* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
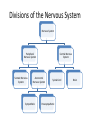
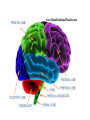
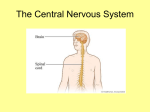
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System Central Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic Spinal Cord Parasympathetic Brain Central Nervous System • Includes the brain and spinal cord • Is where sensory information is received and motor (movement) control is initiated • Protected by – bone • Brain – skull • Spinal cord – vertebrae – 3 protective membranes called meninges • Space between meninges is cerebrospinal fluid (cushions and protects) The Brain • Brain weighs about 3 pounds • Has hundreds of billions of neurons • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful The unconscious brain – parts of the brain that work without us thinking about them • Medulla oblongata – Closest to spinal cord – Controls heart rate, breathing, bp, reflex reactions (coughing, sneezing, vomiting, hiccupping, swallowing) • Thalamus – Receives sensory information (except for smell) from all parts of the body – Sends this info to the cerebrum for further processing • Cerebellum – Balance and complex muscular movement/coordination – Butterfly shaped – Receives sensory info from inner ear • hypothalamus – Regulation of homeostasis – Maintains internal environments – Detects hunger, sleep, thirst, body temp, water balance, bp – Controls the pituitary gland • Link between nervous system and endocrine (hormone) system – Responsible for fight or flight response – Pleasure centers located here • corpus callosum – Horizontal connecting piece between 2 halves of the brain – Transmits info between the right and left cerebral hemispheres The conscious brain – The cerebrum • Largest most prominent, most highly developed part of the brain • Intellect, learning, memory and sensations are formed here • Divided into the right and left cerebral hemispheres – Right hemisphere controls the LEFT side of the body – Left hemisphere controls the RIGHT side of the body • Left Brain Right Brain Test What each hemisphere does Left Hemisphere Right hemisphere “logical side” “Intuitive side” Speaks Creates images Process data Processes senses Evaluates Symbolizes Analyzes differences Seeks similarities Is factual Is spiritual Is structured Is spontaneous Has time and measures Has no time and measures Speaks but cannot know Knows but cannot speak Talking Feeling Setting goals Speculating Planning Visualizing Measuring Empathizing Cerebral Lobes • Frontal lobe: movement, higher intellectual processing – Problem solving, concentration, planning, judging consequences • Parietal lobe: sensations – Touch, temperature, pressure, pain – Understanding speech and using words • Temporal lobe: hearing, smelling, interpreting experiences – Memory • Occipital lobe: vision Spinal Cord • The “super highway” of the nervous system • Contains central canal filled with cerebrospinal fluid • Gray matter – – – – Inner layer Contains cell bodies of neurons Looks like a butterfly with open wings Cells bodies receive sensory information and send the motor information where it needs to go • White matter – Outer layer – Contains long fibers of internuerons bundled together in tracts – Tracts connect spinal cord to brain