTANDING CNS STRUCTURE THROUGH DEVELOPMENT Special Features of the Human CNS Many convolutions on the surface : Sulcus / Gyrus The lobes of the human cerebrum A GUIDE TO THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Common Features of Cerebral Cortex Cell bodies in layers of sheets Surface layer separated from pia mater Apical dendrites form multiple branches A GUIDE TO THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Areas of Neocortex Brodmann construted a cytoarchitectural map : Cortical areas that look different perform different functions A GUIDE TO THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Areas of Neocortex Neocortical Evolution and S-F Relationship Cortex amount has changed, but not structure Leah Krubitzer : Primary sensory areas, secondary sensory areas, motor areas Jon Kaas : Expansion of secondary sensory areas Association areas : ex) ability to interpret behavior in terms of mental state