* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription and Translation
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
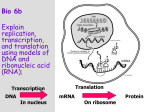
Transcription and Translation From DNA Code to Proteins Chapter 13 Lesson 2 Learning Goals: We will identify the types of RNA and their role in protein synthesis. Standard: SC.912.L.16.5 Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation and how they result in the expression of genes. Recall: DNA vs. RNA DNA 1. Strands? 2. Sugar? 3. Bases? RNA 1. Strands? 2. Sugar? 3. Bases? Both contain a sugar, phosphate, and base. Recall: DNA vs. RNA DNA Double stranded Deoxyribose sugar Bases: C,G A,T RNA 1. Strands? 2. Sugar? 3. Bases? Both contain a sugar, phosphate, and base. Recall: DNA vs. RNA DNA Double stranded Deoxyribose sugar Bases: C,G A,T RNA Single stranded Ribose sugar Bases: C,G,A,U Both contain a sugar, phosphate, and base. Recall: DNA & the Genetic Code DNA contains a genetic code, the instructions to make an organism function. DNA strands contain the nitrogen bases Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, and Thymine. DNA is able to replicate itself prior to cell division to ensure both new cells have the same DNA. DNA code can be used in Protein Synthesis. What are Proteins? Made up of amino acids. Polypeptide- string of amino acids. Assembled at the ribosome. 20 amino acids are arranged in different orders to make a variety of proteins. What is Protein Synthesis? Process by which DNA codes are turned into proteins for the body to use. 2 Steps: Transcription - Creating mRNA with DNA’s code Translation – Using mRNA’s code & ribosomes to create proteins. Recall: Transcription Transcription is the first step in Protein Synthesis. Occurs in the nucleus. Segments of DNA code serve as templates to produce messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. mRNA contains the nitrogen bases Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, and Uracil instead of Thymine. Check Point Question: If a template DNA strand is TACGATACGAT, what is the mRNA code? Check Point Question: If a template DNA strand is TACGATACGAT, what is the mRNA code? AUGCUAUGCUA mRNA Processing Prior to leaving the nucleus, the mRNA must be modified DNA sequence has coding regions (exons) Newly made mRNA strand and non-coding regions (introns) Exon Intron Exon Intron Intron Intron Exon Intron Exon Modified mRNA strand Intron Introns must be removed before mRNA and can leave nucleus Transcription to Translation Once the mRNA has been modified, it can then leave the nucleus to be used by the ribosome to make proteins. Translation is the process by which a ribosome uses the mRNA message to produce a specific amino acid chain (polypeptide protein). Occurs outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. Translation – Codons & Amino Acids The ribosome reads the code three letters at a time. These three letters are called codons. Each codon codes for a particular amino acid. Check Point Question How many codons are in this particular sequence: AUGAACUCUGCCUAAGCGUAU Check Point Question How many codons are in this particular sequence: Seven: AUG AAC UCU GCC UAA GCG UAU Translation - Codons Codons code for particular amino acids, those amino acids are the building blocks of _______. Translation - Codons Codons code for particular amino acids, those amino acids are the building blocks of Proteins. Translation - Codons We can use codon charts to determine which codons code for which particular amino acids. Ribosomes Ribosomes read codons without codon charts They use the sequence of codons on mRNA and the assistance of tRNA to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains. Recall Question: What is the role of the tRNA? Welcome Transfer RNA (tRNA)! tRNA brings the amino acids to the ribosome. An Anticodon on the other end matches with the mRNA’s code. Three different views: Translation: The Finale The polypeptide chain grows until it reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide chain is released and folded into a protein. Transcription and Translation: Review Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.___ is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. ______ DNA is used to create 3. ______ Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4. ______ at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. ______ mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. ______ DNA is used to create 3. ______ Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4. ______ at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. ______ mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. Nucleus DNA is used to create 3. ______ Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4. ______ at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. ______ mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. Nucleus DNA is used to create 3. mRNA Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4. ______ at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. ______ mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. Nucleus DNA is used to create 3. mRNA Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4.amino acids at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. ______ mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. Nucleus DNA is used to create 3. mRNA Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4.amino acids at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. cytoplasm mRNA is used to create 6. ______ Transcription vs. Translation Review On your Check Point Paper, answer the following blanks: Transcription Process by which genetic information encoded in 1.DNA is copied onto messenger RNA Translation Occurs in the 2. Nucleus DNA is used to create 3. mRNA Process by which information encoded in mRNA is used to assemble a chain of 4.amino acids at a ribosome Occurs in the 5. cytoplasm mRNA is used to create 6. proteins How to read a Codon Chart Two kinds: Square table Round Chart How to Read a Codon Chart/Table Using the Codon AUG (start codon) Locate the first letter of your codon using the left side of the table. Look for the A Codon: AUG The second letter of your codon is ‘U’ Look at the top of the table where you see the title ‘2nd letter’ Find the letter ‘U’ and follow it down until it intersects with the letter ‘A’. Codon: AUG Look to the right for the third letter, “G” Move your finger from the ‘G’ on the left over to the left and you should land on ….. Methionine (start codon) Yes you did it! Now, try another codon Try the codon CAC – Write your Answer on your sheet Try the codon CAC – Answer: Histidine Write your Answer on your sheet