* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grimmer presentation
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
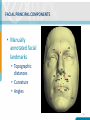
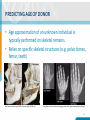
PREDICTIVE ASSOCIATIONS FROM GENOMIC DATA: FACIAL MORPHOLOGY AND AGE OF DONOR NANI GRIMMER RESEARCH SCIENTIST Supported by the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) via Department of Interior Interior Business Center (DoI/ICB) contract number D15PC0002. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Governmental purposes notwithstanding any copyright annotation thereon. DISCLAIMER • The views and conclusions contained herein are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as necessarily representing the official polices or endorsements, either expressed or implied, of IARPA, DoI/IBC, or the US Government. 2 BACKGROUND • There is growing interest in the forensic science and intelligence communities to determine observable physical characteristics (phenotype) based on genomic information • A predictive phenotypic tool would benefit from incorporating multiple characteristics including • • • • Biogeographic Ancestry Physical Traits (i.e. hair and eye color) Potential craniofacial morphology Age of an Individual 3 FACIAL PREDICTION APPROACH • Deeper investigation into the morphology of one discrete area of the face vs whole face interrogation • Use of one population cohort to limit potential variation due to biogeographic ancestry • Use of 3D imagery 4 TECHNICAL CONCEPT • Discrete Facial Feature • Nasal Region • Population cohort • European-Caucasian biogeographic ancestry • No history of nasal reconstructive surgery or breakage • Adults (18-60+ years old) • 3-D Imagery using the 3dMD® Face System 5 GENOMIC DATA • Obtaining Genomic Data • Whole genome sequencing • Human genotyping microarrays • Targeted re-sequencing (Targeted DNA Capture) • Gene regions identified by Genome Wide Association studies (GWAs) 6 TARGET CAPTURE • Targeted DNA capture • Illumina® Miseq sequencer http://coregenomics.blogspot.com/201 5/03/a-better-way-tosequence-exomes.html • Sequencing-bysynthesis (SBS) • Detection of single bases as they are incorporated • Base-by-base data for region of interest 7 DNA PROCESSING • Sequencing of 18 genes • Known to be significantly correlated with nasal development • Sequenced area includes areas outside of the known gene region to include potential regulatory regions • Identification of potential causal variants (SNPs) not yet discovered for observed nasal phenotypes 8 TARGETING A GENE REGION • Gene Region: RDH1 • 2000 bp upstream and downstream from gene region https://genome.ucsc.edu/ 9 FACIAL PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS • Manually annotated facial landmarks • Topographic distances • Curvature • Angles 10 FACIAL PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS • Facial PCs generated by algorithms developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) 11 DATA ANALYSIS • Principal Component Analysis (PCA) • Predictor Variables • Genotype of detected variants (SNPs) • Sex • Subjective attributed characteristics • Age THE IMPORTANCE OF AGE DETERMINATION http://www.nytimes.com/2015/02/24/science/dna-generated-faces.html 13 PREDICTING AGE OF DONOR • Age approximation of an unknown individual is typically performed on skeletal remains. • Relies on specific skeletal structures (e.g. pelvic bones, femur, teeth) http://www.livescience.com/35332-face-bones-aging-110104.html http://www.sfu.museum/forensics/eng/pg_media-media_pg/anthropologie-anthropology/ 14 PREDICTING AGE OF DONOR • A number of studies have identified specific DNA regions where the degree of methylation is significantly correlated with the age of a donor. http://jap.physiology.org/content/109/1/243 15 DNA METHYLATION • • • http://www.precisionnutrition.com/epigenetics-feast-famine-and-fatness 16 Method of gene silencing without altering the nucleotide sequence C-G dinucleotides are affected • Most non-methylated C-G dinucleotides are correlated with housekeeping, developmental, and tissue-specific genes • Clusters of non-methylated CG dinucleotides = CpG islands Methylation status is designated by the β-value (ratio of methylated vs. nonmethylated cytosines) PREDICTING AGE OF DONOR • Problem: • Which CpG islands are targeted? • How many are needed? • Recommendations differ across publications • Tissue type • Method of methylation status determination • Example: • As few as three CpGs for saliva samples • Between 3 and 8 CpGs for blood samples • Over 300 to compare across tissue types 17 TECHNICAL CONCEPT • Evaluate age-predicting CpG loci • Targeting over 300 sites • Investigate the accuracy and discriminatory power of DNA methylation patterns • Blood sample • Associations between methylation age, attributed age, and chronological age • Subjective analysis of age 18 DNA PROCESSING: AGE • Bisulfite-modification of DNA • • Custom padlock probes • • • Non-methylated Cytosines (C) to Uracils (U) Targets sites of interest Bisulfite-sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq β-values will be determined for each locus in each sample 19 FUTURE GOALS • Predicting facial morphology • Continue data collection • 3D imagery with DNA collection • Identify the most efficient DNA processing method or approach • Comparative investigations between populations • Ethnic populations • Twins • Identify the most effective facial phenotyping method • Investigate other epigenetic factors on facial morphology • Predicting Age of Donor • Optimization of assay for different tissues • Validate method to establish performance metrics 20 Questions? [email protected] 21