* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epigenetics 12
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
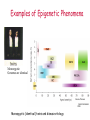
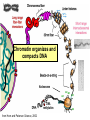
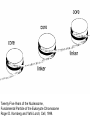
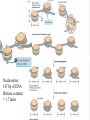
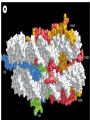
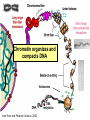
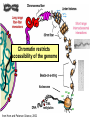
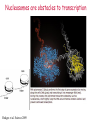
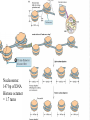
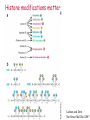
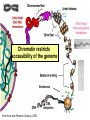
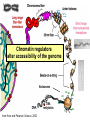
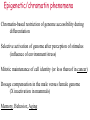
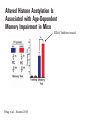
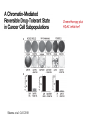
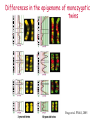
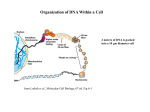
Lecture outline 1. Class organization 2. Introduction to Epigenetics Lecture outline 1. Class organization a. Target audience b. Organization: lecture, research lecture, student presentations Lecture outline 1. Class organization a. Target audience b. Organization: lecture, research lecture, student presentations c. What is expected: • attendance, participation, questions for the student papers • 2 exams (recitations before them) • student presentations • (grad and CAMB enrolled: final proposal) Student presentations 1. TWO volunteers for next week (September 13th): chromatin assembly 2. For all other slots: everyone needs to present, choose a date or topic and e-mail me as soon as possible IMPORTANT: if you decide to drop the class and have chosen a presentation date already please let me know 3. If >19 students then we double up on papers one students presents the background of the field plus the first half of the paper the second student does the second half of the paper and future directions Lecture outline 1. Class organization 2. Introduction to Epigenetics what are epigenetic phenomena where does epigenetic regulation occur Epigenetic phenomena: heritable alternative states of gene activity that do not result from altered nucleotide sequence Examples of Epigenetic Phenomena Monozygotic: Genomes are identical Examples of Epigenetic Phenomena Monozygotic: Genomes are identical Arturas Petronis 2006 Monozygotic (identical) twins and disease etiology Examples of Epigenetic Phenomena Monozygotic: Genomes are identical Rainbow and Copycat Cloned cat: Genome is identical Yet looks different from mother Rainbow and Copycat Calico cat coat color cannot be cloned!!! Not based on genetics Based on Epigenetics: Color gene is X-linked Random X-inactivation of cells in blastula all daughter cells will inherit that pattern Genetics vs. Epigenetics +germline invariable * transient (not heritable) * mitotically heritable * meiotically heritable Plants: many examples of meiotically heritable or transgenerational epigenetic phenomena http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/epigenetics/inheritance/ Animals: fewer examples known http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/epigenetics/inheritance/ Animals: fewer examples known Kaati, G., Bygren, L.O., Pembrey, M., and Sjostrom, J. (2007). Transgenerational response to nutrition, early life circumstances and longevity. European Journal of Human Genetics 15: 784-790. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/epigenetics/inheritance/ Human transgenerational epigenetic phenomena? Time magazine 2010 Utah Epigenetics website View NOVA special “A ghost in your genes” http://en.sevenload.com/videos/tX02lnf-Nova-The-Ghost-In-Your-Genes-1-6 The material for Epigenetics Nucleus; chromatin Starting at the beginning The conundrum Human DNA: 2 m Human nucleus r = 10 µm 10,000 x compaction The solution DNA is compacted via interaction with proteins THIS IS THE TEMPLATE FOR EPIGENTIC PHENOMENA Chromatin organizes and compacts DNA Nucleosome ac DNA methylation from Horn and Peterson Science, 2002 ac ac ac ac Chromatin structures Woodcock and Dimitrov, COGD, 2001 Caterino and Hayes, Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 2007 Primary structure the NUCLEOSOMAL DNA Beads on a string Twenty-Five Years of the Nucleosome, Fundamental Particle of the Eukaryote Chromosome Roger D. Kornberg and Yahli Lorch; Cell, 1999. Nucleosome: 147 bp of DNA Histone octamer = 1.7 turns The nucleosome: histones plus DNA HISTONES Two classes of histones (canonical) Core Histones H2A conserved H2B conserved H3 highly conserved H4 very highly conserved Linker Histones H1 not conserved Small proteins, ca. 10 kD, very basic Three domains A. Histone fold B. Histone fold extension C. Extended N (and C)-termini Histone fold: 3 conserved alpha helices Histone fold extension and N-termini Linker histone Tails are K (lysine) and R (argenine) rich C-termini HISTONE/ DNA INTERACTIONS 1. Charge neutralization: basic residues lysine, argenine 2. Hydrophobic side chains; threonine, proline, valine, isoleucine with deoxyribose 3. Main chain amide with phosphate oxygen Canonical histones and histone variants Secondary structure linker histone 30 nm fiber Chromatin organizes and compacts DNA Nucleosome ac DNA methylation from Horn and Peterson Science, 2002 ac ac ac ac Chromatin restricts accessibility of the genome Nucleosome ac DNA methylation from Horn and Peterson Science, 2002 ac ac ac ac Types of Chromatin Euchromatin Transcriptionally active, less compacted Heterochromatin Less transcriptionally active, very compacted a) constitutive heterochromatin centromeres, telomeres b) facultative heterochromatin rDNA, transposons, inactive X chromosome www.nenno.it/publications/mnphdthesis/diss08.jpg Heterochromatin (stained) http://www.biology.wustl.edu/faculty/elgin/hp2chrom.jpg Barr Body Region * Immunofluorescent straining of the human interphase nucleus. * The white box indicates the Barr body region where the inactive X chromosome resides during interphase. Chadwick and Willard (2004) PNAS Nucleosomes are obstacles to transcription Hodges et al. Science 2009 Transcription happens outside of condensed chromatin 2003 Transcription happens outside of condensed chromatin 2003 DNA that contacts histones is not readily accessible Nucleosome: 147 bp of DNA Histone octamer = 1.7 turns Nucleosome position and spacing matters Linker size is variable: 10-50 bp Regular linker size: common in inactive chromatin Irregular linker size: common in active chromatin Histone tails are modified, this influences accessibility of the genomic DNA Luger et al. Nature, 1995 Histone modifications matter Latham and Dent Nat Struct Mol Biol 2007 DNA methylation status is important Nature News, May 2006 All levels of chromatin condensation have been implicated in controlling accessibility of the genomic DNA effect on: replication, recombination, repair, and transcription Chromatin restricts accessibility of the genome Nucleosome ac DNA methylation from Horn and Peterson Science, 2002 ac ac ac ac Chromatin regulators alter accessibility of the genome Nucleosome ac DNA methylation from Horn and Peterson Science, 2002 ac ac ac ac Mechanism exist to “open up” chromatin Chromatin remodeling complexes alter primary structure of chromatin Histone modifying enzymes alter histone tail modifications Leschziner lab, Harvard Mechanism exist to “condense” chromatin Histone modifying enzymes alter histone tail modifications DNA methylases, Recruitment of chromatin binding proteins Polycomb proteins Heterochromatin Protein Francis Science 2005 Mechanism exist to “open up” chromatin Chromatin remodeling, histone modifications Mechanism exist to “condense” chromatin Histone modifications, DNA methylation, chromatin binding proteins Can alter gene activity without change in DNA Is it the existing chromatin state heritable? Regulatory roles of chromatin if yes: EPIGENETIC REGULATION if no: CHROMATIN REGULATION Epigenetic/chromatin phenomena Chromatin-based restriction of genome accessibility during differentiation Selective activation of genome after perception of stimulus (influence of environment/stress) Mitotic maintenance of cell identity (or loss thereof in cancer) Dosage compensation in the male versus female genome (X inactivation in mammals) Memory, Behavior, Aging HDAC Inhibitor treated Pelag et al., Science 2010 Chemotherapy plus HDAC inhibitor? Sharma et al. Cell 2010 Change in histone modification alters lifespan Greer et al., Nature 2010 Lecture outline 1. Class organization check blackboard site 2. Introduction to Epigenetics next chromatin assembly chromatin remodeling histone modifications histone variants Glossary Chromatin: nucleosomal arrays Nucleosome: DNA plus histone octamer DNA wound around the histone octamer: core DNA DNA between nucleosomes: linker DNA Differences in the epigenome of monozygotic twins Fraga et al. PNAS, 2005