* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
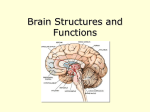
Chapter 6 Body & Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System The Organization of the Nervous System Nervous system Peripheral nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Somatic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system Two Divisions of the Nervous System • Central Nervous System (CNS) – Made up of the brain and spinal cord. • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Nerves branching out from the spinal cord. Two Divisions of the PNS • Somatic NS – controls voluntary behaviors • Autonomic NS – controls involuntary behaviors – Sympathetic – “fight or flight” – Parasympathetic – “rest and digest” The Neural Impulse Synapse - The gap between neurons. Neurotransmitters • Neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers that relay neural messages across the synapse. ANIMATION 3 Types of Neurons: -Sensory (afferent) neurons - carry messages from sense receptors towards the brain. -Motor (efferent) neurons - carry messages from brain toward muscles and glands. -Interneurons - carry messages between nerve cells. Section 2 Studying the Brain 3 Parts of the Brain: 1. Forebrain 2. Midbrain 3. Hindbrain Forebrain • A part of the brain that covers the brain’s central core. Includes: • • • • • • • Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebral cortex Cerebrum Limbic system Amygdala Hippocampus Forebrain Thalamus – Integrates sensory input; relay station for all the information that travels to and from the brain. Hypothalamus – Controls functions such as hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior; also controls temperature. Cerebral cortex – Outer layer of the forebrain; gives you the ability to learn and store complex and abstract information. Forebrain Cerebrum – Inner layer of the forebrain. Limbic system – Various structures in the brain that regulate our emotions and motivations (includes: amygdala, hippocampus) Midbrain • A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward. RAS: • Alerts the rest of the brain to incoming signals and is involved in the sleep/wake cycle. Hindbrain • Located at the rear base of the skull; involved in the basic processes of life. Includes: • Cerebellum • Medulla • Pons Hindbrain Cerebellum – Helps control posture, balance, and voluntary movements. Medulla – Controls breathing, heart rate, and other reflexes. Pons – Produces chemicals the body needs for sleep. Parts of the Brain • • • • • Thalamus Pons Cerebellum Medulla Brain stem The 4 Lobes: Frontal lobe (organization, planning, creative thinking) Parietal lobe (touch sensations) Occipital lobe (visual signals) Temporal lobe (hearing, speaking) Left v Right Hemisphere Split-Brain Operations • A treatment option for those suffering from grand mal seizures. Video – Separating the brain hemispheres by severing the corpus callosum lessons the number and severity of seizures. Mr. Split-Brainy How do we study the BRAIN? 1. Recording (EEG) 2. Stimulation 3. Lesions 4. Accidents - Phineas Gage 5. Images (CAT, PET, MRI) Recording • Electroencephalograph (EEG): – A machine used to record electrical activity in the brain. Stimulation • Wilder Penfield stimulated the brains of his patients during surgery to determine what functions the various parts of the brain perform. – He was able to localize the malfunctioning parts of the brain. Lesions • Lesions: cutting or destroying parts of the brain. • If the animal behaves differently after the operation, we can assume the destroyed brain area is involved with that type of behavior. Accidents • Psychologists can learn about the brain when people are involved in accidents. • Psychologists try to draw a connection between the damaged parts of the brain and a person’s behavior. Accidents – Phineas Gage • His frontal lobe was damaged, which caused his personality to change* • He became short-tempered and said inappropriate things. • Therefore, damage to the frontal lobe prevents censoring of thoughts and ideas. Images • CAT (computerized axial tomography) – Used to pinpoint injuries in the brain. • PET (positron emission tomography) – Used to see which brain areas are being activated while performing tasks. • MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) – Used to study brain structures. Section 3 The Endocrine System (the body’s chemical messenger system) Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 Endocrine System - Glands • Pituitary gland – Control center of the endocrine system that secretes a large number of hormones. • Known as the master gland. • Produces growth hormones. Video Clip - Gigantism Endocrine System - Glands • Thyroid gland – Produces the hormone thyroxin. – Hypothyroidism – makes people feel lazy and lethargic. – Hyperthyroidism – causes people to lose weight and be overactive. Endocrine System - Glands • Adrenal glands – Release adrenaline into the bloodstream. • Causes heart rate and breathing to increase • Heightens emotions (fear, anxiety) Endocrine System - Glands Sex glands: – Ovaries • Produce eggs and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. – Testes • Produce sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone. Hormones vs Neurotransmitters • Endocrine System – Glands release hormones into the bloodstream. • Nervous System – Neurons release neurotransmitters to either excite or inhibit other neurons. Section 4 Heredity & Environment Heredity • The genetic transmission of characteristics from parents to their offspring. Nature v Nurture Nature – The characteristics a person inherits – Biological makeup – GENETICS Sir Francis Galton • Nurture – ENVIRONMENT – Family, culture, education, and individual differences John Watson Genes – the basic building blocks of heredity. Twin Studies • Identical twins – Come from ONE fertilized egg; also called monozygotic twins. • Fraternal twins – Come from TWO different eggs fertilized by two different sperm; also called dizygotic twins. WHY STUDY TWINS??? End of Chapter 6