* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Brain
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
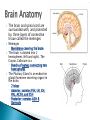
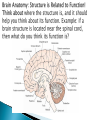
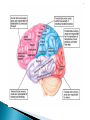
Today: The Brain – The Centre of All Homeostasis Homeostasis Summative Lab – Examining the Brain in More Detail… Reminders: Catalase Lab due on FRIDAY! No exceptions! Turnitin also. YELLOW BLACK PURPLE ORANGE BLUE GREEN BLUE RED YELLOW What do you put in a toaster? Did you say toast? The answer is bread, silly! Say the word “silk” 5 times. Spell the word silk Now tell me what cows drink Did you say milk? Cows drink water, silly! A red house is made of red bricks. A blue house is made of blue bricks. A yellow house is made of yellow bricks. What is a green house made out of? Glass! You are driving a bus and you make the following stops. Do these calculations without a calculator You start with 50 bus passengers You stop in Toronto and drop off 5 people but pick up 10 You stop in Mississauga and drop off 7 people but pick up 11 You stop in Brampton and drop off 2 people and pick up 5 How old is the bus driver? Did you read the question carefully...it said YOU are driving a bus... The human nervous system is organized into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) The CNS is comprised of the brain and spinal cord Together, the CNS is the main processing centre for feedback. The spinal cord and brain receive messages (inputs) from the body, process the information, and send a response (recall lesson 1: feedback mechanisms). In doing so, the CNS helps the body achieve homeostasis. The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a canal inside the vertebrae of the backbone It carries impulses between the brain and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (nerves of the body) The brain and spinal cord are surrounded with, and protected by, three layers of connective tissue called the meninges Meninges ◦ Membrane covering the brain The brain is divided into 2 hemispheres (left and right). The Corpus Callosum is a ◦ Bundle of nerves connecting two hemispheres The Pituitary Gland is an endocrine gland (hormone secreting organ) in the brain. ◦ 2 lobes ◦ Anterior: secretes FSH, LH, GH, PRL, ACTH, and TSH ◦ Posterior: secretes ADH & Oxytocin Medulla Oblongata (aka Medulla) Cerebellum Pons ◦ Connects brain to spinal cord. Coordinates reflexes and maintains homeostasis (e.g. heart rate, etc., especially involuntary responses) ◦ “Little brain”. Coordinates posture, reflexes, motor skills, especially voluntary responses ◦ AKA Brainstem: RELAYS information between different areas of the brain The midbrain is in the ‘middle’ of the brain. Notice that it is above the brainstem and spinal cord. Those structures close to the spinal cord function in reflexes (close to nerves) and RELAYING or CONNECTING peripheral nerves to the brain. Since the midbrain is close to this area, it receives information and... Midbrain: ◦ Processes information from sensory neurons in eye, ears, nose. The forebrain is at the forefront! Think about structure and function again. If a structure is at the forefront, what kinds of functions would be associated with it? Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebrum ◦ “Relay station”. Connects forebrain & hindbrain and sensory system (besides smell) ◦ Regulates temperature, blood pressure, needs, emotions, and coordinates the pituitary gland to help release hormones ◦ Largest part of brain. Divided into right and left hemispheres. Contain centres for intellect, memory, language. “Left Brain” = logic, math, sequences “Right Brain” = artistic, visual, intuitive Right hemisphere controls left half of body & vise versa. Hemispheres are separated by the corpus callosum Outer portion = cerebral cortex 4 major lobes of the cerebrum ◦ Frontal lobe Conscious thought Motor cortex ◦ Parietal Lobe Sensory (temp, touch, pain, pressure from skin) ◦ Occipital Lobe vision ◦ Temporal Lobe Hearing and smelling