* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
By, Dr. Shamanthakamani
Narendran, M.D.
THE BRAIN
The adult human brain weighs an average of 1.4
kg, or about 2 percent of the total body weight.
Despite this relatively small mass, the brain
contains approximately 100 billion neurons.
Functioning as a unit, these neurons make up the
most complex and highly organized structure on
Earth.
THE BRAIN
The brain is responsible for many of the qualities
that make each individual unique-thoughts,
feelings, emotions, talents, memories, and the
ability to process information.
Much of the brain is dedicated to running the
body, the brain is responsible for maintaining
Homeostasis by controlling and integrating the
various systems that make up the body.
1. The brain is the main switching unit of the
central nervous system; It is the place to which
impulses flow and from which impulses
originate.
2. The spinal cord provides the link between the
brain and the rest of the body.
3. The brain has three main parts:
1. The cerebrum
2. The cerebellum
3. The brain stem
The Brain is a highly organized ORGAN that
contains approximately 100 billion neurons and
has a MASS of 1.4 Kilograms.
The Brain is Protected by a BONY Covering
called the SKULL.
The Brain is also WRAPPED in
THREE LAYERS of
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
known as the MENINGES.
Connective Tissue connects one tissue to another.
The INNER most layer, which covers and is bound
to the surface of the brain, is called PIA MATER.
It is a FIBEROUS LAYER made up of many
Blood Vessels which carry FOOD and OXYGEN
to the Brain.
The OUTER Layer, called the DURA MATER, is
composed of Thick Connective Tissue.
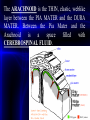
The ARACHNOID is the THIN, elastic, weblike
layer between the PIA MATER and the DURA
MATER. Between the Pia Mater and the
Arachnoid
is
a
space
filled
with
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID.
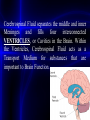
Cerebrospinal Fluid separates the middle and inner
Meninges
and
fills
four
interconnected
VENTRICLES, or Cavities in the Brain. Within
the Ventricles, Cerebrospinal Fluid acts as a
Transport Medium for substances that are
important to Brain Function.
The Cerebrospinal Fluid is a clear liquid that
PROTECTS the Brain from mechanical injury by
acting as a Shock Absorber.
In order for the Brain to perform its functions, it
must have a constant supply of Food and Oxygen.
If the Oxygen supply to the brain is cut off even
for a few minutes, the brain will usually suffer
enormous damage. Such damage may result in
DEATH.
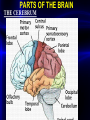
PARTS OF THE BRAIN
THE CEREBRUM
THE CEREBRUM IS THE CONTROL CENTER
OF THE BRAIN.
The LARGEST and most PROMINENT part of
the Human Brain is the CEREBRUM. 85% OF
THE WEIGHT OF A HUMAN BRAIN.
The Cerebrum is responsible for all the
VOLUNTARY (CONSCIOUS) ACTIVITIES
OF THE BODY. It is the site of INTELLIGENCE,
LEARNING AND JUDGMENT.
IT FUNCTIONS IN LANGUAGE, CONSCIOUS
THOUGHT,
MEMORY,
PERSONALITY
DEVELOPMENT, VISION, AND OTHER
SENSATIONS.
The Cerebrum takes up most of the space in the
cavity that houses the Brain. (SKULL)
The CEREBRUM IS DIVIDED INTO TWO
HEMISPHERES, THE LEFT AND RIGHT
CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES.
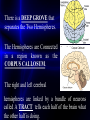
There is a DEEP GROVE that
separates the Two Hemispheres.
The Hemispheres are Connected
in a region known as the
CORPUS CALLOSUM.
The right and left cerebral
hemispheres are linked by a bundle of neurons
called A TRACT tells each half of the brain what
the other half is doing.
The MOST Obvious FEATURE on the surface of
each hemisphere are NUMEROUS FOLDS.
These FOLDS and the GROOVES INCREASE
the Surface Area of the Cerebrum. The Ridges are
called GYRI, and the grooves are called
SULCUS.
The Cerebrum, which looks like a wrinkled
mushroom, is positioned over the rest of the brain.
It contains thick layers of Unmyelinated Neurons,
which look GRAY. ("GRAY MATTER")
The increased
surface area
permits the large
number of neurons
to fit easily within
the confines of the
Skull.
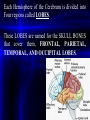
Each Hemisphere of the Cerebrum is divided into
Four regions called LOBES.
These LOBES are named for the SKULL BONES
that cover them, FRONTAL, PARIETAL,
TEMPORAL, AND OCCIPITAL LOBES.
The RIGHT hemisphere is associated with
creativity and artistic ability. The LEFT
hemisphere is associated with analytical and
mathematical ability.
Sometimes blood vessels in the brain are blocked
by blood clots, causing a disorder called A
STROKE. During a Stroke, circulation to an area
in the brain is blocked and the brain tissue dies. A
severe Stroke in one side of the brain may cause
PARALYSIS of the other side of the body.
The Cerebrum consists of TWO SURFACES
The FOLDED OUTER SURFACE is called the
CEREBRAL CORTEX and consists of GRAY
MATTER (UNMYELINATED NEURONS).
The INNER SURFACE is called the
CEREBRAL MEDULLA, which is made up of
bundles of MYELINATED AXONS. THE
WHITE MATTER.
The Myelin gives the White Matter its White
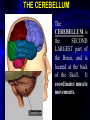
THE CEREBELLUM
The
CEREBELLUM is
the
SECOND
LARGEST part of
the Brain, and is
located at the back
of the Skull.
It
coordinates muscle
movements.
The Cerebellum coordinates and balances the
actions of Muscles so that the body can move
gracefully and efficiently.
The Cerebellum CONTROLS BALANCE,
POSTURE, and COORDINATION.
The Cerebellum receives sensory impulses from
muscles, tendons, joints, eyes, and ears, as well as
input from other brain centers.
It processes information about position and
controls posture by keeping skeletal muscles in a
constant state of partial contraction.
The Cerebellum Coordinates rapid and ongoing
movements.
This is a small CAULIFLOWER SHAPED
Structure.
A Major part of learning how to perform physical
activities seems to be related to training the
Cerebellum to coordinate the proper muscles.
Because the function of the Cerebellum is
INVOLUNTARY (not under conscious control),
learning a completely new physical activity can be
very difficult.
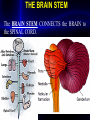
THE BRAIN STEM
The BRAIN STEM CONNECTS the BRAIN to
the SPINAL CORD.
The brain stem, which maintains life support
systems, consist of the diencephalon, medulla
oblongata, pons, and the midbrain.
The Brain Stem Controls Vital Body Processes.
The Brain stem not only coordinates and integrates
all INCOMING INFORMATION; it also serves as
the place of entry or exit for ten of the Twelve
Cranial Nerves.
The Upper Brain Stem, the Diencephalon, contains
important relay centers for information entering an
exiting the brain.
The Lower Brain Stem consists of the MEDULLA
OBLONGATA, PONS, AND MIDBRAIN.
The Lowest Part of the Brain Stem is the Medulla
Oblongata (Sometimes just called the Medulla).
The Medulla contains WHITE MATER that
conducts impulses between the Spinal Cord and
Brain.
The MEDULLA controls involuntary functions
that include, breathing, blood pressure, heart rate,
digestion, swallowing, and coughing.
Another important part of the Medulla is a
GROUP of CELLS known as THE RETICULAR
ACTIVATING SYSTEM or RETICULAR
FORMATION (RAS).
The Reticular Activation System (RAS) actually
helps to alert, or awaken, the upper parts of the
Brain, including the Cerebral Cortex. Such actions
keep the Brain alert and conscious.
The RAS also helps to control respiration and
circulation and serves as a filtering system for
incoming sensory signals. For example, we
awaken to the sound of an alarm clock, to a bright
light flash, or to a painful pinch because activity in
the RAS that arouses the Cerebral Cortex.
Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to
form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this
area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter
that provides a link between the cerebral cortex
and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and
continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest
division of the lower brain stem.
DIENCEPHALON
THE THALAMUS AND HYPOTHALAMUS
The Thalamus and Hypothalamus are found in
the part of the brain between the Brain Stem and
Cerebrum.
The Thalamus, which is composed of Gray
Matter, serves as a SWITCHING STATION
FOR SENSORY INPUT. With the Exception of
SMELL, each Sense Channels its Sensory Nerves
through the Thalamus.
The Thalamus passes information to the proper
region of the Cerebrum for further processing.
Immediately Below the Thalamus is the
Hypothalamus, which is the CONTROL
CENTER for hunger, thirst, fatigue, anger, and
body temperature.
Parts of the Diencephalon and the Cerebrum are
included in an important group of connected Brain
Centers called the LIMBIC SYSTEM.
The Limbic System includes the Thalamus, the
Hypothalamus, some deeper parts of the Cerebral
Cortex, and centers in the Temporal Lobes.
The Limbic system plays an important role in
emotions, memory, and motivation, among other
things.
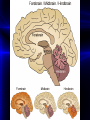
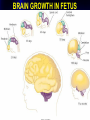
BRAIN GROWTH IN FETUS
SENSORY SYSTEMS
Human experience is effected by both internal and
external stimuli.
Humans are able to distinguish among many
different types of stimuli by means of a highly
developed system of SENSE ORGANS.
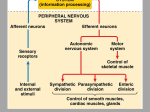
Sensory Systems represent an integration of the
functions of the Peripheral Nervous System and
the Central Nervous System.
The Sensory Division of the Peripheral Nervous
System gathers information about the Body's
Internal Conditions and External Environment.
Sensory Systems translate light, sound,
temperature, and other aspects of the Environment
to Electrical Signals and transmit these signals, in
the form of Action Potentials, to the Central
Nervous System, where they are Interpreted.