* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 2 - Pegasus Server
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
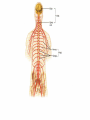
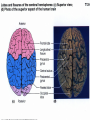
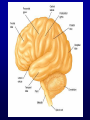
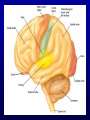
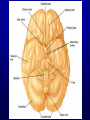
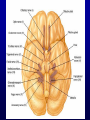
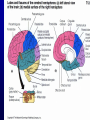
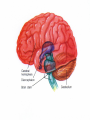
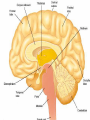
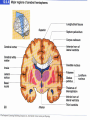
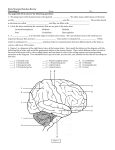
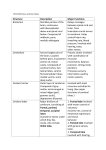
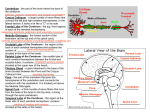
Announcements • • • • Pegasus server access Books on reserve Thebrainmcgill website Jan 17, 19 and 24, 20-30 minutes of class end, brain models will be available as needed for students to study Organization of the Nervous System Overview of the Central (CNS), Peripheral (PNS), Autonomic (ANS), Enteric (ENS) Nervous Systems Atlas Online • connection.lww.com/products/bear/sample material.asp • Read chapters 1 and 2 • Read the illustrated atlas • Use chapters 3 and 4 as extra reading if needed for exam 2 Views of the Brain • • • • • • • Link to the brain mcgill: From simple to complex Neurological level intermediate level Planes link button Beginner level 3D view of brain Thebrainmcgill • • • • • • Link to the brain mcgill: From simple to complex Neurological level beginner level Each lobe link button The physical brain link button Brain General Divisions • Superficial Structures – Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem (midbrain, pons, medulla) • Cerebral Hemispheres, – Right & Left • Four Lobes per Hemisphere – Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal • Deep Structures Basal Ganglia and Thalamus Vocabulary • • • • • Gyrus & Sulcus Grey and White Matter Nuclei and Ganglia Fissures Anterior, Posterior, Rostral, Caudal, Dorsal Ventral, Sagittal, Horizontal, Frontal/Coronal Gyrus (gyri) and Sulcus (sulci) Gyrus=folds on surface of brain Sulcus= grooves on brain’s surface Purpose: increases surface area of the cortex so you can accommodate more neurons most developed part of brain most recently evolved part of the brain. Cerebrum • Paired cerebral hemispheres both together referred to as cerebrum Cerebral Hemispheres • Right controls left side muscle and sensory • Right involved in spatial reasoning/parallel processing • Left controls right side muscle and sensory • Left involved in logical reasoning • In most humans, right controls language Four Lobes in Each Hemisphere External surface divided into 4 lobes Frontal lobe process conscious control of movement and behavior & personality Parietal lobe processes sensory information from muscle and skin Temporal lobe is involved in processing hearing, and language Occipital lobe subserves visual systems Regional Specialization • Processing of information is segregated in specific areas of the brain and separated by function. Microscopic Cortical Organization • cerebral cortex: outer layers have gray matter with soma, synapses dendrites • Inner area has white matter=Myelinated afferent and efferent axons Nuclei Collection of neuronal somas in the deeper brain structures