* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
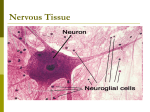
• Neurons in brain and spinal cord= Central Nervous System (CNS) • Nerves that connect CNS to rest of body= Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • Neuronstransmit electrochemical “information” as nerve impulses along nerve fibers • Nerve impulses are carried to Effectors (muscles and glands) Neuron Structure • Cell body- main structure • Dendrites- receive impulses, one or many • Axon- sends impulses, branched, usually only one • Large axons of peripheral neurons are enclosed in sheaths of neuroglia called Schwann cells – Myelin sheathcontains lipidprotein – Surrounded by membrane called Neurilemma • Nodes of Ranvier- gaps between Schwann cells of myelin sheath • Myelinated cell fibers appear white (white matter) • Unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies appear gray (gray matter) Path of travel Sensory Neurons---Interneurons---Motor Neurons Figure 12.10 Types of Neuroglia • Microglial cells- support and phagocytosis in CNS • Oligodendrocytes- form myelin sheaths in brain and spinal cord (CNS) • Astrocytes- between neurons and blood vessels; support, nutrient regulation, form scar tissue (CNS) • Ependymal cells- form epithelial-like membrane that covers parts of brain and forms inner lining that encloses spaces within brain and spinal cord (CNS) Schwann cells- myelinate PNS Satellite cells: surround cell bodies of PNS ganglia • All resting neurons are polarized (different charge outside than inside), – determined by ions, channel pores in membrane • K+ crosses easily; Na+ and Ca++ with more difficulty Greater Na+ concentration outside Greater K+ concentration inside • Due to diffusionresting nerve cell always has a slight surplus of positive charge outside and slight surplus of negative charge inside – This is called resting potential • A threshold potential must be reached to achieve an action potential – Na+ permeability suddenly increases, resulting in an inward rush (action potential) • Nerve impulse- when one action potential stimulates adjacent portions of nerve fiber to reach threshold potential and thus action potential – Results in a wave of action potentials moving down a nerve fiber • The firing of a nerve is an “All or None” response (due to threshold potential) • Certain local anesthetics decrease membrane permeability to sodium ions • Synaptic transmission occurs between axon of one neuron (sending signal) and dendrite or cell body of another neuron (receiving signal) • At this gap, Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles • Certain neurotransmitters increase ion permeability (excitatory) • Others decrease permeability (inhibitory) Small Molecule Neurotransmitter Substances Acetylcholine (ACh) Dopamine (DA) Norepinephrine (NE) Serotonin (5-HT) Histamine Epinephrine Amino Acids Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Glycine Glutamate Soluble Gases Aspartate Nitric Oxide Neuroactive Peptides - partial list!!</FONT< (NO) td> Carbon Monoxide bradykinin beta-endorphin bombesin calcitonin cholecystokinin enkephalin dynorphin insulin gastrin substance P neurotensin glucagon secretin somatostatin motilin vasopressin oxytocin prolactin thyrotropin angiotensin II sleep peptides galanin neuropeptid eY thyrotropinreleasing hormone gonadotropninreleasing hormone growth hormonereleasing hormone luteinizing hormone vasoactive intestinal peptide