* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Nervous System
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
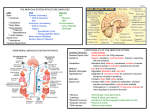
Introduction to the Nervous System 1- Both the nervous system and the endocrine system share the responsibilities for maintaining the normal homeostasis of the body. Both systems detect changes in the physiologic set point of the body (temp., BP) they integrate the information they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) b- Interneuron control c- Motor output (neuron) 2- ALL behavior is controlled by the nervous system 3- The nervous system is one of the smallest but most complex of the 11 organ systems. The nervous system (brain and nerve) has a total mass of about 2 kg or about 3% of body weight. The nervous system is divided into two sections a- bc- 4- The structure of the nervous system a- The structures that make up the nervous system include the brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia, enteric plexus and sensory receptors b- The peripheral nerves exist outside the CNS and are classified according to their origin, each follows a well defined path and services a specific part of the body 1- Cranial nerves – a- There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves (I – XII) b- Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Accessory, Hypoglossal c- Pneumonic contest 2- Spinal nerves – a- There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. They are named and numbered according to the level of the spinal cord from which they emerge b- C1-C8, T1-T12, L1-L5, S1-S5, Co1 c- C1 exits between the atlas vertebrae and the occipital bone of the skull, all others exit directly from the vertebral column 3- Ganglia – 4- Enteric Plexus – 5- Sensory Receptors – 5-Organization of the nervous system 1- Most nerve impulses that stimulate muscles to contract and glands to secrete originate in the CNS 2- The target of these impulses is usually in the PNS 3- The PNS is further subdivided into the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS) 4- The SNS contain the sensory neurons and receptors for the special senses (vision, hearing, taste and smell), which transmit to the CNS. The SNS also includes the motor neurons to the skeletal muscle. This part of the PNS is voluntary 5- The ANS consists of a- Sensory neurons that convey information to the CNS from sense receptors b- Motor neurons that conduct impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands c- For this reason the ANS is generally considered involuntary. d- The ANS is divided into three sections i. Sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic and enteric systems 6- Diagram – Subdivisions of the PNS 7- Parts of a Neuron a- Nissl Bodies - b- Synaptic end bulb - c- Schwann cells - d- Nodes of Ranvier – 8- Gray and White Matter a- White matter – b- Gray matter – c- Diagrams -