* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Long-term memory
Long-term potentiation wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Hippocampus wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Reconstructive memory wikipedia , lookup
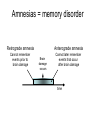
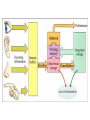
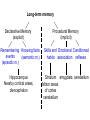
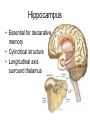
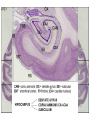
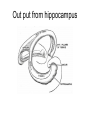
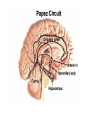
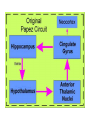
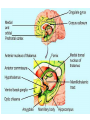
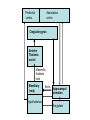
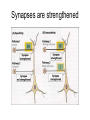
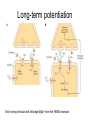
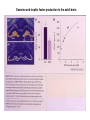
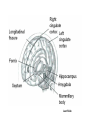
Memory Human Neurobology 217 Jana Vukovic [email protected] Key points: • Famous cases of memory deficit • Brain structures involved – hippocampus • Circuitry of memory – Papez Circuit • synapse strengthening and long-term potentiation (LTP) What is memory? • Memory is defined as the acquisition, storage, and retrieval of information. • All animals learn things from their interaction with the environment • Human brain forms memories more effectively than others • Maximum behavioural flexibility and most efficiently adaptation to environment. Amnesias = memory disorder Retrograde amnesia Anterograde amnesia Cannot remember events prior to brain damage Cannot later remember events that occur after brain damage Brain damage occurs time HM & NA • Which brain structures were removed from HM’s brain? – Hippocampus, hippocampal gyrus, amygdala, uncus were removed on both sides • Which brain structures are damaged in NA? – Thalamus and medial temporal lobe, mammilary bodies missing on both sides • Can HM and NA form new long-term memories (declarative)? – NO. • Can HM and NA learn new skills (procedural)? – YES. • What kind of amnesia do HM and NA have? – Sever anterograde amnesia. NA • Korsakoff's syndrome: – Found mostly in alcoholics who get most of their calories from alcohol and become vitamin deficient (thiamine deficiency) – Damages mammilary bodies and other nearby parts of the hypothalamus and thalamus – This damage produces an amnesia similar to the type of NA and HM (sever anterograde amnesia) • Altzheimer’s disease: – Loss of neurons in hippocampal and prefrontal cortex produce first signs of memory loss. • Long-term memories are biologically different from short-term memories • Long-term memories are stored throughout the brain, but the hippocampus is necessary for the information to reach long-term storage. Long-term memory Declarative Memory (explicit) Remembering Knowing facts events (semantic m.) (episodic m.) Hippocampus Nearby cortical areas, diencephalon Procedural Memory (implicit) Skills and Emotional Conditioned habits association reflexes Striatum amygdala cerebellum Motor areas of cortex cerebellum Hippocampus • Essential for declarative memory • Cylindrical structure • Longitudinal axis surround thalamus Out put from hippocampus Prefrontal cortex Association cortex Cingulate gyrus Anterior Thalamic nuclei Mammillo thalamic tract Mamillary body Hypothalamus fornix Hippocampal formation Amygdala Strengthening of synapses • Long-term potentiation (LTP) is the long-lasting strengthening of the connection between two neurons • can last from hours to days, months, and years. Long-term potentiation of synapses • Hippocampal slice preparation to study LTP • single stimulation to input path • measure hippocampal response baseline • Give train of stimulation to input path • Again give single stimulation to input path • hippocampus response is larger (potentiated) • Give single stimulation a week later • Hippocampus response still potentiated (long term potentiation) Synapses are strengthened More dendritic spines on dendrites where new synapses are made Dendritic spines from a cerebellar Purkinje cell, drawn by Cajal (Ramón y Cajal, 1899b). Long-term potentiation Only strong stimulus will dislodge Mg2+ from the NMDA receptor Exercise and trophic factor production in the adult brain Describe Papez circuit? Last Slide