* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
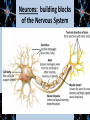
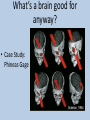
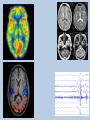
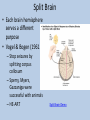
Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior AP Psychology Ms. Egan The Biology Behind the Psychology • “Everything Psychological is ultimately Biological.” – What does this say to you? Neurons: building blocks of the Nervous System Neural Communication • • • • Action potential: a neural impulse Threshold: minimum intensity needed to fire impulse Neuron firings are all-or-none responses Synapse: gap between neurons (also called a synaptic gap or cleft) • Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that bind to receptor sites on receiving neuron • Reuptake: sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters Demonstrations Action Potential Synaptic Transmission Types of Neurons • Sensory Neurons (afferent) ~ 2 million – Sends messages from sense organs brain • Motor Neurons (efferent) ~ 2-3 million – Sends messages from brain muscles, organs, glands • Interneurons ~ Billions & Billions – Relay messages between sensory & motor neurons • Glial cells – “The forgotten cell” – Glue cells which help connections, insulate, and clean up Influence of Neurotransmitters • Each neurotransmitter has a specific effect on behavior & emotions • • • • • • Acetylcholine: muscle action, learning, memory Dopamine: movement, learning, attention, emotion Serotonin: mood, hunger, sleep, arousal Norepinephrine: alertness, arousal GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid): inhibitory neurotransmitter Glutamate: excitatory neurotransmitter, memory • Find a condition or disease associated with the blockage or increase in one of these neurotransmitters. Drugs & Neurotransmitters • Endorphins: natural “opiates” released in response to pain or vigorous exercise • Why not flood the brain with artificial opiates?? – Brain will stop producing natural ones – Withdrawal symptoms • Drugs affect communication at the synapse – Agonist Molecule: excites, mimics neurotransmitter – Antagonist Molecule: inhibits, blocks neurotransmitter Neuron FAQ’s • 100 Billion neurons in the human body – It would take you 3,171 years to count all the neurons (1 per second) • 4-100 Microns wide (1 micron=1/1000th of a millimeter) • Your neurons are for life! You will have less and less as you get older The Nervous System Neuron to Central Nervous neuron System communication Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (Links CNS with muscles, glands, sense receptors) Somatic Autonomic (Skeletal) (Internal Organs) Sympathetic (Arousing) • Nerves: neural cables containing many axon Parasympathetic (Calming) Endocrine System • Slower than nervous system • Uses hormones (another chemical messenger) to communicate • Flow from tissues through bloodstream to other tissues • Adrenal glands: above kidneys; secrete hormones to arouse body during stress • Pituitary glands: controlled by hypothalamus, regulates growth and controls endocrine glands The Brain How does our brain produce behavior and mental processes? What’s a brain good for anyway? • Case Study: Phineas Gage Case Study: Phineas Gage • Which part of the brain did Gage injure? • Why did Gage feel no pain after the injury? • What were the “treatments” given to Gage after the injury? • What was the major change in Gage after the accident? • What is localization of the brain? Studying the Brain • Electroencephalogram (EEG) – Measures brains electrical waves by attaching electrodes to the scalp • Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan) – Injection of radioactive glucose (brain sugar) to detect where fuel goes under different situations • Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – Magnet aligns spinning atoms of brain to show tissue and brain anatomy • Functioning MRI (fMRI) – Shows brain function & bloodflow Brain Structures • Brain Map (BBC) OR 3-D Brain (PBS) • Using the Brain Links, complete your brain concept map. Give an example of how each structure influences your behavior or emotions: YOU SHOULD KNOW THE FOLLOWING!!! Brainstem Midbrain Cerebral Cortex Occipital Lobes Limbic System Pituitary Gland Pons Cerebrum Parietal Lobes Temporal Lobes Amygdala Hippocampus Medulla Oblongata Frontal Lobe Thalamus Cerebellum Hypothalamus Corpus Callosum Split Brain • Each brain hemisphere serves a different purpose • Vogel & Bogen (1961) – Stop seizures by splitting corpus collosum – Sperry, Myers, Gazzaniga were successful with animals – HE-ART Split Brain Demo Right vs. Left Brain • We only use 10% of our brain • Your brain does not grow new cells • Some people are right-brained, others left-brained • Brain damage cannot be repaired