* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lies outside the central nervous system
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
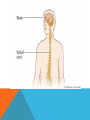
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
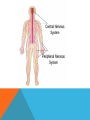
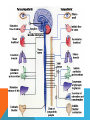
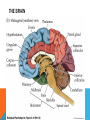
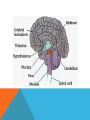
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) Consists of the spinal cord and the brain Both covered with a protective membrane called meningens Impulses are received at the spinal cord and the brain via the PNS- initiates voluntary motor control Sup PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (PNS) -Lies outside the central nervous system -Contains cranial and spinal nerves that send signals to and from the CNS SOMATIC VS. AUTONOMIC SYSTEM Somatic system – includes nerves that take stimuli from PNS to the CNS and motor commands from the CNS to the skeletal muscles. Voluntary responses Autonomic System Regulates activity of smooth muscle and glands Divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions SYMPATHETIC DIVISION Neurons arise from the middle of the spinal cord Involved with “fight or flight” responses that are important during emergency situations. If you need to fend of a foe or flee from danger, your muscles need a quick supply of glucose and oxygen. To accomplish this, the sympathetic division accelerates the heartbeat and dilates the bronchi, but inhibits the digestive tract. The neurotransmitter released during this is norepinephrine (NE) PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION Involves a cranial nerves and nerves that arise from the bottom of the spinal cord Promotes all internal responses associated with a relaxed state. Causes the pupil of the eye to contract, promotes digestion of food and slows down the heartbeat The neurotransmitter released during this is acetylcholine (Ach) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J968Wco1u0s THE BRAIN MEDULLA OBLONGATA -Lies between the spinal cord and the PONS -Regulates heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure -Reflex center for vomiting, sneezing, swallowing, and coughing CEREBELLUM -Separated from the brainstem -Passes on both sensory and motor information -Maintains normal muscle tone, posture and balance -Makes sure all skeletal muscles function together for smooth and coordinated movement (like playing the piano or swinging a baseball bat) THALAMUS -Integrates sensory information -Serves as a central relay station for impulses travelling up to the cerebrum -Involved in higher mental functions such as memory and emotion HYPOTHALAMUS -The integrating center for the autonomic system -Also helps maintain homeostasis Regulating hunger, sleep, thirst, body temperature and water balance -Controls the pituitary gland PITUITARY GLAND -Located on the hypothalamus -An endocrine gland Secretes hormones involved with growth, blood pressure, breast milk production, body temperature, ect. -Hormonal secretion controlled by the hypothalamus THE CEREBRUM -Largest portion of the human brain -Has two halves connected by the corpus callosum -Highest center to receive sensory input and carry out integration before commanding voluntary motor response -Works with other parts of the brain to regulate activities -Carries out higher thought processes required for learning, memory, language and speech