* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 0.-Nat-5-REVISION-nervous
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
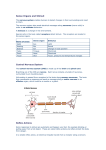
Unit 3 – Key Area 1 Divisions of the nervous system and parts of the brain KA 1: Divisions of the nervous system and parts of the brain (a) CNS Central Nervous System (b) PNS Peripheral Nervous System The Nervous System (c) Medulla and Cerebellum (f) Localisation of brain functions (e) Cerebral Cortex (d) Limbic System • Multi-cellular organisms are made of trillions of specialised cells that work together to ensure survival of that organism. • Internal communication is needed to bring this about this co-operation is provided by the nervous system. The Nervous System • Made of 3 parts: – Brain – Spinal Cord Central Nervous System or CNS – Nerves – (Peripheral NS) • The CNS is connected to all parts of the body by the nerves The Brain • Control centre of CNS • Protected by skull • Adult brain – 1.3 – 1.4 kg • Newborn brain – 350 – 400g • 2% of adult weight in healthy individual • 100 billion neurons Cerebrum Medulla Cerebellum Spinal Cord Part of brain Function Cerebrum Cerebellum Medulla Controls breathing and heart rate Enables conscious thought, memory, learning and intelligence Controls balance and muscular coordination CNS SENSORY NERVES RECEPTORS (e.g. sense organs) STIMULI e.g. touch/light MOTOR NERVES EFFECTORS (e.g. muscle & glands) RESPONSE e.g. movement/ hormone release Sensory neurone Synapse Relay neurone Response: arm muscles contract and hand withdraws Motor neurone Effector: muscles of the arm Harmful stimulus from a hot object Nervous System: N5 Revision 1) What 2 parts of the body make up the central nervous system (CNS) Brain and spinal cord. 2) Name the 3 types of neurons present in the nervous system. Sensory, relay and motor neurons. 3) What is the purpose of a reflex action. To protect the body from harm. 4) The following diagram shows a human brain. Which letter indicates the site of memory and conscious responses? A 5. The diagram below shows a section through the human brain. Which labelled part co-ordinates movement and balance? B 6. The diagram below shows a human brain. Which letter shows the site that controls heart rate and breathing rate? C 7. Which of the diagrams below identifies neurons and the direction of travel of nerve impulses? 8. The following stages occur in a reflex action. 1 The effector produces a response. 2 A sense organ is stimulated. 3 An impulse passes along a sensory neurone. 4 An impulse passes along a motor neurone. The correct order of the stages is A 2, 3, 4, 1 B 2, 1, 4, 3 C 1, 2, 3, 4 D 3, 4, 1, 2. 9. The diagram below shows neurones connecting the eye with the central nervous system. Which line in the table below identifies correctly the types of neurones and the direction of impulses which travel along them? 10. The pathway for a reflex arc involves the following. 1. Central nervous system 2. Sensory neurone 3. Motor neurone Which of the following correctly represents the pathway of a reflex arc? A1>2>3 B1>3>2 C2>1>3 D2>3>1