TaqMan-Based Real-Time PCR for Genotyping Common
... disease (2 ). Thus, development of a simple, highthroughput HP genotyping method is needed to facilitate these association studies. Several methods for phenotyping HP1 and HP2 have been described. High-pressure gel-permeation chromatography and gel electrophoresis methods rely on differences in the ...
... disease (2 ). Thus, development of a simple, highthroughput HP genotyping method is needed to facilitate these association studies. Several methods for phenotyping HP1 and HP2 have been described. High-pressure gel-permeation chromatography and gel electrophoresis methods rely on differences in the ...
NO sensing by FNR: regulation of the Escherichia coli NO
... the ¯avohaemoglobin-encoding gene of E.coli, hmp, is upregulated by NO and RNS; this appears not to involve SoxRS (Poole et al., 1996). We have reported (MembrilloHernaÂndez et al., 1998) a mechanism of hmp gene regulation that involves interaction between S-nitrosothiols and Hcy. Intracellular Hcy ...
... the ¯avohaemoglobin-encoding gene of E.coli, hmp, is upregulated by NO and RNS; this appears not to involve SoxRS (Poole et al., 1996). We have reported (MembrilloHernaÂndez et al., 1998) a mechanism of hmp gene regulation that involves interaction between S-nitrosothiols and Hcy. Intracellular Hcy ...
A survey on computational methods for enhancer and
... It is also important to note that these high-throughput experimental methods have been mainly used for testing enhancer candidates already defined by some other means, but not for discovering enhancers ab initio. In theory it should be possible to tile a major portion of a genome for testing the en ...
... It is also important to note that these high-throughput experimental methods have been mainly used for testing enhancer candidates already defined by some other means, but not for discovering enhancers ab initio. In theory it should be possible to tile a major portion of a genome for testing the en ...
to view
... is very small. Why such type of adjustment is there in higher organisms? Ans.Female gamete is large and non motile, is an adaptation for storing more food which will be required for the future development. The male gamete has to move to reach the counterpart, so it has the machinery for its reaching ...
... is very small. Why such type of adjustment is there in higher organisms? Ans.Female gamete is large and non motile, is an adaptation for storing more food which will be required for the future development. The male gamete has to move to reach the counterpart, so it has the machinery for its reaching ...
Control of DNA excision efficiency in Paramecium
... within F1 progeny relative to F2 progeny demonstrates that Paramecium IES excision efficiency is sensitive either to a conjugation-specific trans-acting factor provided by the zygotic genome, or to homologous chromosome cross-talk. INTRODUCTION Programmed DNA rearrangements occur in a wide range of ...
... within F1 progeny relative to F2 progeny demonstrates that Paramecium IES excision efficiency is sensitive either to a conjugation-specific trans-acting factor provided by the zygotic genome, or to homologous chromosome cross-talk. INTRODUCTION Programmed DNA rearrangements occur in a wide range of ...
NPTEL-Module-1: Introduction to Bioorganic Chemistry Dr. S. S. Bag
... Enediynes are a class of bacterial natural products characterized by either nine- and tenmembered rings containing two triple bonds separated by a double bond. In the mid to late 1980s, it became clear that an emerging series of naturally occurring antitumor antibiotics such as calicheamicin, espera ...
... Enediynes are a class of bacterial natural products characterized by either nine- and tenmembered rings containing two triple bonds separated by a double bond. In the mid to late 1980s, it became clear that an emerging series of naturally occurring antitumor antibiotics such as calicheamicin, espera ...
Cohesin`s ATPase Activity Couples Cohesin Loading
... MAU2 [9, 10]. Experiments in yeast have shown that cohesin complexes deficient in ATP hydrolysis associate with chromatin in a Scc2-dependent but transient manner [11], whereas topological loading of cohesin onto DNA in vitro is stimulated by the loading complex and depends on cohesin’s ATPase activ ...
... MAU2 [9, 10]. Experiments in yeast have shown that cohesin complexes deficient in ATP hydrolysis associate with chromatin in a Scc2-dependent but transient manner [11], whereas topological loading of cohesin onto DNA in vitro is stimulated by the loading complex and depends on cohesin’s ATPase activ ...
Correct answers are marked with red
... 1) pass substances out of the cell through the membrane by diffusion 2) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pore 3) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pit 4) pass substances out of the cell in vesicles 5) identify substances in the envir ...
... 1) pass substances out of the cell through the membrane by diffusion 2) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pore 3) release substances directly into the extracellular fluid through a pit 4) pass substances out of the cell in vesicles 5) identify substances in the envir ...
Properties of Mitotic and Meiotic Recombination in the
... in the frequency of inter-homolog recombination. They estimated that greater than 90% of the DSBs induced by X-rays in G2 were repaired by sister-chromatid exchange. A variety of other systems for the analysis of sister-chromatid mitotic recombination have been developed (Jackson and Fink, 1981; Sz ...
... in the frequency of inter-homolog recombination. They estimated that greater than 90% of the DSBs induced by X-rays in G2 were repaired by sister-chromatid exchange. A variety of other systems for the analysis of sister-chromatid mitotic recombination have been developed (Jackson and Fink, 1981; Sz ...
Dissection of molecular interactions of replication protein A in
... My studies showed RPA binds different locations along ssDNA and that generally RPA does not undergo global changes in conformation when bound to ssDNA. However, with a subset of label locations, some RPA-DNA complexes showed rare changes in conformation. These observations were most consistent with ...
... My studies showed RPA binds different locations along ssDNA and that generally RPA does not undergo global changes in conformation when bound to ssDNA. However, with a subset of label locations, some RPA-DNA complexes showed rare changes in conformation. These observations were most consistent with ...
Mitotic Spindle Assembly by Two Different Pathways in Vitro
... direct the assembly of polarized microtubule arrays, which we term half-spindles; half-spindles then fuse pairwise to form bipolar spindles. In contrast, when sperm nuclei are added to extracts that are induced to enter interphase and arrested in the following mitosis, a single sperm nucleus can dir ...
... direct the assembly of polarized microtubule arrays, which we term half-spindles; half-spindles then fuse pairwise to form bipolar spindles. In contrast, when sperm nuclei are added to extracts that are induced to enter interphase and arrested in the following mitosis, a single sperm nucleus can dir ...
A Physical Gene Map of the Bacteriophage P22 Late
... map coordinate 0.958. A packaging fragment extending from pat to SmaI site 1 should be present. However, due to the small size (less than 200 base pairs) and low yield of this fragment, it has not been detected. XhoI digestion of P22 DNA also produces two bands (Fig. 1). Again, the upper band contai ...
... map coordinate 0.958. A packaging fragment extending from pat to SmaI site 1 should be present. However, due to the small size (less than 200 base pairs) and low yield of this fragment, it has not been detected. XhoI digestion of P22 DNA also produces two bands (Fig. 1). Again, the upper band contai ...
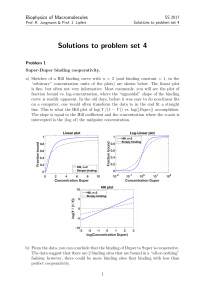
Biophysics of Macromolecules: Problem set 4
... a) The minimum and maximum RMS values are 1.122112 nm and 5.755623 nm, respectively. b) Single layer origami structures are based on parallel DNA double helices that are connected to each other by inter-strand crossovers every 32 bp. As discussed in class, this value was chosen to be approximately c ...
... a) The minimum and maximum RMS values are 1.122112 nm and 5.755623 nm, respectively. b) Single layer origami structures are based on parallel DNA double helices that are connected to each other by inter-strand crossovers every 32 bp. As discussed in class, this value was chosen to be approximately c ...
History of Discoveries in Molecular Biology
... The idea was not the product of a painstaking laboratory discipline, but was conceived while cruising in a Honda Civic on Highway 128 from San Francisco to Mendocino. "I do my best thinking while driving," the scientist with the tanned face and bleached hair once explained. For this brilliant idea b ...
... The idea was not the product of a painstaking laboratory discipline, but was conceived while cruising in a Honda Civic on Highway 128 from San Francisco to Mendocino. "I do my best thinking while driving," the scientist with the tanned face and bleached hair once explained. For this brilliant idea b ...
Role of histone deacetylase 2 and its
... involved in the regulation of the amount, function, and localization of many proteins. For example, phosphorylation is a critical modification for enzymatic activation (5), binding to DNA (6), forming complexes (7), and subcellular localization (8). Polyubiquitination, a continued link of ubiquitin ...
... involved in the regulation of the amount, function, and localization of many proteins. For example, phosphorylation is a critical modification for enzymatic activation (5), binding to DNA (6), forming complexes (7), and subcellular localization (8). Polyubiquitination, a continued link of ubiquitin ...
WOTD - Brookwood High School
... Bellringer: do a test cross for a Homozygous recessive mom with a heterozygous dad, what is the phenotype ratio of curly (C) to striaght ...
... Bellringer: do a test cross for a Homozygous recessive mom with a heterozygous dad, what is the phenotype ratio of curly (C) to striaght ...
New peptide and gene coding for same
... 151 amino acids wherein a sequence of from 26 to 151 corresponds to the sequence of the 7-hANP set forth in Figure 1; Figure 3 represents a base sequence coding for the amino acid sequence set forth in Figure 1; Figure 4 represents a base sequence coding for the amino acid sequence set forth in Figu ...
... 151 amino acids wherein a sequence of from 26 to 151 corresponds to the sequence of the 7-hANP set forth in Figure 1; Figure 3 represents a base sequence coding for the amino acid sequence set forth in Figure 1; Figure 4 represents a base sequence coding for the amino acid sequence set forth in Figu ...
Selection for TnlO Tet Repressor Binding to tet Operator
... Tet repressor protein with a total length of 207 amino acid residues is represented by a linear bar with both the N- and C-terminal ends indicated. The solid portion defines the potential a-helix-turn-ahelix motif, which is thought to be involved in DNA binding (amino acid residues 26 to 47; ISACKSO ...
... Tet repressor protein with a total length of 207 amino acid residues is represented by a linear bar with both the N- and C-terminal ends indicated. The solid portion defines the potential a-helix-turn-ahelix motif, which is thought to be involved in DNA binding (amino acid residues 26 to 47; ISACKSO ...
Mcm10: A Dynamic Scaffold at Eukaryotic Replication Forks
... The NTD is common among Mcm10 proteins from yeast to humans, but is not essential and less well conserved than the central ID (Figures 1 and 3) [74,75]. Functionally, the NTD contributes to self-oligomerization and partner protein interaction [39,50]. Homocomplex formation of Xenopus and human Mcm10 ...
... The NTD is common among Mcm10 proteins from yeast to humans, but is not essential and less well conserved than the central ID (Figures 1 and 3) [74,75]. Functionally, the NTD contributes to self-oligomerization and partner protein interaction [39,50]. Homocomplex formation of Xenopus and human Mcm10 ...
as a PDF - CiteSeerX
... Replication, DNA organization, and mismatch repair (MMR) can influence recombination. We examined the effects of altered replication due to a mutation in the polymerase d gene, long inverted repeats (LIRs) in motifs similar to those in higher eukaryotes, and MMR on intrachromosomal recombination bet ...
... Replication, DNA organization, and mismatch repair (MMR) can influence recombination. We examined the effects of altered replication due to a mutation in the polymerase d gene, long inverted repeats (LIRs) in motifs similar to those in higher eukaryotes, and MMR on intrachromosomal recombination bet ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.