* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
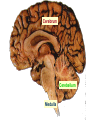
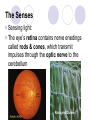
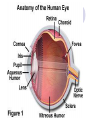
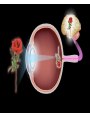
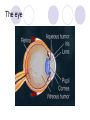
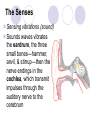
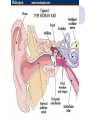
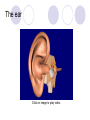
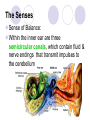
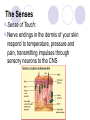
Unit 10 Chapter 36 The Nervous System The Nervous System Neurons Nerves cells, the basic unit of structure & function of the nervous system The Nervous System Neuron structure: Dendrites Branchlike extensions that receive impulses & carry them toward the cell body Cell body Location of the nucleus & much of the cytoplasm Axons Extensions carrying the impulse away from the cell body The Nervous System Categories of neurons: Sensory neurons carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord & brain Motor neurons carry impulses from the spinal cord & brain to the body Interneurons are found within the spinal cord & brain, pass response impulses between sensory & motor The Nervous System Transmitting an Impulse: Each impulse consists of an electrical charge that travels the length of a neuron’s cell membrane to a gap, called a synapse The impulse is caused by the depolarization of chemicals surrounding the cell membrane Chemicals called nuerotransmitters, are released into the synapse, which stimulates a charge in the next neuron Transmitting an impulse along the axon Click on image to play video. Transferring signals across the synapse to an adjoining neuron Click on image to play video. The Nervous System Division of the Nervous System: Central Nervous System (CNS) Consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Consists of the nerves that carry messages to & from the CNS The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the Brain: Cerebrum Largest lobe, controlling voluntary movement, intelligence, memory, & the senses Cerebellum Located at the back, controlling balance, posture, and coordination Medulla oblongata Located within the brain stem, controlling involuntary (vital) activities Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla The Peripheral Nervous System Somatic Nervous System (SNS) Made up of cranial & spinal nerves, relaying voluntary information between the CNS and the skin & muscles Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Made up of the sympathetic & parasympathetic systems, relaying involuntary responses, not under conscious control The Peripheral Nervous System Reflexes An automatic, unconscious response for protecting the body This response travels to the spinal cord where it responds directly back to a muscle The Senses Sensing Chemicals: Odor chemicals stimulate nerve endings in the nasal passages, which transmit through the olfactory nerve to the cerebrum Chemical dissolved in saliva stimulate nerve endings in the taste buds of your tongue, detecting only sweet, sour, bitter & salty The Senses Sensing light: The eye’s retina contains nerve enedings called rods & cones, which transmit impulses through the optic nerve to the cerebellum Rods and Cones The eye The Senses Sensing vibrations (sound) Sounds waves vibrates the eardrum, the three small bones—hammer, anvil, & stirrup—then the nerve endings in the cochlea, which transmit impulses through the auditory nerve to the cerebrum The ear Click on image to play video. The Senses Sense of Balance: Within the inner ear are three semicircular canals, which contain fluid & nerve endings that transmit impulses to the cerebellum The Senses Sense of Touch: Nerve endings in the dermis of your skin respond to temperature, pressure and pain, transmitting impulses through sensory neurons to the CNS