Genetic polymorphisms among C57BL/6 mouse inbred strains
... Abstract Mice from the inbred C57BL/6 strain have been commonly used for the generation and analysis of transgenic and knockout animal models. However, several C57BL/6 substrains exist, and these are genetically and phenotypically different. In addition, each of these substrains can be purchased fro ...
... Abstract Mice from the inbred C57BL/6 strain have been commonly used for the generation and analysis of transgenic and knockout animal models. However, several C57BL/6 substrains exist, and these are genetically and phenotypically different. In addition, each of these substrains can be purchased fro ...
Methods and strategies of peptide ligation
... CT-COOH), the functional group can be placed either at the side chain or at the ␣-amine (or as an ester). A common combination for an NT-amine-nucleophile is to place the nucleophile at the side chain of an NT-amino acid. This spatial configuration is found in many naturally occurring amino acids. E ...
... CT-COOH), the functional group can be placed either at the side chain or at the ␣-amine (or as an ester). A common combination for an NT-amine-nucleophile is to place the nucleophile at the side chain of an NT-amino acid. This spatial configuration is found in many naturally occurring amino acids. E ...
Ret/PTC3 is the most frequent form of gene rearrangement
... papillary thyroid carcinomas only for ret/PTC1 rearrangements and found no rearrangement; Ishizaka et al. (1991) found one ret/PTC1 rearrangement among 11 carcinomas, and Wajjwalku et al. (1992) found only one such alteration among 38 carcinomas. On the basis of those observations, RET gene rearrang ...
... papillary thyroid carcinomas only for ret/PTC1 rearrangements and found no rearrangement; Ishizaka et al. (1991) found one ret/PTC1 rearrangement among 11 carcinomas, and Wajjwalku et al. (1992) found only one such alteration among 38 carcinomas. On the basis of those observations, RET gene rearrang ...
NGRLW_SPODS_2.2 - National Genetics Reference Laboratories
... could be either a forward or reverse primer with respect to the gene orientation). With respect to sequencing, it is therefore important to be aware of the orientation of the sequence that will be generated using a particular universal primer with a particular amplicon. The tagged primers can be use ...
... could be either a forward or reverse primer with respect to the gene orientation). With respect to sequencing, it is therefore important to be aware of the orientation of the sequence that will be generated using a particular universal primer with a particular amplicon. The tagged primers can be use ...
Comparison of different PCR tests for detecting Shiga toxin
... may arise from more than one strain, hindering interpretation. Ambiguity arises when both stx and rfbO157 genes are detected in a sample containing different strains of E. coli. In this situation, it is not possible to ensure that the signal obtained in multiplex PCR is displayed by STEC O157. The m ...
... may arise from more than one strain, hindering interpretation. Ambiguity arises when both stx and rfbO157 genes are detected in a sample containing different strains of E. coli. In this situation, it is not possible to ensure that the signal obtained in multiplex PCR is displayed by STEC O157. The m ...
Array-based sequencing of filaggrin gene for
... with links to skin diseases, however it has a highly repetitive nucleotide sequence containing very limited stretches of unique nucleotides for precise mapping to reference genomes. Sequencing strategies using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and conventional Sanger sequencing have been successful fo ...
... with links to skin diseases, however it has a highly repetitive nucleotide sequence containing very limited stretches of unique nucleotides for precise mapping to reference genomes. Sequencing strategies using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and conventional Sanger sequencing have been successful fo ...
arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007
... have one trait in common: they employ nanoscale probes to examine the structural or electronic signatures of individual DNA bases. That is, they rely on physical differences between the bases. This is a major departure from existing sequencing paradigms which rely on chemical techniques and physical ...
... have one trait in common: they employ nanoscale probes to examine the structural or electronic signatures of individual DNA bases. That is, they rely on physical differences between the bases. This is a major departure from existing sequencing paradigms which rely on chemical techniques and physical ...
Control of DNA excision efficiency in Paramecium
... micronuclei undergo meiosis, whereas the macronuclei degenerate. The fusion of two gametic nuclei produces a zygotic nucleus. This nucleus divides twice and the daughter nuclei then differentiate into a micronucleus or a macronucleus. In the second case, the whole genome is processed through chromos ...
... micronuclei undergo meiosis, whereas the macronuclei degenerate. The fusion of two gametic nuclei produces a zygotic nucleus. This nucleus divides twice and the daughter nuclei then differentiate into a micronucleus or a macronucleus. In the second case, the whole genome is processed through chromos ...
Deletions of NF1 gene and exons detected by multiplex ligation
... (SSCP),26 or denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC)15 27 with varying degrees of sensitivity for each method. Direct DNA sequencing is then used to confirm and characterise mutations detected by each of these approaches, and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) is used to det ...
... (SSCP),26 or denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC)15 27 with varying degrees of sensitivity for each method. Direct DNA sequencing is then used to confirm and characterise mutations detected by each of these approaches, and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) is used to det ...
`Candidatus Phytoplasma mali`, `Candidatus Phytoplasma pyri` and
... 16SrX group (Lee et al., 2000) within the AP subclade, which is one of the major branches of the phytoplasma clade. The four phytoplasmas differ from each other in <2?5 % of 16S rDNA nucleotide sequence positions. Thus, the objective of this work was to examine whether the above-mentioned requiremen ...
... 16SrX group (Lee et al., 2000) within the AP subclade, which is one of the major branches of the phytoplasma clade. The four phytoplasmas differ from each other in <2?5 % of 16S rDNA nucleotide sequence positions. Thus, the objective of this work was to examine whether the above-mentioned requiremen ...
Rh phenotype prediction by DNA typing and its
... DNA-based phenotype prediction and of serology-based phenotyping. RH genotyping may eventually replace current serological Rhesus testing, if two major obstacles can be overcome. A more comprehensive understanding of the RH locus and its variant organization in different populations needs to be achi ...
... DNA-based phenotype prediction and of serology-based phenotyping. RH genotyping may eventually replace current serological Rhesus testing, if two major obstacles can be overcome. A more comprehensive understanding of the RH locus and its variant organization in different populations needs to be achi ...
Quantitative Trait Analysis with Merlin and QTDT
... individuals, ALL variants within that stretch will also be shared IBD (markers, QTLs, disease genes) Allows surveys of large amounts of variation even when a few polymorphisms measured ...
... individuals, ALL variants within that stretch will also be shared IBD (markers, QTLs, disease genes) Allows surveys of large amounts of variation even when a few polymorphisms measured ...
Calculation of IBD probabilities
... individuals, ALL variants within that stretch will also be shared IBD (markers, QTLs, disease genes) Allows surveys of large amounts of variation even when a few polymorphisms measured ...
... individuals, ALL variants within that stretch will also be shared IBD (markers, QTLs, disease genes) Allows surveys of large amounts of variation even when a few polymorphisms measured ...
From RNA to protein
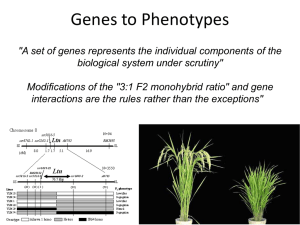
... understanding the genetic basis of a difference in phenotype is to use progeny to understand the parents. • Mendelian analysis is straightforward when one or two genes determine the trait. • Expected and observed ratios in cross progeny will be a function of o the degree of homozygosity of the paren ...
... understanding the genetic basis of a difference in phenotype is to use progeny to understand the parents. • Mendelian analysis is straightforward when one or two genes determine the trait. • Expected and observed ratios in cross progeny will be a function of o the degree of homozygosity of the paren ...
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) of the Endothelial Nitric
... accession number NP_000594) was identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing analysis. The specific genotype was identified with PCR followed by restriction fragment length polymorphism using the restriction enzymes MboI and BanII (New England Bio Labs, Ipswich, Massachusetts) to ...
... accession number NP_000594) was identified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing analysis. The specific genotype was identified with PCR followed by restriction fragment length polymorphism using the restriction enzymes MboI and BanII (New England Bio Labs, Ipswich, Massachusetts) to ...
Genomic variations and distinct evolutionary rate of rare alleles in
... neutral sites [17]. Hence, critical advances in relevant area are feasible on three basic hypotheses proposed to explain beyond a neutral model. First, it can be expected that low allelic frequency might have arisen from a recent selective sweep of an advantageous allele at a locus [18–21], or from ...
... neutral sites [17]. Hence, critical advances in relevant area are feasible on three basic hypotheses proposed to explain beyond a neutral model. First, it can be expected that low allelic frequency might have arisen from a recent selective sweep of an advantageous allele at a locus [18–21], or from ...
Package `trio`
... character string specifying which likelihood ratio test should be added to the output. If "2df", 2 degree of freedom likelihood ratio tests comparing the fitted models (containing one parameter for the SNP and one for the gene-environment interaction) with models containing no factor will be perform ...
... character string specifying which likelihood ratio test should be added to the output. If "2df", 2 degree of freedom likelihood ratio tests comparing the fitted models (containing one parameter for the SNP and one for the gene-environment interaction) with models containing no factor will be perform ...
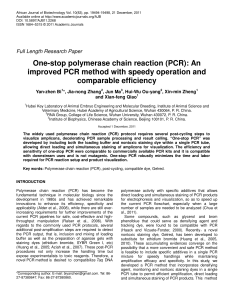
One-stop polymerase chain reaction (PCR): An improved PCR
... with gradient template amount at dilutions of 1/1, 1/10, 1/100. All the PCR products were separated on 2% agarose gel. “-” was negative control with the absence of template. Three PCR kits (Taq DNA polymerase, DreamTaq DNA polymerase and 2× Blue master mix) were purchased from Shenergy (Shanghai, Ch ...
... with gradient template amount at dilutions of 1/1, 1/10, 1/100. All the PCR products were separated on 2% agarose gel. “-” was negative control with the absence of template. Three PCR kits (Taq DNA polymerase, DreamTaq DNA polymerase and 2× Blue master mix) were purchased from Shenergy (Shanghai, Ch ...
Analyzing Loss of Heterozygosity in in Partek Genomics Suite™ v6.6
... may be used in conjunction with duo or trio workflows to detect identity by descent (IBD). To learn more on duo and trio workflows, please consult the respective documentation. An advantage of the LOH analysis is that it provides a solution to a problem associated with the copy number approach: the ...
... may be used in conjunction with duo or trio workflows to detect identity by descent (IBD). To learn more on duo and trio workflows, please consult the respective documentation. An advantage of the LOH analysis is that it provides a solution to a problem associated with the copy number approach: the ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... conserved sequence falls between bases 477 and 526 which are approximately 130 to 180 nucleotides 5' to the ATG initiation codon. Whether this has significance with respect to promoter function will await Of deletion or site-directed mutagenesis analysis of these sequences. the 27 base changes that ...
... conserved sequence falls between bases 477 and 526 which are approximately 130 to 180 nucleotides 5' to the ATG initiation codon. Whether this has significance with respect to promoter function will await Of deletion or site-directed mutagenesis analysis of these sequences. the 27 base changes that ...
Rhizopus Raw-Starch-Degrading Glucoamylase: Its
... probes were labeled by the methods of Donis-Keller et al.13) Colony hybridization was carried out by the method of Grunstein et al.1A) The hybridization conditions were 18hr at 40°C for the 14-mer mixed probes and 65°C for the probe derived from the genomic gene. The nucleotide sequence was found by ...
... probes were labeled by the methods of Donis-Keller et al.13) Colony hybridization was carried out by the method of Grunstein et al.1A) The hybridization conditions were 18hr at 40°C for the 14-mer mixed probes and 65°C for the probe derived from the genomic gene. The nucleotide sequence was found by ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS)
... average DNA concentration (0.161±0.002µg/µl) was determined from absorbance at 260 nm (Jenway, Genova Model, UK). All samples had a 260/280 nm absorbance ratio between 1.4 and 1.63. The integrity of the DNA was checked by electrophoresis on 2 % agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. Genotyping o ...
... average DNA concentration (0.161±0.002µg/µl) was determined from absorbance at 260 nm (Jenway, Genova Model, UK). All samples had a 260/280 nm absorbance ratio between 1.4 and 1.63. The integrity of the DNA was checked by electrophoresis on 2 % agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. Genotyping o ...
Molecular Inversion Probe

Molecular Inversion Probe (MIP) belongs to the class of Capture by Circularization molecular techniques for performing genomic partitioning, a process through which one captures and enriches specific regions of the genome. Probes used in this technique are single stranded DNA molecules and, similar to other genomic partitioning techniques, contain sequences that are complementary to the target in the genome; these probes hybridize to and capture the genomic target. MIP stands unique from other genomic partitioning strategies in that MIP probes share the common design of two genomic target complementary segments separated by a linker region. With this design, when the probe hybridizes to the target, it undergoes an inversion in configuration (as suggested by the name of the technique) and circularizes. Specifically, the two target complementary regions at the 5’ and 3’ ends of the probe become adjacent to one another while the internal linker region forms a free hanging loop. The technology has been used extensively in the HapMap project for large-scale SNP genotyping as well as for studying gene copy alterationsand characteristics of specific genomic loci to identify biomarkers for different diseases such as cancer. Key strengths of the MIP technology include its high specificity to the target and its scalability for high-throughput, multiplexed analyses where tens of thousands of genomic loci are assayed simultaneously.






![arXiv:0708.2724v1 [cond-mat.other] 20 Aug 2007](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014946021_1-c477dba1add7a260e278ca181f537c79-300x300.png)