* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Three- The Brain
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
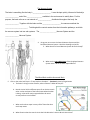
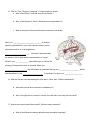
Psychology Unit 2- The Parts and Functions of the Brain Conscious vs. Subconscious The Brain From Top to Bottom Web Quest Scavenger Hunt Visit the site: http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/index_d.html Directions: Answer the following questions about the Brain as they correspond to the different categories on the website. Have fun! The Four Lobes of the Brain 1. Click on “From the Simple to the Complex” – Anatomy by Level of Organization a. Drag your cursor over the different lobes of the brain to find out what they are called, where they are located and what they do. Frontal Lobe: Parietal Lobe: Temporal Lobe: Occipital Lobe: 2. On the left had side of the page are ORANGE, RED, BLUE squares that are links to other pages, click on the ORANGE top left link that will bring you to: http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/3d/index.html a. Play around with the 3-D brain and get a feel for the location for each lobe. b. Go to EXPLORE THE BRAIN, in the drag down menu search the brain for the following functions: Where are these functions located? Touch Emotion Taste Movement Speech Short –term Memory 3. Label the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain: Which hemisphere controls the right side of your body? Which hemisphere controls the left side of your body? The Nervous System The brain is something like the body’s ____________________. It must be kept quickly informed of the body’s _______________ and of the _________________ available in the environment to satisfy them. For this purpose, the brain relies on a vast network of _______________ distributed throughout the body: the _______________. Together with the brain and the ____________________, the nerves constitute the _________________________. To distinguish the control centers from the information pathways, we divide the nervous system into two sub-systems: The _____________________Nervous System and the _______________ Nervous System. 4. Drag your cursor over the Central Nervous System and the Peripheral Nervous System. Label the drawings to the left. a. What does the Central Nervous System do for the body? b. What are the two subdivisions of the Peripheral Nervous System exist? What are each responsible for? The Wired Brain and the Hormonal Brain 5. Click on the other Sub-Topic in “From Simple to Complex” – Function by Level of Organization a. The Brain’s wiring consists of Axons, what are Axons? What do they do? b. Neural circuits link the different parts of our brains to each other so that each part of the brain knows what the other is doing—what other major responsibilities do neural circuits perform in our bodies? c. What are the three steps in every reflex? Describe what each step means. d. What function does the neural circuit that links Wernicke’s Area to Broca’s Area serve? 6. What is the major difference between the speed of the way the hormonal brain and the wire brain communicate? 7. What are three examples of hormonal states of the brain? 8. Go back to the main menu—click on Evolution and the Brain a. Describe the three layers of the brain and what they are primarily responsible for controlling: i. Reptilian: ii. Limbic: iii. Neocortex: 9. Visit http://www.learner.org/discoveringpsychology/brain/brain_flash.html and look more closely at what parts specifically make up the three layers of the brain. a. List the five parts of the Central Core, give a brief description of each part. b. List the three parts of the Limbic System, give a brief description of each part. c. List the four parts of the Cerebral Cortex, give a brief description of each part. Memory 10. Click on “Memory and the Brain” – How Memory Works a. What is short-term memory? What part of the brain controls short-term memory? b. What is the hippocampus? How does this part of the brain help form the long-term memory? 11. Click on the other Sub-Topic-- Forgetting and Amnesia a. Why do we forget? b. What is the difference between forgetting and amnesia? c. What are two specific things you can do to improve your memory? 12. Click on the first ORANGE “Beaker” Link and go to: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chmemory.html and play at least three of the short-term memory games. a. Describe the game you played. How well did you do? b. Describe the game you played. How well did you do? c. Describe the game you played. How well did you do? 13. How does Amnesia affect your brain? a. What are the two types of amnesia and how do they affect your memories differently? Movement 14. What is the Motor Cortex? Where is it located? a. What information does your motor cortex need from other lobes of your brain before it can carry out any movements? b. Read the information written in the ORANGE TEXT BOX. Then Click on the first ORANGE “Beaker” Link and go to: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/brain/probe.html and probe the brain!!! Activation Sequence of Motor Areas The basic function of the brain is to ____________________ which are, first and foremost, movements. Several different regions of the ________________ are involved in controlling the body's movements. These regions are organized into a hierarchy like the _____________________. On an ancient galley, for example, the ______________ determined the destination for a voyage by assessing the various factors that might make such a trip worthwhile. Then his _________________ calculated the direction that the ship had to travel to reach that destination, based on weather conditions. Finally, the lieutenants transmitted their orders to the ___________ manning the oars, who used their muscles to move the ship in the desired direction. Similarly, in the _______________________, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion of the ___________________. This part of the cortex receives information about the individual's current position from several other parts. Then, like the ship's captain, it issues its commands, to _______________. Area 6 acts like the ship's lieutenants. It ______________________________________ to achieve the required movement, then issues the corresponding orders to the "rowers"— _____________________________, also known as Area 4. This area in turn activates specific muscles or groups of muscles via the motor neurons in the _____________________________. 15. Click on “From Thought to Language”—Communicating in Words a. Who is Paul Broca? How and what did he discover? b. Who is Carl Wernicke? What is Wernicke’s area responsible for? c. What is the name of the nerve fibers that connects the two areas? When you _______________________________, an auditory signal is processed first in your brain’s primary auditory cortex, which then sends it on to the neighboring ___________________________. Wernicke’s area associates the structure of this signal with the representation of a word stored in your ______________, thus enabling you to retrieve the meaning of the particular word. In contrast, when you ______________________, the information is perceived first by your ____________________, which then transfers it to the _____________________, from which it is sent on to __________________. 16. What are the two most lateralized parts of the brain? What, then, is Brain Lateralization? a. What does it mean when someone is ambidextrous? b. Why is the right side of our brain in control of our left-side of our body and vice versa? 17. How do we communicate without words? What are some examples? a. What is the difference between denotative and connotative language? b. Why might someone misunderstand what you are saying if they have right hemisphere damage? 18. Click on the “Senses”—Vision. Skim the reading. How are the fields of vision tied to the hemispheres of the brain? a. Scroll back up to the top and click on the ORANGE “Beaker” Link and go to: http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/capsules/experience_jaune06.html and play around with your blind spot. Click on some of the “Beaker” links at the bottom of that page to continue to test your blind spot. Can you create your own blind spot test? 19. Click on “Emotions and the Brain”—Fear, Anxiety, Anguish a. What is the amygdale? What is its major role?