* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
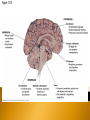
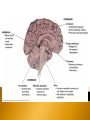
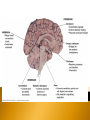
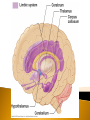
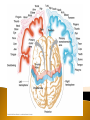
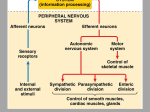
Identify Principle Parts of the Brain Identify the principle parts of the nervous system Describe the cells that make up the nervous system Describe what starts and stops a nerve impulse (action potential) The role of neurotransmitters Compare the functions of the CNS & PNS Identify the principle parts of the brain Brain receives incoming info from spinal cord and nerves integrates/processes info and generates responses 3 anatomical & functional divisions 1) Hindbrain – basic autonomic and vital tasks 2) Midbrain – muscle groups, responses to sights & sounds 3) Forebrain – receives & integrates sensory input & determines our more complex behavior Connected to spinal column Oldest, most primitive brain division Most similar among animals Structures: 1) Medulla oblongata 2) Cerebellum 3) Pons Controls autonomic functions ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Heart rate Blood pressure Respiratory information – O2 & CO2 levels Cough reflex Swallowing Sneezing Vomiting This is where the neurons cross over to the other side and the left brain controls the right side of the body and vice versa Located just behind the medulla oblongata and coordinates basic (unconscious) movements Ensures that antagonistic muscles don’t contract at the same time Stores sequenced information – tying shoes Receives sensory input from joint & muscle receptors, balance & position receptors in ear and visual receptors Excess alcohol disrupts these functions Located just above and partly surrounding the medulla oblongata Contains groups of axons that extend from the cerebellum to the rest of the CNS & Coordinates the flow of information between the cerebellum and the higher brain centers Aids the medulla oblongata in regulating respiration Visual & auditory sensory input passes through the midbrain before being relayed to the higher brain centers Coordinates movements of the head related to vision and hearing (e.g. turning towards sound or flashing lights) Controls eye movement and pupil size Monitors unconscious movement of skeletal muscles (smooth moves) Reticular formation located here-neuron bundle aids in posture, balance & muscle tone, level of wakefulness Emotions Conscious thought Parts: 1) Hypothalmus 2) Thalmus 3) Limbic system 4) Cerebrum 5) Glands – 2 – pineal, pituitary Located @ base of forebrain just above midbrain Coordinates some autonomic fxns, pituitary gland, water & solute balance, T control, carbohydrate metabolism, breast milk production Monitors sensory signals: sight, smell, taste, noise, body T Hunger center Thirst center Together w/hypothalmus maintains homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives Limbic activities are monitored by hypothalmus and modified by cerebrum (social norms) Most developed brain region Language Decision making Conscious thought Left and right cerebral hemispheres are connected in the middle by the corpus callosum = enables 2 hemispheres to share sensory-motor info Consists of an outer layer of mostly gray matter (unmylenated CNS neurons, neuroglial cells) Inner portion consists of white matter containing mylenated nerve axons connecting the lower brain area to the cerebral cortex This structure - inner section of ascending and descending axons and an outer layer of cells – makes it ideally suited to ◦ direct incoming info to the proper brain region for processing ◦ Integrate and process info ◦ Route outgoing motor activity to appropriate areas of the body