* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Human Brain
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
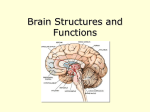
Inside the Human Brain Introduction to Anthropology, Sociology & Psychology—HSP 3M Inside the Teenage Brain Adolescence is characterized by extreme mood swings and participation in risk-taking behaviour. Many changes are occurring in the frontal cortex which account for these behaviours. The frontal cortex, which is responsible for reason and logic, is not fully developed in adolescents. Inside the Teenage Brain Due to this, many adolescents misinterpret emotions causing conflict with parents, peers and teachers. Example: Misinterpreting one’s behaviour as anger. The adolescent brain does not interpret environmental information in the same manner as adult do. Inside the Teenage Brain The cerebellum, responsible for organizing thoughts and cognition, changes the most during adolescence. The cerebellum is not fully developed until a person is 21 years old. This lack of development can account for adolescents not always hearing or understanding what their parents or teachers are trying to communicate and their lack of organization. So why do we treat adolescents like adults if they are not cognitively the same? Inside the Teenage Brain Getting adequate sleep is one of the best things adolescents can do to enhance learning and brain development. Adolescents need 9 ¼ hours sleep a night to function properly. Despite this, on average adolescents get only 7 ½ hours sleep per night. This continuous sleep deficit causes significant gaps in learning. Inside the Teenage Brain Adolescents circadian clock keeps teens up late at night, however as school starts early they are forced to get up before they have received enough sleep. As a result most adolescents are not able function properly in school as they are still in a sleep like state. Studies show that when teens get adequate sleep they perform better on cognitive tasks. Teens that are sleep deficient show significant gaps in their ability to retain information and perform cognitive tasks. Inside the Teenage Brain So why does school start so early? Later school start studies indicate that when school starts later (10 am4:30 pm), teens perform better academically and they are less frequently absent. However they are less likely to participate in extra curricular activities which are also beneficial to healthy development. Inside the Teenage Brain The most important factor to adolescent development is the relationships, connections and support systems formed with family and peers. The Human Brain--Functions The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is the most complex organ in any creature on earth. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over five times as large as the "average brain" of a mammal with the same body size. Human Brain The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the limbic system). The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum. The hindbrain is made of the cerebellum, pons and medulla. Often the midbrain, pons, and medulla are referred to together as the brainstem. Human Brain The cerebrum or cortex is the largest part of the human brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Human Brain Right Hemisphere The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body Temporal and spatial relationships Analyzing nonverbal information Communicating emotion Left Hemisphere The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body Produce and understand language Human Brain Frontal Lobe- associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving Parietal Lobe- associated with movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli Occipital Lobe- associated with visual processing Temporal Lobe- associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech Human Brain The cerebellum, or "little brain", is similar to the cerebrum in that it has two hemispheres and has a highly folded surface or cortex. This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. The Human Brain Thalamus is a large mass of gray matter deeply situated in the forebrain at the topmost portion of the diencephalon. The structure has sensory and motor functions. Almost all sensory information enters this structure where neurons send that information to the overlying cortex. The Human Brain Hypothalamus- The structure is involved in functions including homeostasis, emotion, thirst, hunger, circadian rhythms, and control of the autonomic nervous system. Examples: Moods and motivation Sexual maturation Temperature regulation Hormonal body processes The Human Brain Amygdala- involved in memory, emotion, and fear. The amygdala is both large and just beneath the surface of the front, medial part of the temporal lobe. Human Brain Hippocampus- This part of the brain is important for learning and memory. Specifically for converting short term memory to more permanent memory, and for recalling spatial relationships in the world about us. Human Brain Pons- It is involved in motor control and sensory analysis... for example, information from the ear first enters the brain in the pons. It has parts that are important for the level of consciousness and for sleep. Some structures within the pons are linked to the cerebellum, thus are involved in movement and posture. Human Brain Medulla- this structure is the caudal-most part of the brain stem, between the pons and spinal cord. It is responsible for maintaining vital body functions, such as breathing and heart rate.