* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Students know
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
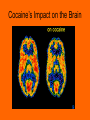
Human Physiology The impact of stimulants on brain chemistry Standards 9a. Students know how the complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. • 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. • 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. • 9e.Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response Objectives: • Understand the function of the nervous system. • Explain how the nervous system maintains homeostasis. • Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. • Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. Why is the brain so important? • Brain-controls nervous system, maintains normal function of the body, contains 100 billion neurons What are stimulants? • Drugs change how the brain works, by changing the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the synapses. Methamphetamines • An addictive stimulant that is closely related to amphetamine, but has longer lasting and more toxic effects on the central nervous system. It has a high potential for abuse and addiction. • Speed, meth, chalk, ice, crystal, glass. • Increases wakefulness and physical activity and decreases appetite. Chronic, long-term use can lead to psychotic behavior, hallucinations, and stroke. Methamphetamines Stats • In 2006, 1.9 million Americans age 12 and older had abused methamphetamine at least once in the year prior to being surveyed. Source: National Survey on Drug Use and Health; http://www.samhsa.gov/. The NIDA-funded 2007 Monitoring the Future Study showed that 1.1% of 8th graders, 1.6% of 10th graders, and 1.7% of 12th graders had abused methamphetamine at least once in the year prior to being surveyed. Source: Monitoring the Future http://www.monitoringthefuture.org/. Crystal Meth Stimulants-Cocaine • Obtained from the leaves of the coco plant • Acts on neurons (pleasure centers of brain) • Causes the release of dopamine and serotonin (normally released when a basic need is fulfilled) • Depletes supply of dopamine, leads to depression and a need for more of the drug • Overdose-heart attacks, kidney failure, seizures, strokes, coma, and death. • Long term effects on brain-seizures, bleeding of the brain, permanent brain damage, psychosis and hallucinations, changes structure of the brain Cocaine’s Impact on the Brain Stimulants-Ecstasy • MDMA-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine • Causes the brain’s neurons to release serotonin, a neurotransmitter • Produces a feeling of euphoria and calm, heightened sensitivity to stimuli (touch, colors, lights) • Overdose-Overheating of the body, liver, heart, kidney, and brain damage, seizures, strokes • Long term effects on the brain-Wrong “rewiring” of the brain, paranoia, depression, impaired memory, hallucination, difficulty learning, permanent brain damage, seizures Ecstasy’s Impact on the Brain Summary Questions • What are stimulants? • How do stimulants impact how the brain functions? • What are the long terms effects of cocaine, ecstasy, and methamphetamines on the brain?